Introduction
Conformal coating plays a vital role in protecting printed circuit boards (PCBs) from environmental stressors like moisture, dust, and chemical contaminants. For electric engineers, ensuring PCB reliability in harsh conditions is a top priority. Implementing an automated conformal coating machine offers significant advantages over manual methods, enhancing precision and consistency. This article explores the benefits of automated systems, focusing on conformal coating process optimization and quality improvement. It also addresses strategies for conformal coating failure reduction and defect prevention. By adopting automation, engineers can achieve superior protection for electronic assemblies while adhering to strict industry standards. The following sections provide a detailed look into the technical principles, practical solutions, and best practices for integrating automation into the conformal coating process.
What Is Automated Conformal Coating and Why It Matters
Conformal coating is a thin protective layer applied to PCBs to shield them from environmental factors. These coatings, typically made from materials like acrylic, silicone, or polyurethane, guard against moisture, corrosion, and mechanical stress. Automated conformal coating involves the use of specialized machinery to apply this layer with high precision and uniformity. Unlike manual application, automation minimizes human error and ensures consistent thickness across complex board geometries.
The importance of automation in this context cannot be overstated. For electric engineers, reliability is critical, especially in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices where failure is not an option. Automated systems contribute to conformal coating quality improvement by reducing variability in application. They also support conformal coating failure reduction by eliminating issues like uneven coverage or missed areas. In high-volume production, automation saves time and labor costs while maintaining strict quality standards.
Technical Principles of Automated Conformal Coating
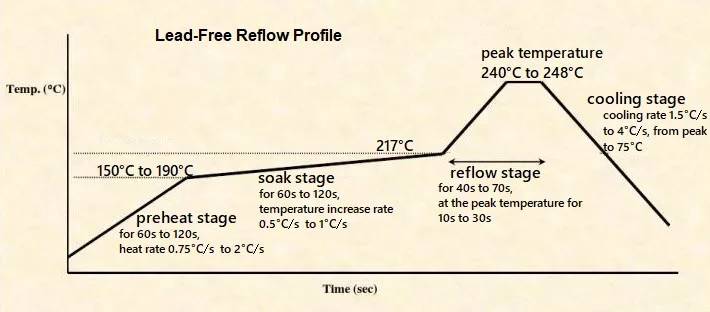
Automated conformal coating machines operate on principles of precision engineering and process control. These systems use robotic arms or programmable nozzles to apply coating materials with exacting accuracy. The process begins with loading the PCB into the machine, where it is scanned or aligned to ensure proper positioning. Coating material is then dispensed based on predefined parameters such as thickness, coverage area, and curing time.
Several application methods exist within automated systems. Spray coating, for instance, uses atomized material to cover large areas quickly. Selective coating targets specific regions, avoiding sensitive components like connectors. Dip coating immerses the entire board, though it is less common in automation due to material waste. Each method can be optimized for specific PCB designs, contributing to conformal coating defect prevention.
Control systems in these machines monitor variables like viscosity and flow rate. This ensures uniform application, a key factor in conformal coating quality improvement. Additionally, many systems integrate inspection tools to detect defects immediately after application. By adhering to standards such as IPC-CC-830C, which governs conformal coating material performance, engineers can ensure that automated processes meet industry benchmarks for reliability.
Benefits of Automated Conformal Coating Machines
The advantages of using an automated conformal coating machine are numerous for electric engineers seeking to enhance PCB reliability. Below are the primary benefits, with a focus on the target areas of process optimization and defect prevention.
- Consistency and Precision: Automation ensures uniform coating thickness, critical for protecting against environmental damage. This directly supports conformal coating quality improvement by minimizing weak spots.
- Time Efficiency: Automated systems apply coatings faster than manual methods, ideal for high-volume production. This efficiency aids in conformal coating process optimization.
- Reduced Human Error: Manual application often leads to uneven layers or missed areas. Automation eliminates these risks, contributing to conformal coating failure reduction.
- Material Savings: Precise dispensing reduces waste of costly coating materials. This cost-effectiveness is a significant automated conformal coating machine benefit.
- Scalability: Automated systems can handle varying production volumes without sacrificing quality. This flexibility is essential for meeting tight deadlines.
Furthermore, automation supports traceability by logging process parameters for quality assurance. Engineers can reference these logs to identify and address potential issues, further aiding in conformal coating defect prevention.
Practical Solutions for Conformal Coating Process Optimization
Optimizing the conformal coating process with automation requires a systematic approach. Electric engineers can follow these best practices to maximize reliability and efficiency while focusing on conformal coating process optimization.
Equipment Selection and Setup
Choosing the right automated machine involves assessing production needs. Factors like board size, coating type, and throughput must guide the decision. Proper setup is equally important. Calibrating the machine to apply the correct thickness prevents overcoating or undercoating, both of which can compromise protection.
Material Compatibility
Not all coating materials suit every PCB or environment. Engineers must select materials based on operating conditions and compatibility with board components. Standards like IPC-CC-830C provide guidelines for material performance, ensuring selections align with reliability goals.
Programming and Customization
Automated machines allow programming of specific patterns to avoid coating-sensitive areas. Customizing these settings for each PCB design enhances precision. Regular updates to programming can address new design challenges, supporting conformal coating quality improvement.
Routine Maintenance
Machines must be maintained to prevent downtime or defective application. Cleaning nozzles and checking calibration regularly ensures consistent performance. This proactive approach aids in conformal coating defect prevention.
Integration with Inspection Systems
Post-application inspection is critical for quality control. Automated optical inspection systems, guided by standards like IPC-A-610H, can detect defects such as bubbles or voids. Integrating these systems into the workflow allows immediate corrective action, reducing failure risks.
Strategies for Conformal Coating Failure Reduction
Failures in conformal coating often stem from improper application or material issues. Automated systems address these root causes through structured processes. Below are strategies to minimize failures, focusing on conformal coating failure reduction.
First, ensure proper surface preparation. Contaminants like dust or oil on the PCB can prevent coating adhesion. Cleaning boards before application, following guidelines from standards like IPC-A-600K, is essential. Automation can integrate cleaning steps to streamline this process.
Second, control environmental conditions during application. Temperature and humidity affect coating curing. Automated machines often include environmental controls to maintain optimal conditions, reducing the risk of defects.
Third, conduct regular testing of coated boards. Standards such as IPC-TM-650 provide test methods for evaluating coating performance under stress. Automated systems can log test data, helping engineers identify trends or recurring issues.
Finally, train personnel on machine operation and troubleshooting. Even with automation, human oversight is necessary. Well-trained staff can spot anomalies early, preventing widespread quality issues and supporting conformal coating defect prevention.
Insights into Conformal Coating Defect Prevention
Preventing defects in conformal coating requires attention to detail at every stage. For electric engineers, understanding common defects and their causes is the first step. Bubbles, for instance, often result from trapped air during application. Uneven coating can occur due to improper machine settings. Voids may form if the material cures too quickly.
Automated systems mitigate these issues through precise control. Adjusting flow rates and nozzle angles can eliminate bubbles. Programming specific paths ensures even coverage. Monitoring curing times prevents voids. Additionally, adhering to standards like IPC-A-610H helps define acceptable quality levels, guiding defect prevention efforts.
Engineers should also consider post-coating handling. Improper storage or transport can damage the coating before it fully cures. Automated systems can integrate protective measures, such as controlled cooling zones, to safeguard boards during these stages.
Conclusion
Implementing automated conformal coating is a transformative step for improving PCB reliability. The benefits of automated conformal coating machines include enhanced precision, reduced errors, and optimized material use. Through careful process design, engineers can achieve conformal coating process optimization and quality improvement. Strategies for conformal coating failure reduction and defect prevention further ensure that PCBs withstand harsh environments. By adhering to industry standards and leveraging automation, electric engineers can protect critical electronics with confidence. The insights and practices discussed here provide a roadmap for integrating automation into manufacturing workflows, ultimately delivering robust and reliable PCB assemblies.
FAQs
Q1: How does an automated conformal coating machine benefit PCB reliability?
A1: Automated conformal coating machines enhance PCB reliability by ensuring uniform application of protective layers. This consistency prevents weak spots that could lead to failures from moisture or contaminants. As a key automated conformal coating machine benefit, it reduces human error and speeds up production, making it ideal for high-volume runs while maintaining strict quality standards for electric engineers.
Q2: What steps are crucial for conformal coating process optimization in automation?
A2: Conformal coating process optimization requires proper machine calibration, material selection, and environmental control. Programming specific application patterns avoids sensitive areas, while regular maintenance prevents downtime. Integrating inspection systems ensures immediate defect detection. Following industry standards for material and process control is vital for engineers to achieve consistent, reliable results.
Q3: How can conformal coating failure reduction be achieved with automated systems?
A3: Conformal coating failure reduction is achieved by using automated systems to control application precision and material consistency. Proper surface cleaning before coating, maintaining optimal curing conditions, and routine testing per industry guidelines minimize risks. Automation logs process data for traceability, allowing engineers to address potential issues before they escalate into failures.
Q4: What are common methods for conformal coating defect prevention in automated setups?
A4: Conformal coating defect prevention in automated setups involves adjusting machine settings to avoid bubbles or uneven layers. Monitoring curing times prevents voids, while pre-application cleaning ensures adhesion. Automated inspection systems detect issues early. Adhering to quality standards helps define acceptable outcomes, guiding engineers in maintaining defect-free coatings on PCBs.
References
IPC-CC-830C — Qualification and Performance Requirements for Electrical Insulating Compounds for Printed Wiring Assemblies. IPC, 2018.
IPC-A-610H — Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies. IPC, 2020.
IPC-A-600K — Acceptability of Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
IPC-TM-650 — Test Methods Manual. IPC, Current Version.