Introduction
Conformal coatings play a critical role in protecting printed circuit boards (PCBs) from environmental hazards such as moisture, dust, chemicals, and thermal stress. For electrical engineers, selecting the appropriate conformal coating material is essential to ensure the reliability and longevity of electronic assemblies in diverse applications. This guide explores the nuances of conformal coating material selection, providing a detailed comparison of material properties to aid in decision-making. From acrylic to silicone, urethane, and epoxy coatings, understanding their unique characteristics and application methods, including the use of specialized equipment like acrylic conformal coating machines, is vital. This article aims to equip engineers with the knowledge to make informed choices, ensuring optimal performance and protection for PCB designs across industries.
What Is Conformal Coating and Why It Matters
Conformal coating is a thin polymeric layer applied to PCBs to shield electronic components from environmental stressors. These coatings conform to the intricate shapes of the board, providing a protective barrier against moisture, corrosion, vibration, and temperature fluctuations. For electrical engineers, the importance of conformal coatings lies in their ability to enhance the durability and operational reliability of electronic devices, particularly in harsh environments like automotive, aerospace, and industrial settings.
The right conformal coating material selection can prevent failures due to short circuits, corrosion, or thermal shock. Without proper protection, PCBs are vulnerable to degradation, leading to costly repairs or system downtime. By understanding the properties and applications of various coatings, engineers can design more robust systems that meet stringent performance and safety standards, ensuring long-term functionality in challenging conditions.
Technical Principles of Conformal Coating Materials
Conformal coatings are formulated from different base materials, each offering distinct properties suited to specific environmental and operational needs. The primary types include acrylic, silicone, urethane, and epoxy coatings. Below, a conformal coating material properties comparison highlights their characteristics, helping engineers align material selection with project requirements.
Acrylic Coatings
Acrylic coatings are widely used due to their ease of application and reworkability. They provide good moisture resistance and dielectric properties, making them suitable for general-purpose applications. Acrylics are typically applied using automated equipment like an acrylic conformal coating machine, which ensures uniform coverage. However, they offer limited resistance to harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures, restricting their use in demanding environments.
Silicone Coatings
Silicone coatings excel in high-temperature and flexible PCBs. They maintain performance across a wide temperature range and resist moisture and vibration effectively. Application often involves a silicone conformal coating machine to achieve consistent thickness on complex geometries. While silicone provides excellent protection, it can be challenging to rework and may not adhere well to certain surfaces without proper preparation.
Urethane Coatings
Urethane coatings offer robust chemical resistance and durability, ideal for environments with exposure to solvents or abrasive conditions. They are often applied using a urethane conformal coating machine for precision. Urethanes provide strong adhesion and wear resistance but can be less flexible than silicones, potentially leading to cracking under mechanical stress. Reworking urethane coatings is also more difficult compared to acrylics.
Epoxy Coatings
Epoxy coatings are known for their exceptional mechanical strength and chemical resistance. They form a hard, durable layer, protecting against harsh conditions in industrial or military applications. An epoxy conformal coating machine is typically used for accurate application. However, epoxies lack flexibility, making them unsuitable for boards subject to vibration or thermal expansion. Removal for repairs is often labor-intensive.
Key Properties Comparison
- Acrylic: Moisture resistance — Good; Temperature range — Moderate; Chemical resistance — Low; Flexibility — Moderate; Ease of rework — High.
- Silicone: Moisture resistance — Excellent; Temperature range — Wide; Chemical resistance — Moderate; Flexibility — High; Ease of rework — Low.
- Urethane: Moisture resistance — Good; Temperature range — Moderate; Chemical resistance — High; Flexibility — Low; Ease of rework — Moderate.
- Epoxy: Moisture resistance — Excellent; Temperature range — Moderate; Chemical resistance — Excellent; Flexibility — Low; Ease of rework — Low.
This comparison underscores the importance of aligning material properties with the specific environmental challenges a PCB will face.
Factors Influencing Conformal Coating Material Selection
Selecting the right conformal coating material involves evaluating several critical factors to ensure compatibility with the PCB design and application environment. Below are key considerations for electrical engineers during the conformal coating material selection process.
Environmental Conditions
The operating environment dictates the level of protection required. For instance, PCBs exposed to high humidity or saltwater environments, such as in marine applications, benefit from silicone coatings due to their superior moisture resistance. In contrast, industrial settings with chemical exposure may necessitate urethane or epoxy coatings for their robust resistance to solvents and acids.
Thermal Requirements
Temperature fluctuations can impact coating performance. Silicone coatings are preferred for applications with extreme heat or cold due to their wide operating range. Acrylics and urethanes may suffice for moderate temperature conditions but could degrade under thermal cycling if not properly specified.
Mechanical Stress
PCBs subjected to vibration or flexing require a coating with high flexibility to prevent cracking. Silicone coatings are ideal in such scenarios, while epoxy coatings, though durable, may fail under mechanical stress due to their rigidity.
Application Method and Equipment
The choice of coating material often correlates with the application method. Automated systems like an acrylic conformal coating machine ensure even distribution for high-volume production. Similarly, silicone, urethane, and epoxy conformal coating machines cater to specific material viscosities and curing requirements, impacting the final quality of the protective layer.
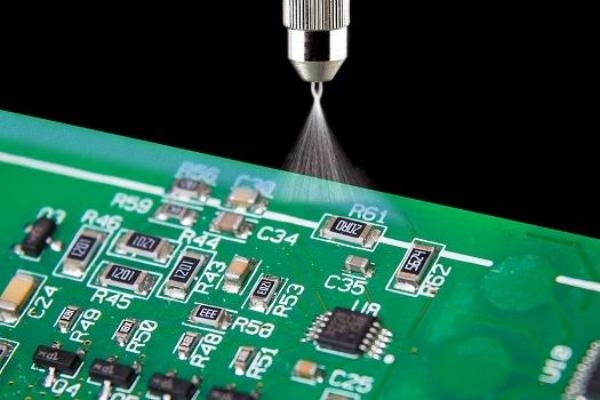

Regulatory and Standards Compliance
Compliance with industry standards is non-negotiable in conformal coating material selection. Standards such as IPC-CC-830C provide guidelines for the qualification and performance of conformal coatings, ensuring materials meet dielectric, environmental, and reliability criteria. Engineers must verify that chosen materials align with such standards for quality assurance.
Practical Solutions for Applying Conformal Coatings
Effective application of conformal coatings requires attention to preparation, method, and equipment to achieve optimal protection. Below are best practices for electrical engineers to follow during the coating process.
Surface Preparation
Before applying any coating, the PCB surface must be clean and free of contaminants like flux residues, oils, or dust. Contamination can compromise adhesion, leading to coating failure. Cleaning processes should adhere to guidelines outlined in standards like IPC-A-600K for acceptability of printed boards.
Selecting the Right Application Method
Conformal coatings can be applied via brushing, dipping, spraying, or automated selective coating. Automated methods using equipment such as a silicone conformal coating machine or urethane conformal coating machine are preferred for consistency in PCB mass production. Selective coating targets specific areas, minimizing material waste and avoiding sensitive components.
Curing and Inspection
Post-application curing is critical to achieving the desired protective properties. Curing conditions, including time and temperature, must align with material specifications to avoid defects like bubbles or incomplete hardening. After curing, visual and electrical testing per IPC-CC-830C standards ensures the coating meets performance requirements.

Rework and Repair Considerations
Engineers should anticipate the need for rework during the design phase. Acrylic coatings are easier to remove for repairs, while epoxy and silicone coatings pose challenges. Planning for reworkability can save time and reduce damage to the PCB during maintenance.
Troubleshooting Common Conformal Coating Issues
Even with careful conformal coating material selection, issues like delamination, cracking, or insufficient coverage can occur. Addressing these problems requires a systematic approach to identify root causes and implement corrective measures.
Delamination
Delamination often results from poor surface preparation or incompatible materials. Ensuring thorough cleaning and verifying material compatibility with PCB substrates can prevent this issue. Adherence to preparation guidelines in IPC-A-600K is essential for robust bonding.
Cracking
Cracking is common in rigid coatings like epoxy when subjected to thermal or mechanical stress. Switching to a more flexible material like silicone or reducing coating thickness can mitigate this problem, especially in high-vibration environments.
Incomplete Coverage
Uneven application, often due to improper equipment settings on an epoxy conformal coating machine or similar systems, can lead to incomplete coverage. Regular calibration of application equipment and operator training are vital to ensure uniform coating distribution.
Conclusion
Selecting the right conformal coating material for PCBs is a critical decision that impacts the reliability and performance of electronic assemblies. By understanding the properties of acrylic, silicone, urethane, and epoxy coatings through a detailed conformal coating material properties comparison, electrical engineers can make informed choices tailored to specific environmental and operational demands. Factors such as thermal range, mechanical stress, and application methods, including the use of specialized tools like an acrylic conformal coating machine, must guide the conformal coating material selection process. Adhering to industry standards ensures quality and compliance, while practical application and troubleshooting strategies minimize defects. With this comprehensive guide, engineers are equipped to protect their designs effectively, ensuring long-term durability in challenging conditions.
FAQs
Q1: What factors should I consider for conformal coating material selection?
A1: When selecting a conformal coating material, evaluate the operating environment, thermal requirements, mechanical stress, and regulatory compliance. Consider moisture, chemical exposure, and temperature ranges to choose between acrylic, silicone, urethane, or epoxy. Application methods and reworkability also play a role. Standards like IPC-CC-830C provide guidance to ensure the material meets performance criteria for your PCB design.
Q2: How does a silicone conformal coating machine improve application quality?
A2: A silicone conformal coating machine enhances application quality by providing precise control over coating thickness and coverage. It ensures uniform distribution across complex PCB geometries, reducing defects like uneven layers or missed areas. This automation is ideal for high-volume production, improving consistency and reliability while minimizing material waste in demanding applications requiring flexibility and temperature resistance.
Q3: What are the advantages of using a urethane conformal coating machine?
A3: A urethane conformal coating machine offers precision in applying urethane coatings, which are known for chemical resistance and durability. It ensures even application, critical for protecting PCBs in harsh environments with solvent exposure. Automated systems reduce human error, enhance repeatability, and support high-throughput manufacturing, making them suitable for industrial applications needing robust protection.
Q4: How does an epoxy conformal coating machine benefit industrial PCB protection?
A4: An epoxy conformal coating machine benefits industrial PCB protection by delivering consistent application of epoxy coatings, which provide excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance. This precision ensures complete coverage, vital for harsh industrial settings. Automated equipment supports efficient processing of large batches, maintaining coating integrity to shield electronics from aggressive conditions while adhering to strict performance standards.
References
IPC-CC-830C — Qualification and Performance Specification for Electrical Insulating Compound for Printed Wiring Assemblies. IPC, 2021.
IPC-A-600K — Acceptability of Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.