Introduction
Selecting electronic components for high-reliability applications is a critical task for electrical engineers working in industries such as aerospace, military, medical, and industrial automation. These environments demand components that can withstand extreme conditions while maintaining consistent performance over extended periods. Failure in such systems can lead to catastrophic consequences, including loss of life or significant financial damage. This article explores the essential factors for choosing components that meet stringent reliability standards. From understanding component derating factors to evaluating radiation-hardened components for extreme environments, engineers must navigate a complex landscape of technical specifications and quality controls. The focus will be on practical guidance for ensuring durability and performance in demanding applications like military-grade and aerospace components.
Importance of High-Reliability Electronics Components in Critical Systems
High-reliability applications refer to systems where component failure is not an option due to the critical nature of their function. Examples include flight control systems in aerospace, life-support equipment in medical devices, and communication systems in military operations. The reliability of electronic components in these settings directly impacts safety, mission success, and operational continuity. Engineers must prioritize components that meet strict performance criteria under harsh conditions such as temperature extremes, vibration, and radiation exposure. Selecting components for extreme environments requires a deep understanding of material properties, environmental stresses, and long-term behavior to prevent system failures. This is why standards from organizations like IPC and JEDEC are vital for guiding component selection and ensuring consistent quality.
Core Technical Principles: Environmental Stressors, Derating, and Radiation Hardening
Understanding Environmental Stressors
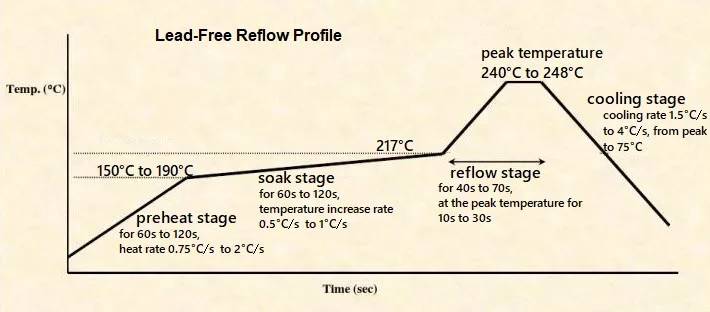
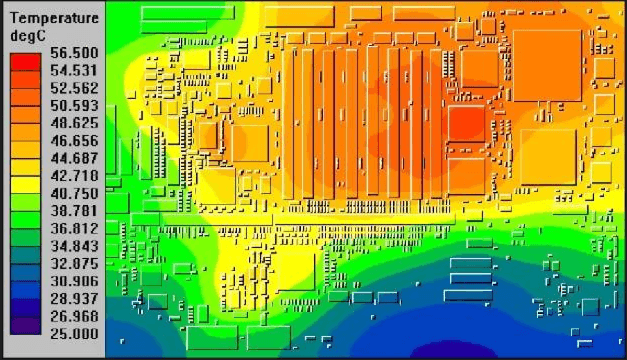
Electronic components in high-reliability applications face a range of environmental challenges. Temperature fluctuations can cause thermal expansion and contraction, leading to mechanical stress on solder joints and materials. Vibration and shock, common in aerospace and military settings, can result in physical damage or connection failures. Radiation exposure, particularly in space applications, can degrade semiconductor performance over time. Engineers must assess these stressors when selecting components for extreme environments to ensure they can endure without performance loss. Standards like JEDEC J-STD-020E provide guidelines for evaluating moisture and reflow sensitivity, which are critical in humid or variable climates.
Component Derating Factors
Component derating involves operating components below their maximum rated specifications to enhance reliability and extend lifespan. This practice reduces stress on materials by limiting factors such as voltage, current, and temperature. For instance, operating a capacitor at 50 percent of its rated voltage can significantly lower failure rates. Derating factors are especially crucial in high-reliability applications where components must function without degradation over long periods. Engineers should consult manufacturer data sheets alongside industry standards to determine appropriate derating levels for specific components. This approach minimizes risks associated with thermal runaway or material fatigue in demanding conditions.
Radiation-Hardened Components for Space and Nuclear Applications
Radiation-hardened components are designed to withstand ionizing radiation, a primary concern in aerospace and nuclear environments. Radiation can cause single-event upsets or long-term degradation in standard semiconductors, leading to system errors. Radiation-hardened designs use specialized materials and fabrication techniques to mitigate these effects. When selecting such components, engineers must evaluate total ionizing dose tolerance and single-event effect immunity. These specifications ensure performance in space missions or near nuclear facilities. Adhering to relevant standards and testing protocols is essential for verifying the suitability of these components in radiation-prone settings.
Suggested Reading: Selecting PCB Components
Practical Guidelines: Military/Aerospace Components, Quality Control, Materials, and Supply Chain
Evaluating Military-Grade and Aerospace Components
Military-grade components and aerospace components—including the aerospace PCB—are built to meet rigorous standards for durability and performance. These components undergo extensive testing for shock, vibration, and temperature extremes to ensure functionality in combat or flight scenarios. Engineers must verify compliance with specific military or aerospace standards, such as those outlined by international bodies, to guarantee reliability. Checking for certifications and test data is a critical step in the selection process. Additionally, traceability of materials and manufacturing processes helps ensure that components meet the required specifications for critical applications.
Component Quality Control Measures
Component quality control is a cornerstone of reliability in high-stakes applications. Engineers must ensure that components undergo thorough testing for defects, consistency, and performance under stress. Incoming inspection protocols, as guided by standards like IPC-A-600K, help identify issues before components are integrated into systems. Batch testing and supplier audits also play a role in maintaining quality. Implementing strict quality control measures reduces the risk of early failures and ensures that components perform as expected in real-world conditions. This is particularly important for applications where repairs or replacements are not feasible.

Material and Design Considerations
The materials used in electronic components significantly influence their reliability. For instance, ceramic capacitors often outperform electrolytic ones in high-temperature environments due to better thermal stability. Similarly, gold-plated connectors resist corrosion better in humid conditions. Design considerations, such as minimizing thermal hotspots through proper layout, also enhance component longevity. Engineers must balance material choices with cost and availability while prioritizing performance in extreme environments. Reviewing material specifications and environmental test data aids in making informed decisions during component selection.
Sourcing and Supply Chain Reliability
A reliable supply chain is vital for obtaining high-quality components for high-reliability applications. Engineers should work with trusted suppliers who provide detailed documentation and adhere to industry standards like ISO 9001:2015 for quality management. Counterfeit components pose a significant risk in critical systems, potentially leading to unexpected failures. Implementing robust sourcing strategies and verifying component authenticity through traceability programs can mitigate these risks. Consistency in supply also ensures that projects are not delayed due to component shortages or quality issues.
Best Practices for Ensuring Long-Term Reliability
Stress Testing and Simulation
Before deployment, components should undergo stress testing to simulate real-world conditions. Thermal cycling, vibration testing, and accelerated aging help identify potential weaknesses. Simulation tools can predict how components will behave under specific stressors, allowing engineers to adjust designs or derating factors accordingly. Following guidelines from standards like IPC-6012E for performance specifications ensures that testing aligns with industry expectations. These practices help confirm that selected components will maintain reliability throughout their operational life in high-stakes environments.
Suggested Reading: Ensuring Reliability: Vibration Analysis for Electronic PCB Components
Documentation and Compliance
Proper documentation is essential for tracking component specifications, test results, and compliance with standards. Engineers must maintain records of environmental tests, derating calculations, and supplier certifications. Compliance with international standards, such as IEC guidelines for electromagnetic compatibility, ensures that components meet global benchmarks for safety and performance. Detailed documentation also facilitates troubleshooting and future design iterations, especially in long-term projects like aerospace missions or military systems.
Lifecycle Management and Obsolescence Planning
Electronic components often face obsolescence due to rapid technological advancements. In high-reliability applications, replacing obsolete parts can be challenging, especially when systems require long-term support. Engineers should plan for lifecycle management by selecting components with extended availability or identifying drop-in replacements. Working with suppliers to monitor end-of-life notices helps prevent disruptions. Proactive obsolescence planning ensures that critical systems remain operational without compromising reliability due to unavailable components.
Conclusion: Building Reliable Systems Through Meticulous Component Selection
Selecting electronic components for high-reliability applications demands a meticulous approach to ensure performance, safety, and longevity. Electrical engineers must consider environmental stressors, component derating factors, and the need for specialized solutions like radiation-hardened components. Military-grade and aerospace components require strict adherence to quality control and industry standards to meet the demands of extreme environments. By prioritizing thorough testing, robust sourcing, and lifecycle planning, engineers can build systems that withstand the harshest conditions. Implementing these best practices fosters confidence in the reliability of critical applications across various industries.
FAQs
Q1: What are the primary challenges in selecting electronic components for high-reliability applications?
A1: Selecting electronic components for high-reliability applications involves addressing challenges like environmental stressors, including temperature extremes and vibration. Components must endure without failure in critical systems. Engineers must also ensure compliance with strict standards and manage risks of obsolescence. Thorough testing and supplier reliability are essential to prevent issues that could compromise safety or performance in demanding scenarios.
Q2: How do component derating factors improve reliability in extreme environments?
A2: Component derating factors enhance reliability by operating parts below their maximum ratings, reducing stress from voltage, current, or heat. This practice minimizes wear and extends lifespan, which is crucial when selecting components for extreme environments. By lowering operational limits, engineers can prevent failures due to thermal or electrical overstress, ensuring consistent performance in harsh conditions over time.
Q3: Why are radiation-hardened components critical for aerospace applications?
A3: Radiation-hardened components are vital for aerospace applications due to high radiation levels in space, which can disrupt standard electronics. These components are designed to resist ionizing effects, preventing errors or degradation. Their use ensures reliable operation of critical systems like navigation and communication during missions. Selecting such components is a priority for maintaining functionality in extraterrestrial environments.
Q4: What role does component quality control play in military-grade component selection?
A4: Component quality control is fundamental in selecting military-grade components, as it ensures consistency and defect-free performance under stress. Rigorous inspection and testing protocols verify durability against shock and extreme conditions. Standards guide these processes to maintain high reliability. Quality control reduces failure risks in combat scenarios, where dependable operation is non-negotiable for mission success.
References
IPC-6012E — Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
IPC-A-600K — Acceptability of Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
JEDEC J-STD-020E — Moisture/Reflow Sensitivity Classification. JEDEC, 2014.
ISO 9001:2015 — Quality Management Systems. ISO, 2015.