
Used in devices such as X-ray high-voltage generators and laser therapy instruments, where high stability and excellent heat dissipation are required, and copper-based PCBs can fully meet these demands.
Ideal for high-power, high-density applications requiring stable and reliable performance.
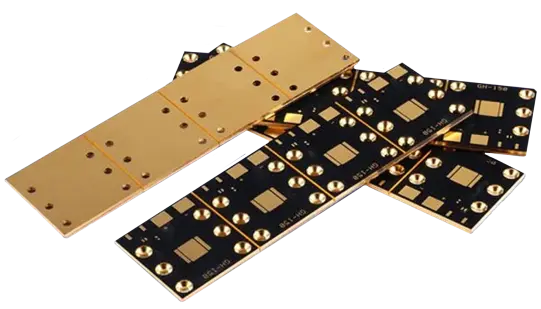
A copper base PCB is a high-thermal-conductivity circuit board that uses high-purity electrolytic copper (≥99.9%) as the core heat-conducting layer, combined with low-thermal-resistance insulating materials such as aluminum nitride ceramic, modified epoxy resin, or polyimide, and conductive copper foil. Through a dual design of direct heat conduction via the copper core and electrical isolation by the insulating layer, it effectively solves the heat dissipation challenges of high-power components, making it an ideal substrate for electronic devices with high power density and operation in high-temperature environments.
A key material for solving heat dissipation challenges in high-power-density devices
Layers: 1–4
Board Thickness: 0.8–3.2 mm (Copper Thickness: 2.0–20 OZ)
Minimum Mechanical Hole Diameter: 0.1 mm (1.0 OZ)
Aspect Ratio: ≤ 12:1
Surface Finish Options: ENIG, ENEPIG, Immersion Silver, Immersion Tin, OSP, Hot Air Solder Leveling, Electroplated Gold.

A new type of PCB designed to meet theheat dissipation requirements of high-power electronic devices.
Layers: 2
Minimum Line Width/Spacing: 4/4 MIL (1.0 OZ)
Board Thickness: 0.4–3.2 mm
Board Material: Copper Base, Aluminum Base
Pad-to-Board Surface Tolerance: ±0.025 mm
Excels inspace utilization, balanced heat dissipation, and structural stability.
Layers: 2
Board Thickness: 0.8–3.2 mm
Minimum Line Width/Spacing: 3/3 MIL (1 OZ)
Surface Finish: ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold)
The metal base uses high-purity electrolytic copper (≥99.95%) with a thermal conductivity of 380–401 W/(m·K). It rapidly absorbs heat generated by electronic components, such as IGBTs or LED chips, acting like a “heat pipe.”
The metal base (1–3 mm thick) serves directly as aheat-dissipating surface, eliminating the need for additional heat sinks. Heat is quickly transferred to the air, significantly reducing component junction temperatures (e.g., lowering LED chip junction temperature from 120°C to below 80°C) and extending component life by30–50%.
The copper core provides exceptional rigidity and structural support, reducing board warping or deformation during thermal cycling or mechanical stress. This ensures stable component placement and reliability in high-power and industrial applications.
Copper’s conductivity reaches58 MS/m(close to silver at 62 MS/m), much higher than aluminum (37 MS/m) and iron (10 MS/m). This results in very lowohmic lossesduring current transmission—for example, reducing signal loss by10–15%in 5G base station RF modules.
Copper surfaces can be plated withnickel, tin, or treated with OSPto resist humidity, salt spray (e.g., marine environments), and chemical corrosion (e.g., industrial soldering environments), extending substrate lifespan—up to 5–8 years in outdoor applications.
Copper core PCBs can be processed using conventional PCB fabrication methods, including SMT assembly, through-hole mounting, and plating, allowing seamless integration into existing production lines without additional modifications.

Used in devices such as X-ray high-voltage generators and laser therapy instruments, where high stability and excellent heat dissipation are required, and copper-based PCBs can fully meet these demands.

Applied in photovoltaic inverters, wind power converters, and new energy charging stations, helping to improve power conversion efficiency and thermal performance.

Used in RF power amplifiers of 5G base stations to reduce signal distortion and enhance transmission quality.

Ideal for equipment such as industrial welders, servo drivers, and high-power power supplies, meeting the needs for high current capacity and efficient heat dissipation.

Used in street lights, interior lighting, and camping lanterns to improve heat dissipation and extend LED lifespan.

Used in headlights and power controllers to enhance thermal stability and ensure consistent performance under high load.

Used in solid-state relays, rectifier bridges, and power converters to improve power conversion efficiency and operational safety.
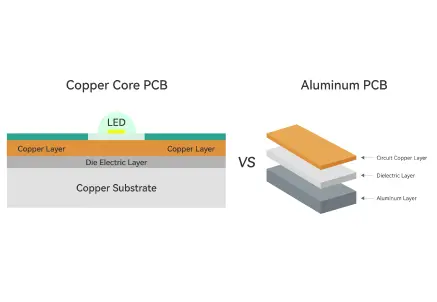
Aluminum core substrates, by contrast, deliver good thermal performance at a much lower cost. With a conductivity of around 200–237 W/m·K, they provide efficient heat dissipation for LED lighting, consumer electronics, communication equipment, and automotive systems. Aluminum is lighter and easier to process, offering a practical balance between performance, weight, and cost.
Copper cores are the better choice for high-performance and heat-intensive applications, while aluminum cores are more suitable for general-purpose or cost-efficient products requiring reliable but moderate heat management.