What are creepage distance and conformal coating in PCBs?
To fully appreciate the role of conformal coating in enhancing PCB reliability, it's essential to first define two core concepts in printed circuit board design. Creepage distance refers to the shortest path that an electrical current could take along the surface of an insulating material between two conductive components, such as traces or pads. This measurement is particularly critical in high-voltage circuit designs, as insufficient creepage can lead to hazardous electrical arcing or even complete electrical breakdown.
Conversely, a conformal coating is a thin, protective polymeric film meticulously applied over a PCB after all components have been assembled. These coatings, typically formulated from materials like acrylics, silicones, or polyurethanes, are designed to shield the electronic circuitry from a myriad of environmental aggressors. Beyond mere physical protection, these coatings actively augment the insulating properties of the PCB's surface, thereby effectively increasing the inherent creepage distance by mitigating the formation of conductive pathways caused by contaminants.
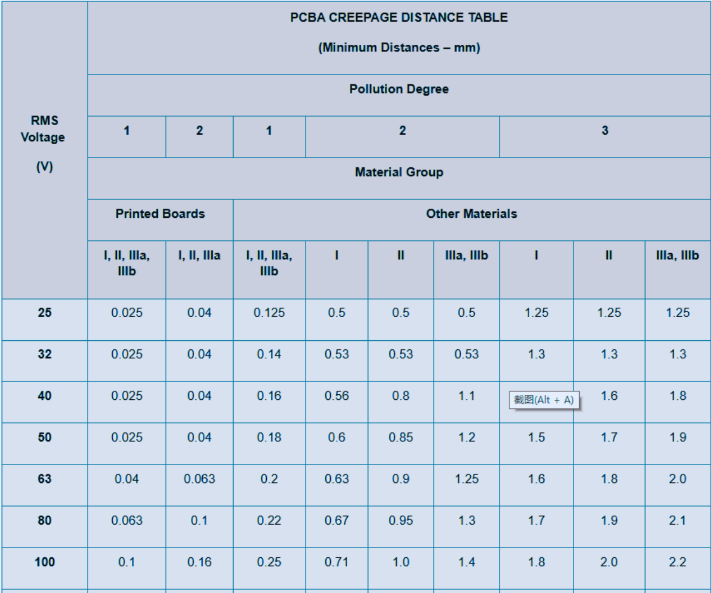
Why adequate creepage distance is critical for PCB safety
Creepage distance is a fundamental design parameter, especially for PCBs operating at high voltages or deployed in challenging environmental conditions. Industry benchmarks, such as those set by IEC 60950 and IPC-2221, specify minimum creepage distances. These standards consider critical variables, including the circuit's operating voltage, the expected degree of environmental pollution (e.g., industrial dust or outdoor humidity), and the specific properties of the PCB's insulating material. For instance, in a moderately polluted industrial setting (Pollution Degree 3), a system operating at 500V might necessitate a creepage distance of at least 8 mm to reliably prevent electrical arcing.
Failing to provide adequate creepage distance can have severe consequences, potentially leading to catastrophic system failures. When conductive contaminants, such as dust particles or moisture droplets, settle on the PCB surface, they can inadvertently create unintended electrical paths. This effectively reduces the actual creepage distance, significantly increasing the likelihood of electrical shorts or dangerous arcing events, which can cause component damage or even initiate fires. Therefore, implementing robust design strategies, complemented by protective measures like conformal coating, is indispensable for ensuring both the long-term reliability and inherent safety of any PCB.
How does conformal coating improve creepage distance?
Conformal coating acts as a vital protective layer that significantly enhances a PCB's surface insulation, thereby directly boosting its effective creepage distance. This is achieved through several key mechanisms that counteract common environmental degradation factors.
Mechanisms of creepage distance enhancement
Firstly, the coating functions as an impermeable barrier against contamination. Moisture, airborne dust, and other particulate matter can drastically reduce the surface resistance of a PCB, creating unintended conductive pathways. By encapsulating the board, the conformal coating prevents these contaminants from settling on the surface, thus preserving the design's intended creepage distance. Secondly, the coating material itself possesses a high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand substantial electrical fields without breaking down. For example, many silicone-based coatings offer dielectric strengths up to 500 V/mil, substantially increasing the effective insulation between adjacent conductive traces and pads.
Thirdly, conformal coating significantly reduces the risk of carbonization. Should an electrical arc inadvertently occur on an uncoated PCB surface, the intense heat can scorch the substrate, leaving a carbonized residue that is electrically conductive. This carbonized path effectively shortens the creepage distance, creating a permanent vulnerability. The protective layer of conformal coating minimizes this risk by shielding the surface from such direct damage. Ultimately, by providing these protective and insulating benefits, conformal coating allows designers to achieve enhanced creepage distance without necessarily having to increase the physical spacing between components, which is invaluable in today’s compact, high-density electronic designs where board space is at a premium.
What types of conformal coatings are best for creepage improvement?
The effectiveness of a conformal coating in enhancing creepage distance and providing environmental protection is heavily dependent on its material composition. Choosing the right type is crucial for meeting specific design requirements and environmental challenges.
Common coating materials and their properties
Acrylic coatings are widely favored for their ease of application and removal, making rework simpler. They offer good resistance to moisture and provide moderate dielectric strength, typically ranging from 300 to 400 V/mil, making them suitable for general-purpose applications. However, they may not perform optimally under extreme temperature variations.
Silicone coatings are highly regarded for their exceptional dielectric strength, often exceeding 500 V/mil, coupled with remarkable flexibility. These properties make them an excellent choice for high-voltage PCBs and devices exposed to harsh environments, including broad temperature ranges (up to 200°C), often seen in industrial applications. Polyurethane coatings provide robust chemical resistance and superior durability, with a dielectric strength around 350 V/mil. They are particularly well-suited for PCBs that might encounter solvents or abrasive conditions.
Epoxy coatings offer the most robust protection and high dielectric strength, typically around 400 V/mil. Their rigid nature makes them ideal for extreme conditions, although this rigidity also makes them challenging to rework or remove for repairs. The selection of the most appropriate conformal coating should be guided by the specific demands of the PCB design, including its operating voltage, the severity of the environmental conditions it will face, and budgetary constraints. For applications specifically prioritizing creepage distance improvement in high-voltage scenarios, silicone or polyurethane coatings are frequently the preferred choices due to their superior insulating capabilities.
Suggested Reading: Choosing the Right Conformal Coating Material for Your PCB: A Comprehensive Guide
How is conformal coating applied for maximum effectiveness?
The successful application of conformal coating is paramount to its ability to enhance creepage distance and provide robust PCB protection. Inconsistent or incomplete coverage can leave vulnerable areas exposed, effectively negating the intended benefits.
Key application methods and best practices
One common method is brushing, a manual technique best suited for small production runs or localized rework. While it allows for precise placement, achieving uniform thickness—which is vital for consistent insulation—can be challenging. Spraying, either with aerosol cans or automated spray guns, offers a faster solution for larger batches. However, this method can struggle to reach areas underneath densely packed components or within tight crevices, potentially missing critical surfaces that require creepage protection.
Dipping involves submerging the entire PCB into the coating material, which typically ensures comprehensive and uniform coverage across the board. While highly effective, this method can be messy and often necessitates masking off connectors, test points, or other sensitive areas that must remain uncoated. Selective coating employs automated machinery to apply the coating precisely to specific, predefined areas, avoiding components that do not require protection. This method provides high precision and is ideal for complex boards where targeted creepage enhancement is needed.
Regardless of the method chosen, it is crucial that the PCB surface is meticulously cleaned and entirely free of contaminants before coating application. Even a thin film of dust, grease, or flux residue can compromise the coating's adhesion, drastically reducing its effectiveness in improving creepage distance. Finally, proper curing—whether through air drying, heat exposure, or UV light—is a critical step to ensure the coating fully achieves its optimal protective and insulating properties.
Additional design strategies for enhancing creepage distance
While conformal coating is an excellent measure for improving creepage distance, its benefits are amplified when integrated with intelligent PCB layout and material selection practices. Combining these approaches ensures maximum protection and reliability.
Complementary design techniques
One fundamental strategy is to actively increase physical spacing between high-voltage traces wherever the PCB layout permits. Adhering to standards like IPC-2221, for instance, might mandate a 2.5 mm creepage distance for a 250V system operating in a Pollution Degree 2 environment. Where physical space is limited, incorporating physical slots or barrier ribs directly into the PCB material between conductive elements can effectively lengthen the creepage path along the surface, redirecting potential current flows.
Selecting PCB substrates with a high Comparative Tracking Index (CTI) is another crucial consideration. CTI measures a material's resistance to forming conductive paths under electrical stress and contamination. Materials with a CTI above 600 offer superior resistance to surface tracking, thereby complementing the protective benefits of conformal coating. Furthermore, designing traces and pads with rounded corners, rather than sharp angles, reduces localized electric field concentrations, which in turn minimizes the risk of electrical discharge and supports the coating's ability to maintain insulation integrity. Integrating these thoughtful design techniques with the application of conformal coating provides a multi-layered approach to maximize creepage distance and ensure the long-term reliability of PCBs in demanding operational conditions.
Challenges and key considerations for using conformal coating
Despite its significant advantages in improving creepage distance, the application of conformal coating comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. Understanding these limitations is vital for making informed decisions throughout the PCB design and PCBA assembly process.
Addressing common issues in coating application
One prevalent issue is achieving comprehensive coverage, especially in complex PCB designs. Areas located underneath components, within very tight spaces, or around intricate pin arrays may not receive an adequate layer of coating, leaving vulnerable spots susceptible to environmental degradation. Utilizing methods like dipping or highly selective automated coating can help mitigate these coverage gaps.
Another consideration is rework difficulty. Some types of coatings, particularly epoxies, are exceptionally rigid and difficult to remove without potentially damaging the underlying circuitry during repairs. If frequent modifications or component replacements are anticipated, opting for a more easily reworkable coating, such as an acrylic, is advisable. Thermal expansion mismatches can also pose a challenge; if the coating and PCB materials expand and contract at significantly different rates, it can lead to cracking or delamination of the coating over time, especially in applications subjected to wide temperature swings. Flexible silicone coatings often perform better in such dynamic thermal environments. Finally, the cost factor cannot be overlooked. High-performance coating materials and advanced automated application processes can add substantially to the overall custom PCB cost, requiring designers to carefully balance the benefits of enhanced creepage distance and protection against budgetary constraints. Addressing these challenges during the initial planning stages ensures that conformal coating effectively delivers the desired results without introducing new risks or unforeseen complications to the PCB’s performance.
Conformal coating: A key to maximizing PCB reliability
Conformal coating stands as a transformative solution in contemporary PCB design, offering a highly effective method for significantly enhancing creepage distance and providing robust protection against a multitude of environmental threats. By functioning as an insulating barrier, this protective film actively prevents contamination, substantially boosts the dielectric strength of the PCB surface, and dramatically reduces the risk of electrical failures. Critically, these benefits are achieved while simultaneously supporting the design of increasingly compact and high-density circuit board layouts.
Whether the application involves demanding automotive systems, rugged industrial electronics, or intricate consumer devices, integrating PCB conformal coating into the design and manufacturing workflow can yield substantial improvements in both operational reliability and inherent safety. The key lies in selecting the most appropriate coating material, a decision that must be guided by the specific voltage requirements, environmental exposure, and thermal conditions of your application. Complementing this choice with intelligent design practices—such as increasing physical spacing where feasible, incorporating physical slots, and utilizing high-CTI substrate materials—will further optimize creepage distance. With a strategic and informed approach, conformal coating becomes an indispensable tool, ensuring that your PCBs operate flawlessly and reliably, even when subjected to the most challenging conditions.