Introduction
This article demonstrates playing music with a buzzer driven by an STM32 microcontroller using STM32CubeIDE as the development environment.
Buzzer Types
Active buzzer
An active buzzer contains an internal oscillator and sounds when powered. Its output frequency is fixed.
Passive buzzer
A passive buzzer does not contain an oscillator. It requires an external signal at a specific frequency on its pin to produce sound.
This example uses a passive buzzer. Varying the control frequency produces different pitches.
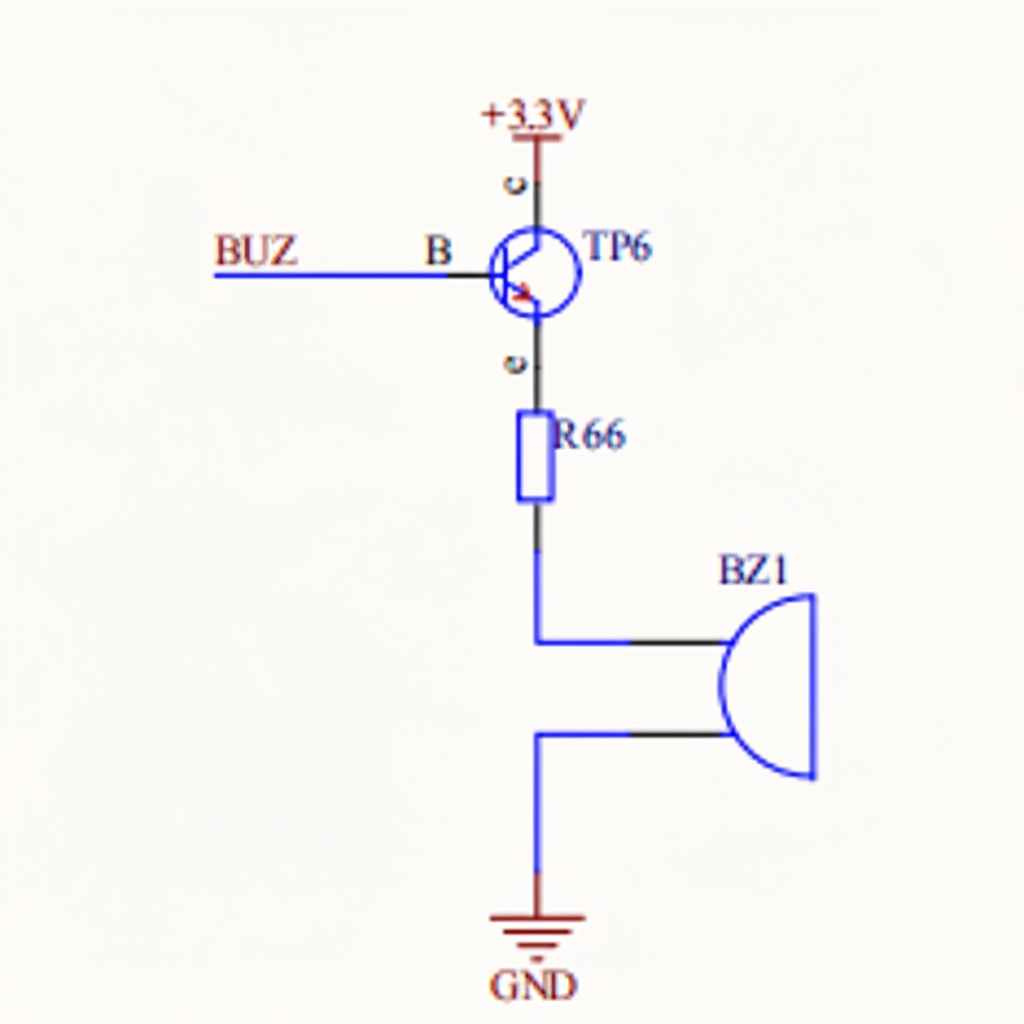
Circuit Diagram
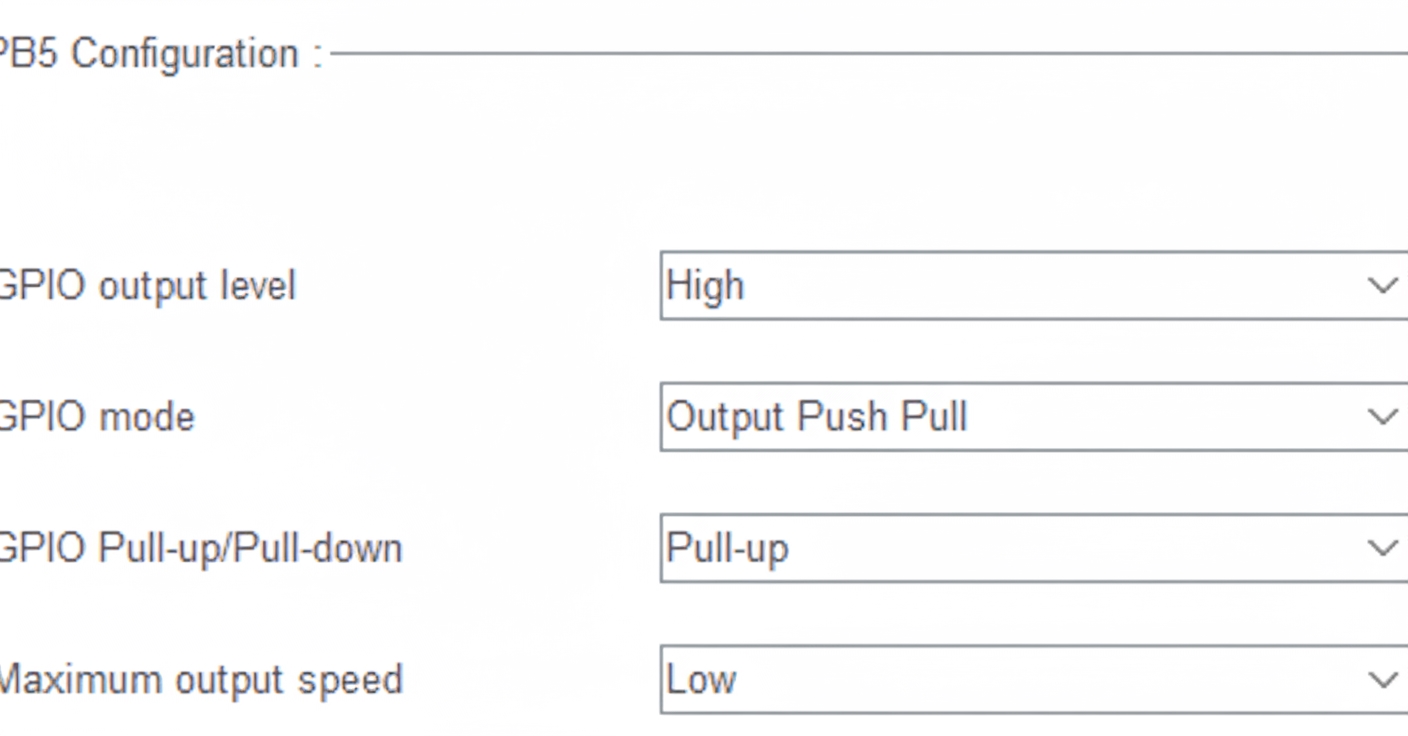
From the schematic, the buzzer is connected to PB5. Toggling PB5 at a certain frequency will make the buzzer sound.
STM32 Project
Open STM32CubeIDE and create a new STM32 project. For STM32CubeIDE usage, see the reference "STM32 PWM configuration and application".
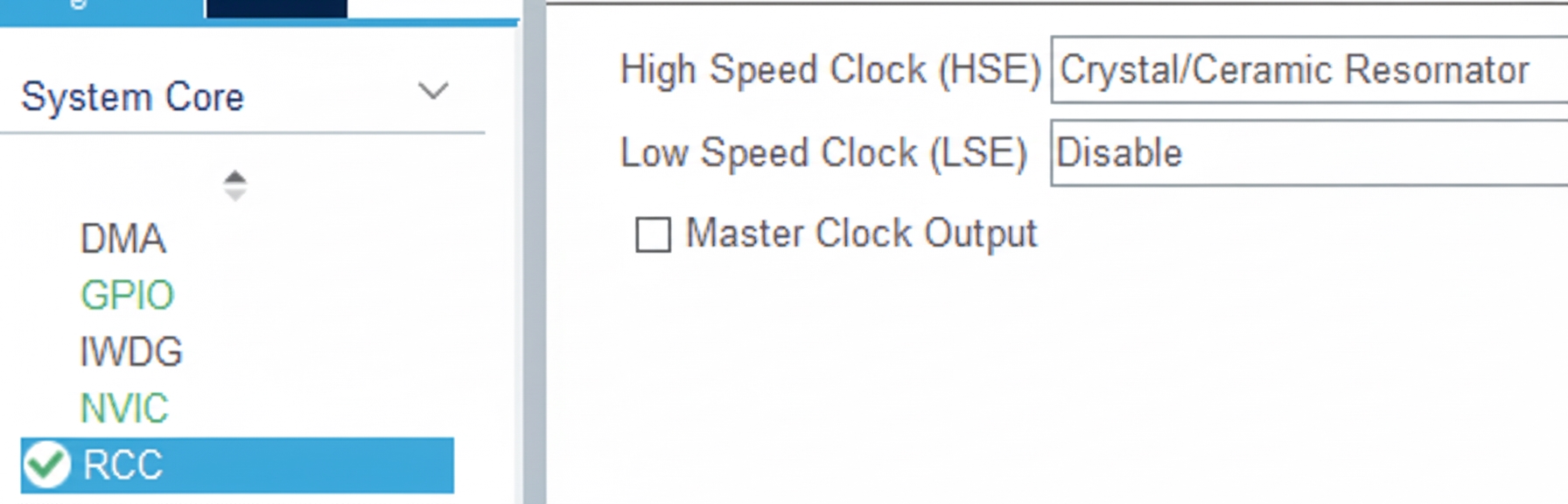
Configure the clock
Project settings

Enable PB5
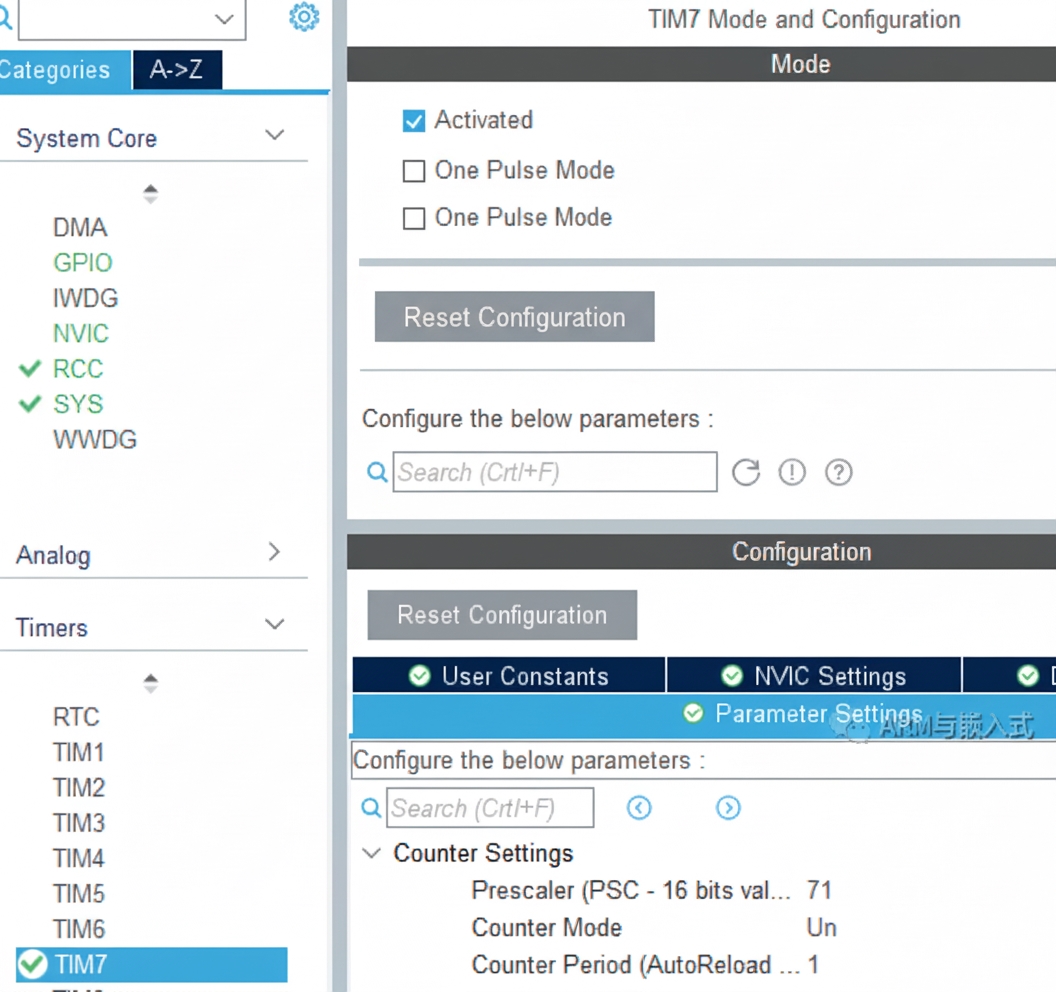
Delay function and timer
Implement a microsecond delay function. Enable timer TIM7 to implement HAL_Delay_us(). For details, see the reference "STM32 HAL custom delay function delay_us()".
Save and generate code.
Playback Logic
Iterate through the music array to get music[i]. Use music[i] as an index into the tone array to obtain the frequency for that note, i.e. tone[music[i]], then call the sound function to drive the buzzer. The duration of each note is controlled by the time array.
The two elements required to play music on the buzzer are frequency and duration, corresponding to pitch and beat in musical notation.