Does Solder Mask Color Affect PCB Heat Dissipation?
When designing a printed circuit board (PCB), every minute detail warrants consideration, including the hue of the solder mask. A common question arises: does solder mask color genuinely impact thermal management? The concise answer is affirmative, but its influence is often marginal when weighed against other design parameters. Darker shades, such as black, tend to absorb more thermal energy, whereas lighter options like white reflect it, potentially aiding in the dispersion of heat. Nevertheless, for the majority of high-power PCB designs, elements such as thermal vias, copper thickness, and integrated heat sinks contribute far more significantly to effective PCB cooling than the choice of solder mask color.
This extensive guide will thoroughly examine the correlation between solder mask color and thermal management. We will explore how various colors interact with heat dissipation, discuss practical considerations pertinent to high-power PCB designs, and offer actionable advice for optimizing the thermal performance of PCBs. Whether you are an engineer working on intricate designs or a hobbyist seeking to enhance PCB cooling, this article aims to equip you with informed decision-making capabilities.
What is a Solder Mask and Why is its Role Significant?
A solder mask constitutes a thin polymer layer meticulously applied to the surface of a PCB. Its primary functions include safeguarding copper traces from oxidation, preventing the formation of solder bridges during the assembly process, and providing electrical insulation against short circuits. This layer also imparts the characteristic color to the PCB—commonly green, but also available in shades such as black, red, blue, white, and others. While its fundamental purpose is protection, the solder mask can, to a minor extent, influence thermal management by affecting the absorption or reflection of heat on the board’s surface.
Effective thermal management is paramount in PCB design, particularly for high-power applications where components generate substantial heat. Inadequate PCB cooling can precipitate component failure, diminish lifespan, and compromise overall operational reliability. As engineers increasingly focus on optimizing heat dissipation, even subtle factors like solder mask color enter into consideration. Let’s dissect its mechanism and determine its true relevance in your design choices.
How Different Solder Mask Colors Influence Heat Dispersion
The chromatic property of an object dictates its interaction with both heat and light. This fundamental principle extends to solder masks on PCBs.
Thermal Behavior of Various Colors
● Black Solder Mask: Black surfaces are known to absorb a greater proportion of light and heat compared to lighter colors. Consequently, a black solder mask can trap heat on the PCB surface, potentially leading to a slight elevation in the board’s temperature. In high-power PCB designs, this characteristic could intensify thermal issues if other cooling strategies are insufficient.
● White Solder Mask: Conversely, white surfaces reflect more light and heat. This property can contribute to a reduction in the amount of heat absorbed by the PCB. While subtle, this might facilitate improved heat dissipation in environments exposed to direct sunlight or elevated ambient temperatures.
● Green, Red, and Blue Solder Masks: These colors occupy the middle ground within the thermal spectrum. Green, being the industry standard, offers a balanced equilibrium between heat absorption and reflection. Red and blue exhibit comparable thermal characteristics, with minor variations dependent on their specific hue and the particular material formulation employed.
Despite these observable differences, academic studies and practical evaluations generally indicate that the impact of solder mask color on PCB thermal management is minimal—often translating to less than a 1-2°C variance in operating temperature under typical conditions. For the majority of designs, the solder mask’s thickness (typically ranging from 0.8 to 1.2 mils) and its material composition exert a more profound influence on heat dissipation than its color alone.
Other Critical Factors in PCB Thermal Management
While the solder mask color plays a modest role in heat dissipation, several other design elements wield a far greater influence on effective PCB cooling. When developing high-power PCB designs, prioritizing these factors is essential for robust thermal management.
Primary Thermal Optimization Elements
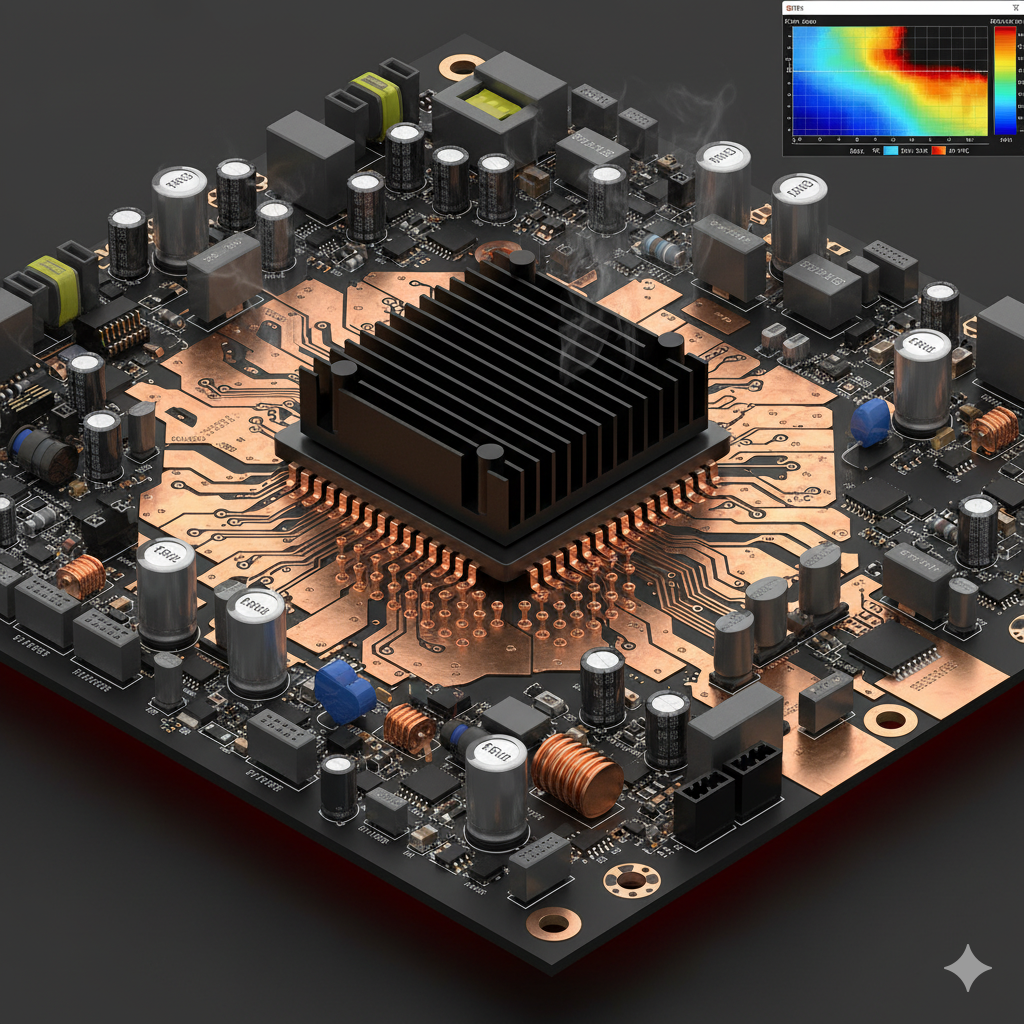
● Thermal Vias: These are small, copper-filled or plated holes engineered to transfer heat from one side of the PCB to another, frequently connecting to a heat sink or a ground plane. For high-power components, such as power transistors or LEDs, incorporating an array of thermal vias (e.g., 0.3 mm diameter, spaced 1.2 mm apart) can reduce component temperatures by 5-10°C or more, depending on the specific design.
● Copper Thickness and Layout: The thickness of the copper layers directly dictates the heat dissipation capacity of a PCB. Utilizing heavy copper PCB instead of the standard 1 oz/ft² (35 μm) can enhance heat spreading by as much as 30%. Furthermore, designing expansive copper pours or planes in proximity to heat-generating components effectively distributes thermal energy across the board.
● Heat Sinks and Dedicated Cooling Solutions: For high-power applications, the attachment of heat sinks to critical components represents one of the most efficacious strategies for managing heat. A heat sink with a thermal resistance of 2°C/W can maintain a power IC within its safe operating temperature range, even under significant electrical loads. Active cooling solutions, such as miniature fans, can further reduce temperatures by 10-20°C in extreme scenarios.
● Strategic Component Placement: Positioning heat-generating components with ample separation from each other and closer to the PCB edges can prevent localized heat accumulation. For example, spacing two high-power ICs at least 10 mm apart can mitigate localized temperature spikes by 3-5°C compared to a clustered arrangement.
In comparison to these robust strategies, the selection of solder mask color is a minor consideration. However, in specific contexts—such as outdoor applications routinely exposed to direct sunlight—opting for a lighter color like white could provide a marginal advantage in heat dissipation.
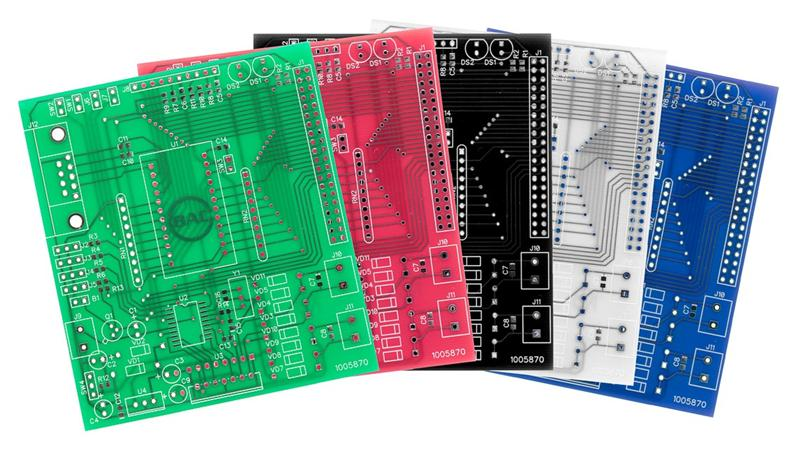
Practical Aspects of Solder Mask Color Selection
While thermal performance is one consideration, various other practical factors frequently dictate the choice of solder mask color in PCB design.
Design and Manufacturing Considerations
● Visibility for Inspection: Green solder masks remain the prevailing industry standard largely because they offer superior contrast against copper traces and components, thereby simplifying visual inspection processes. Conversely, black solder masks, despite their often sleek appearance, can obscure minor defects, potentially leading to an increase in manufacturing errors.
● Aesthetics and Brand Identity: Many corporations select specific solder mask colors to align with their brand identity. A vibrant red or distinctive blue mask can visually differentiate a product, even if its impact on thermal performance is negligible.
● Cost and Availability: Green solder masks are typically the most economical and widely accessible option. Specialty colors like white or black may incur a slight premium or necessitate longer lead times, depending on the chosen manufacturer.
● Environmental Resilience: For PCBs intended for use in outdoor or high-radiation environments, a lighter color might aid in reflecting heat and ultraviolet (UV) light, consequently reducing thermal stress on the board over an extended period.
For most engineers, the decision regarding solder mask color will involve a careful balance of these practical factors alongside any minor thermal advantages. If heat dissipation is a critical engineering concern, it is advisable to concentrate on the aforementioned design elements before prioritizing color.
Strategies for Optimizing PCB Cooling in High-Power Designs
For those engaged in high-power PCB design, effective thermal management must be a paramount objective.
Actionable Cooling Enhancement Tips
● Utilize Simulation Tools: Before finalizing any design, employ thermal simulation software to model heat flow across the PCB. Such tools can accurately predict temperature increases (e.g., a 15°C rise near a power regulator) and assist in refining layouts or integrating additional cooling features.
● Increase Board Thickness: A thicker PCB (e.g., 2.0 mm instead of 1.6 mm) possesses a greater capacity to manage heat due to its increased material mass and enhanced heat spreading capabilities.
● Select High-Thermal-Conductivity Materials: Consider employing substrate materials with superior thermal conductivity, such as copper PCB, these can dissipate heat up to 10 times more efficiently than standard FR-4 materials (which have a thermal conductivity of approximately 0.3 W/m·K, compared to 3-10 W/m·K for metal-core).
● Optimize Airflow: If the design permits, position the PCB in a manner that maximizes either natural convection or forced airflow. Even a modest increase in airflow can reduce operating temperatures by 5-10°C.
● Monitor Operating Conditions: Rigorously test your PCB under actual operating conditions to confirm that it remains within safe temperature limits (typically below 85°C for the majority of components). Employ thermal imaging cameras to precisely identify any localized hot spots.
By concentrating on these comprehensive strategies, you can achieve robust PCB cooling without having to rely on solder mask color as a primary thermal solution.
Concluding Thoughts: Solder Mask Color and Your Thermal Strategy
In the intricate domain of PCB thermal management, the color of the solder mask does exert a measurable, albeit minor, influence on heat dissipation. Darker shades like black tend to absorb more heat, while lighter hues such as white are more reflective. However, this impact is generally marginal—often negligible when compared to the profound effects of other design choices, including thermal vias, optimal copper thickness, and integrated heat sinks. For the vast majority of high-power PCB designs, focusing on these critical engineering elements will yield significantly superior results in PCB cooling than simply altering the solder mask color.
Nonetheless, if your PCB is destined for a unique operating environment (e.g., prolonged exposure to direct sunlight or extreme ambient temperatures), opting for a lighter solder mask color could indeed provide a slight, beneficial edge. Ultimately, the most judicious approach involves prioritizing well-established thermal management techniques while selecting a solder mask color that effectively addresses your aesthetic preferences, brand identity requirements, and essential inspection needs.
AIVON is dedicated to assisting you in designing and manufacturing PCBs that perform dependably under a full spectrum of conditions. Whether your focus is on exploring the thermal properties of a black solder mask or optimizing high-power PCB designs, our expert team is poised to support you with professional guidance and superior manufacturing services. Together, let us engineer cooler, more efficient circuit boards.