Introduction
For electronic hobbyists, creating a printed circuit board (PCB) is an exciting journey from design to assembly. However, one critical step often overlooked is depaneling, the process of separating individual PCBs from a larger panel after manufacturing. Understanding how to depanel a PCB effectively ensures the integrity of your components and prevents damage. This PCB depaneling tutorial will guide hobbyists through essential methods like the V-scoring technique and tab-routing technique. With a focus on manual depaneling guides, this article offers practical steps to achieve clean separations while maintaining board quality. Whether you are prototyping a new project or assembling small batches, mastering these techniques will elevate your skills and project outcomes.
What Is PCB Depaneling and Why It Matters
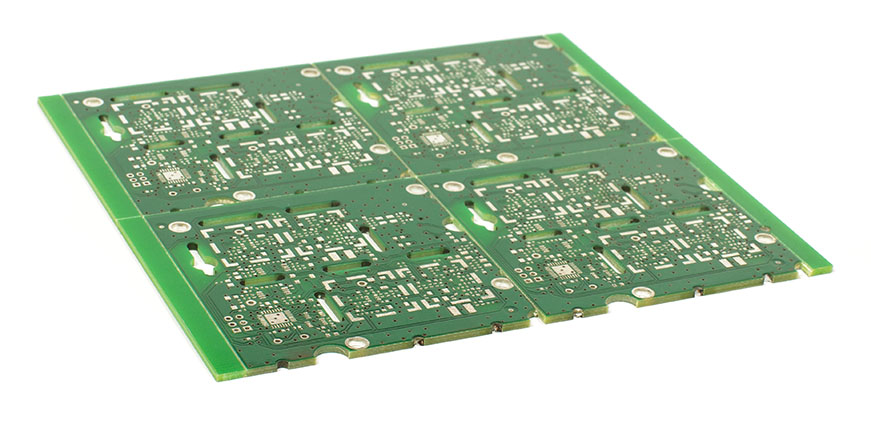
PCB depaneling refers to the process of separating individual circuit boards from a larger panel or array created during manufacturing. Panels are used to streamline production, allowing multiple boards to be fabricated and assembled simultaneously. For hobbyists, depaneling is crucial because improper separation can lead to cracked solder joints, damaged traces, or even complete board failure. A well-executed depaneling process preserves the structural and electrical integrity of each PCB. It also saves time and reduces waste by minimizing errors. As hobbyists often work with limited resources, learning efficient methods like V-scoring and tab-routing ensures cost-effective and reliable results in every project.
Technical Principles of PCB Depaneling
Depaneling methods are designed based on the panel's layout, board material, and component placement. The goal is to minimize mechanical stress during separation. Stress can cause microcracks in the substrate or delamination, which may not be visible but can affect performance over time. Two widely used techniques for hobbyists are V-scoring and tab-routing, each with distinct principles.
V-Scoring Technique
The V-scoring technique involves creating V-shaped grooves along the separation lines of a panel. These grooves weaken the material, allowing the board to be snapped apart by hand or with minimal tools. V-scoring is typically applied to straight-line separations and works best with rigid boards like PCB FR-4. The depth of the groove is critical, as it must be sufficient to facilitate breaking without compromising the board's structure during handling. According to industry guidelines, such as those outlined in IPC-6012E, the remaining material thickness at the groove should be carefully controlled to ensure clean separation.
Tab-Routing Technique
The tab-routing technique uses small, breakable tabs to hold individual boards together within a panel. These tabs are strategically placed along the board edges and are often perforated with holes, known as mouse bites, to ease separation. Tab-routing is ideal for irregular or non-linear board shapes where V-scoring cannot be applied. The technique requires precise design to balance the strength of tabs for handling and ease of breaking during depaneling. Stress concentration around tabs must be managed to avoid damage to nearby components or traces.
Suggested Reading: Choosing the Right PCB Depaneling Method: A Comprehensive Comparison
Practical Solutions for Manual Depaneling
For electronic hobbyists, manual depaneling is often the most accessible and cost-effective approach. This section provides a step-by-step manual depaneling guide focusing on the V-scoring and tab-routing techniques. These methods require minimal tools and can be performed in a home workshop with proper care.
Tools and Safety Precautions
Before starting, gather essential tools such as protective gloves, safety glasses, a flat workbench, and a small vise or clamp for stability. A pair of pliers or a dedicated PCB separator tool can assist with tab-routing separations. Always work in a well-ventilated area and avoid applying excessive force that could damage the board. Ensuring personal safety and board protection is the first step in how to depanel a fast turn PCB successfully.
Step-by-Step Guide for V-Scoring Technique
- Inspect the panel to identify the V-scored lines. These are visible as shallow grooves along the separation edges.
- Place the panel on a flat surface with the scored line aligned over the edge of the workbench or a straight support.
- Apply gentle, even pressure along the scored line using both hands to bend the panel. The board should snap cleanly at the groove.
- If resistance is felt, stop and check for incomplete scoring or misalignment. Avoid forcing the separation.
- Smooth any rough edges with fine sandpaper to prevent injury or damage during handling.
This V-scoring technique is straightforward for hobbyists working with simple, rectangular boards. It minimizes the risk of stress to components if done carefully.
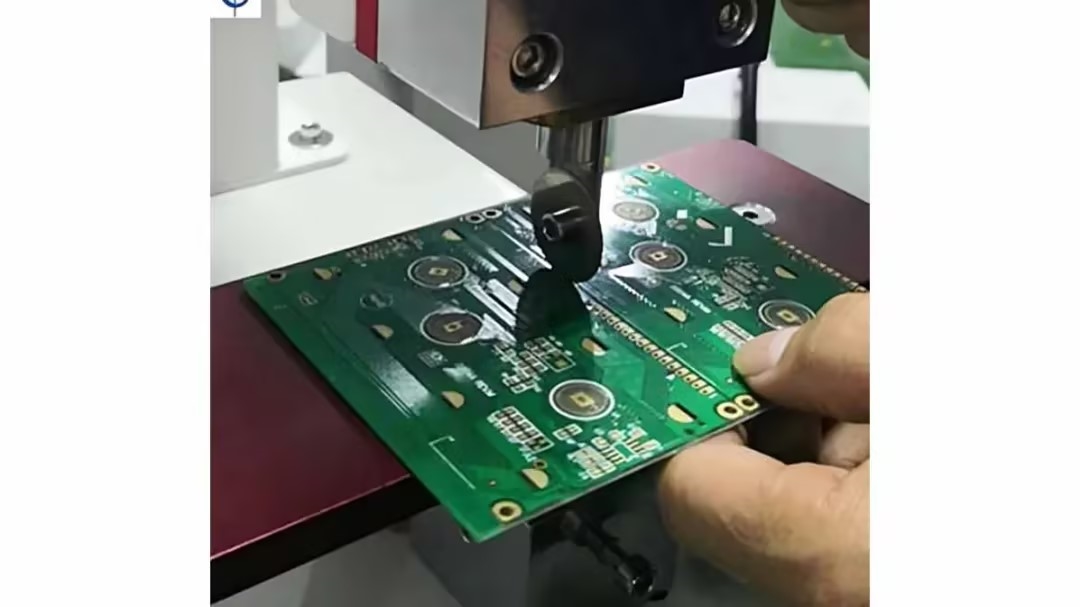

Step-by-Step Guide for Tab-Routing Technique
- Locate the tabs connecting individual boards. These are often marked by small perforations or holes.
- Secure the panel in a vise or clamp to prevent movement during separation. Ensure components are not near the clamping area.
- Use pliers to grip the tab and twist gently until it breaks. Alternatively, apply pressure with a PCB separator tool for cleaner results.
- Repeat for each tab, working systematically around the board's perimeter to avoid uneven stress.
- File down any remaining tab stubs with sandpaper for a polished finish.
The tab-routing technique offers flexibility for complex board shapes, making it a valuable skill for hobbyists tackling custom designs.
Related Reading: Depanelization Techniques: Stamp Holes vs. V-Scoring for PCBs
Best Practices for Clean Depaneling
To achieve optimal results, always align separation forces with the board's natural weak points, whether scored lines or tabs. Avoid bending or twisting the panel excessively, as this can propagate cracks into critical areas. If components are mounted close to separation edges, consider using a protective barrier like cardboard to shield them during the process. Following standards like IPC-A-600K for board acceptability can guide hobbyists in assessing the quality of separated edges and identifying potential issues.
Troubleshooting Common PCB Depaneling Defects
Even with careful preparation, hobbyists may encounter challenges during depaneling. Uneven breaks in V-scored panels often result from inconsistent groove depth or improper alignment during separation. If a board does not snap cleanly, stop and reassess the scoring line before proceeding. For tab-routing, broken tabs may leave jagged edges that can snag on components or cause injury. Using a small file to smooth these edges resolves the issue. Additionally, if a board shows signs of delamination after separation, it may indicate excessive force or material defects. Reducing pressure and working slowly can mitigate such risks.
Conclusion
Mastering PCB depaneling is an essential skill for electronic hobbyists looking to bring their projects to life. By understanding how to depanel a PCB using methods like the V-scoring technique and tab-routing technique, you can achieve clean separations without compromising board quality. This PCB depaneling tutorial has outlined practical steps for manual depaneling, emphasizing safety and precision. With practice, these techniques will become second nature, allowing you to handle panels of varying complexity. Equipped with this manual depaneling guide, hobbyists can confidently tackle their next project while ensuring the integrity of every board.
FAQs
Q1: What is the easiest way to learn how to depanel a PCB as a beginner?
A1: For beginners, starting with the V-scoring technique is the easiest approach to learn how to depanel a PCB. It requires minimal tools, often just your hands, and works well for straight-edged boards. Inspect the scored lines, align the panel over a flat edge, and apply gentle pressure to snap it apart. Practice on scrap panels first to build confidence and avoid damaging critical projects.
Q2: How does the V-scoring technique differ from other depaneling methods?
A2: The V-scoring technique uses pre-cut grooves to weaken the panel along straight lines for easy snapping. Unlike tab-routing, which relies on breakable tabs for irregular shapes, V-scoring is simpler and faster for rectangular boards. It also produces less mechanical stress compared to methods like shearing, making it suitable for hobbyists with basic tools and limited experience.
Q3: What tools are recommended for a manual depaneling guide with tab-routing?
A3: For a manual depaneling guide using the tab-routing technique, basic tools include protective gloves, safety glasses, and pliers for breaking tabs. A small vise or clamp helps secure the panel during separation. A fine-grit sandpaper or file is useful for smoothing rough edges after breaking tabs. These tools are affordable and accessible for hobbyists working in a home setup.
Q4: Can the tab-routing technique be used for all PCB shapes?
A4: Yes, the tab-routing technique is versatile and ideal for non-linear or complex PCB shapes where straight cuts like V-scoring are impractical. Tabs with perforations hold the boards in a panel and can be placed strategically to support irregular outlines. This method allows hobbyists to separate custom designs with precision, though care is needed to avoid stress near components.
References
IPC-6012E — Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
IPC-A-600K — Acceptability of Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.