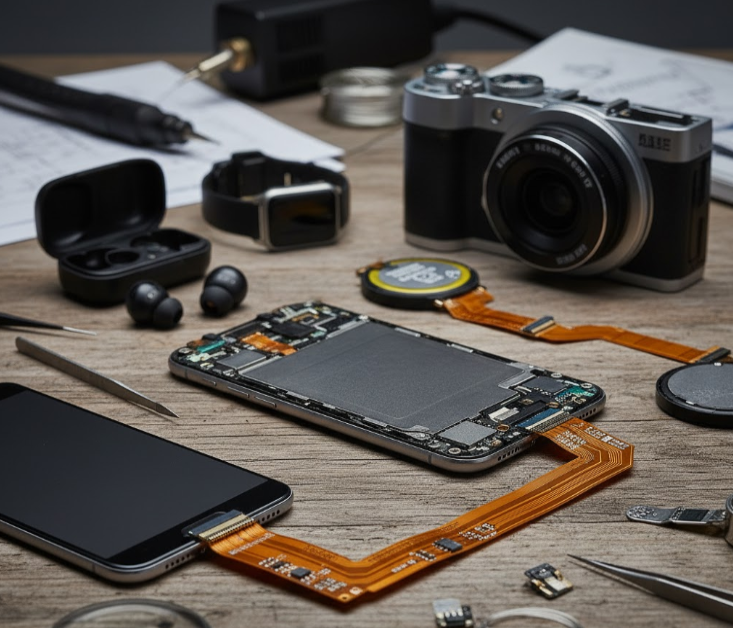
Flexible PCBs are widely used in smartphones, tablets, cameras, and wearables, enabling compact designs, lightweight construction, and reliable connections in slim and foldable devices.
AIVON Delivers High-Precision Flexible PCBs for Complex and Compact Applications
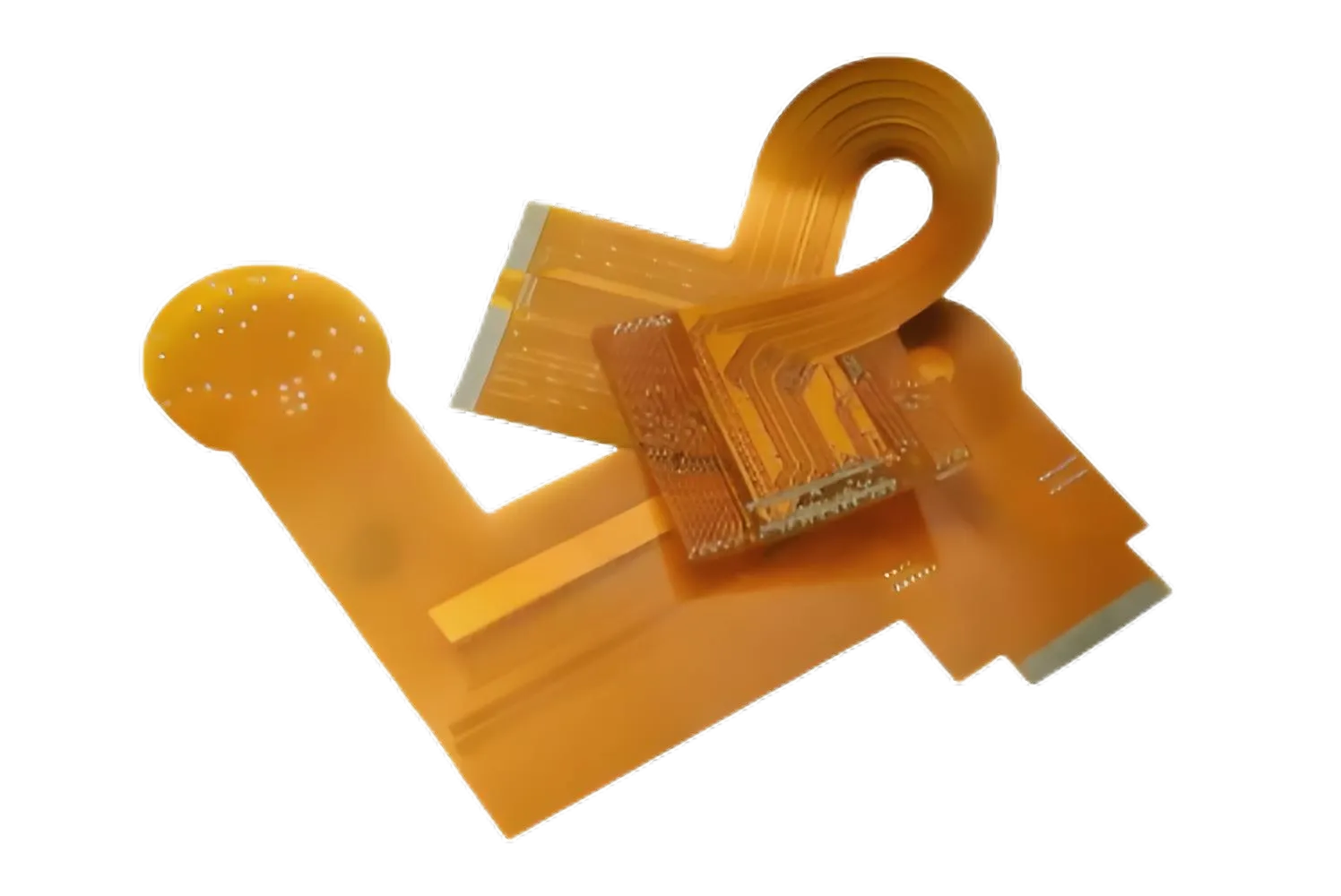

A Flexible PCB (Flex PCB) is a type of printed circuit board made from flexible materials like polyimide, allowing the board to bend and fold without breaking. It is ideal for compact electronic designs, wearables, and devices with moving parts. AIVON manufactures high-quality flexible PCBs with excellent durability, signal integrity, and space efficiency for demanding applications.
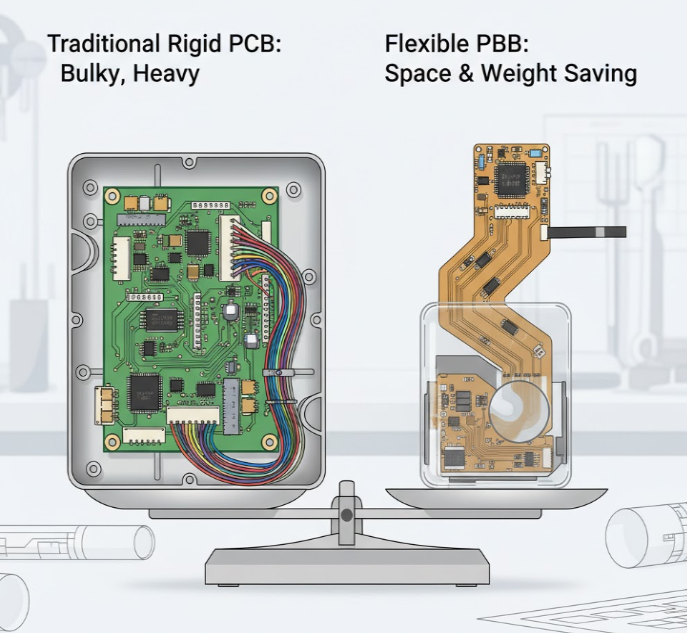
Flexible PCBs are exceptionally thin and lightweight, greatly reducing the overall size and mass of electronic assemblies compared with traditional rigid boards. By eliminating bulky connectors, wiring harnesses, and mechanical interfaces, they enable engineers to design slimmer and more compact products. This advantage is especially valuable in modern electronics where every millimeter counts. As a result, flexible circuits are widely used in portable and miniaturized devices such as smartphones, smartwatches, wearable health trackers, medical diagnostic instruments, and other applications that demand high functionality within limited space.
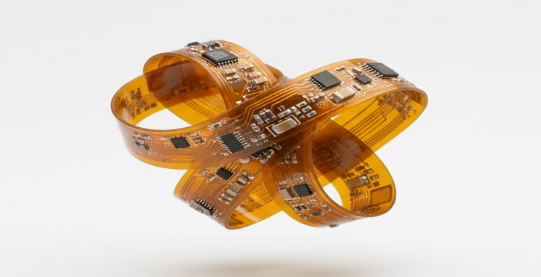
One of the most significant benefits of flexible PCBs is their ability to bend, fold, and twist without compromising performance. This mechanical adaptability allows flexible circuits to fit perfectly into irregular shapes, curved surfaces, or tightly confined spaces that rigid PCBs simply cannot accommodate. Engineers can create complex three-dimensional routing paths and integrate multiple functional layers while maintaining stable electrical performance and excellent signal integrity. This makes flexible PCBs ideal for dynamic applications such as foldable electronics, robotic arms, camera modules, and devices with moving parts.

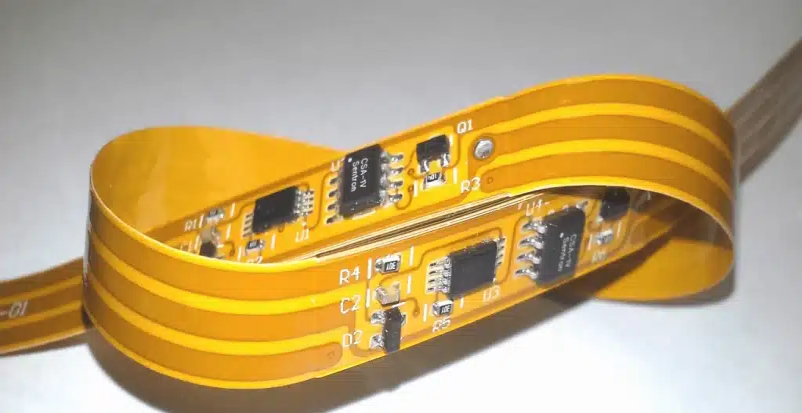
Flexible PCBs inherently reduce the number of interconnects, solder joints, and mechanical connectors—components that often represent the weakest points in conventional electronics. Fewer connection points mean fewer opportunities for mechanical failure, open circuits, or intermittent contact issues. Their ability to absorb shock, vibration, and thermal expansion further enhances system durability. This robust structure leads to longer product life cycles, higher reliability in harsh environments, and improved performance consistency in both consumer electronics and high-reliability industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical technology.

Flexible PCBs utilize thin substrates and advanced material systems that promote efficient heat transfer away from critical components. Their improved thermal conductivity helps distribute and dissipate heat more evenly across the circuit, reducing hotspots that can degrade performance or shorten component lifespan. In high-density assemblies, flexible circuits offer superior thermal management, ensuring stable operating temperatures, preventing overheating, and enhancing long-term reliability. This makes them highly advantageous for compact electronic designs where heat buildup is a major concern.

Flexible PCBs are widely used in smartphones, tablets, cameras, and wearables, enabling compact designs, lightweight construction, and reliable connections in slim and foldable devices.

Used in diagnostic equipment, hearing aids, and implantable devices, flexible PCBs provide high precision, biocompatibility, and durability for demanding medical environments.

Ideal for sensors, lighting systems, and infotainment modules, flexible PCBs offer vibration resistance and design flexibility for advanced automotive systems.

Flexible circuits ensure lightweight, high-reliability performance in aircraft, satellites, and defense systems, where space and durability are critical.

Applied in robotics, automation systems, and control modules, flexible PCBs deliver consistent signal performance and adaptability in high-stress environments.

Flexible PCBs are used in antennas, RF modules, and networking equipment, supporting compact layouts and stable signal transmission in high-frequency applications.