Introduction
Thermal management remains a critical factor in the design and operation of power supplies, especially in high power electronics applications. As electrical engineers strive to improve power supply efficiency and ensure long term reliability, thermal pads have emerged as an essential solution. These materials bridge the gap between heat generating components and heat sinks, facilitating effective heat dissipation. Poor thermal management can lead to overheating, reduced performance, and premature failure of power supply units. This article explores the role of thermal pads for power supplies, diving into their design principles, practical implementation, and impact on system performance. Aimed at electrical engineers, the content provides actionable insights into achieving optimal thermal management for power electronics.
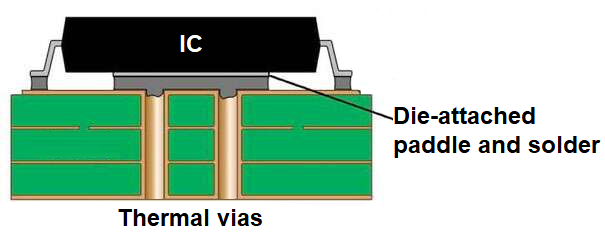
What Are Thermal Pads and Why Do They Matter
Thermal pads are specialized materials used as thermal interface solutions in electronic systems, including power supplies. Typically made from silicone or other thermally conductive compounds, they fill air gaps between components and heat dissipation structures. Their primary function is to transfer heat away from critical parts, such as power transistors or integrated circuits, to prevent thermal buildup. In power supplies, where efficiency and reliability are paramount, thermal pads play a vital role in maintaining safe operating temperatures.
The importance of thermal pads lies in their ability to enhance system longevity and performance. Overheating in power electronics can degrade components, reduce power supply reliability, and cause unexpected failures. By improving heat transfer, thermal pads help maintain stable operation, especially in high power applications. Their design and material properties directly influence the overall thermal management strategy for power electronics, making them indispensable for engineers working on modern power supply designs.
Technical Principles of Thermal Pads in Power Supplies
Thermal pads operate on the principle of thermal conductivity, which measures a material's ability to transfer heat. In power supplies, heat is generated by components like rectifiers, transformers, and switching elements during operation. Without proper dissipation, this heat accumulates, raising the junction temperature of semiconductors beyond safe limits. Thermal pads address this by providing a low resistance path for heat to flow from the component to a heat sink or enclosure.
The effectiveness of a thermal pad depends on several factors. First, the material's thermal conductivity, often measured in watts per meter Kelvin, determines how efficiently heat transfers. Second, the thickness and compressibility of the pad affect contact resistance at the interface. Thinner pads generally offer better performance, but they must conform to surface irregularities for optimal contact. Finally, the pad's thermal impedance, which accounts for both conductivity and contact resistance, is a critical metric for assessing performance in high power thermal solutions.
Another key principle is the pad's ability to withstand environmental stresses in power supplies. Factors such as temperature cycling, humidity, and mechanical vibration can degrade materials over time. Standards like IPC-6012E provide guidelines for evaluating the durability of materials used in electronic assemblies, ensuring they meet reliability requirements. Engineers must consider these factors during design to ensure consistent thermal management for power electronics.
Design Considerations for Thermal Pads in Power Supplies
Designing thermal pads for power supplies requires a balance of thermal performance, mechanical properties, and cost effectiveness. Below are key considerations for electrical engineers focusing on improving power supply efficiency and reliability.
- Material Selection: Choose materials with high thermal conductivity while ensuring electrical insulation if needed. Silicone based pads with ceramic fillers are common due to their balance of performance and flexibility.
- Thickness Optimization: Select a thickness that minimizes thermal resistance while accommodating surface variations. Excessive thickness increases impedance, while overly thin pads may not fill gaps adequately.
- Surface Compatibility: Ensure the pad adheres well to both the component and heat sink surfaces. Surface roughness or contamination can reduce contact efficiency, impacting heat transfer.
- Environmental Durability: Consider operating conditions such as temperature range and humidity. Pads must maintain performance under stress, adhering to standards like IPC-A-600K for material acceptability in electronic systems.
- Application Method: Decide between pre cut pads or dispensable materials based on assembly needs. Pre cut options simplify installation, while dispensable solutions offer flexibility for complex geometries.
By addressing these factors, engineers can tailor thermal pad designs to specific power supply requirements, ensuring effective high power thermal solutions.
Practical Solutions for Implementing Thermal Pads
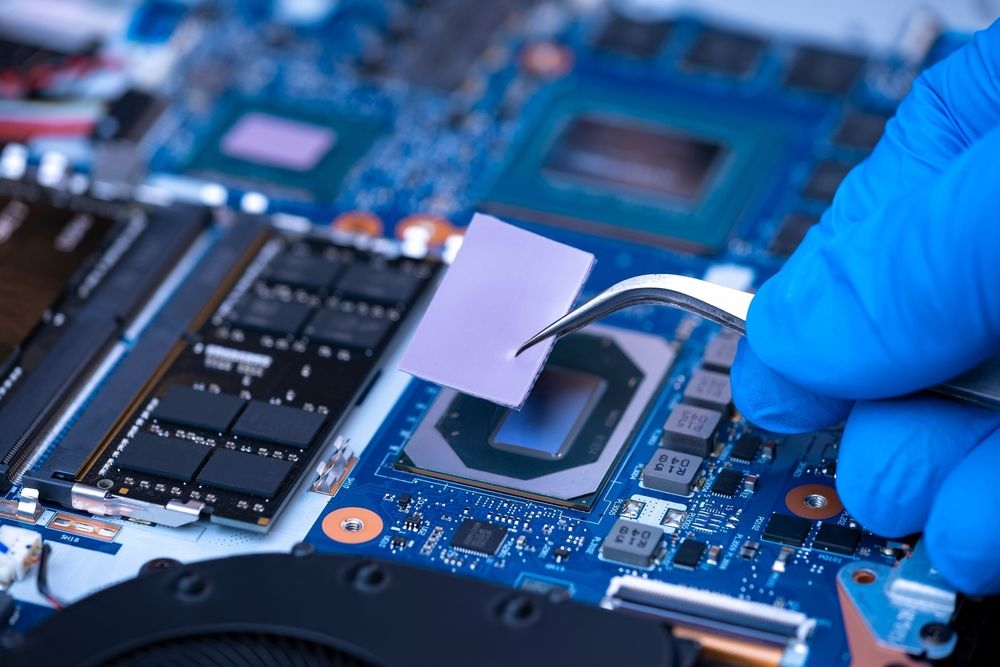
Implementing thermal pads in power supply designs involves several best practices to maximize their benefits. Engineers should start by conducting a thermal analysis of the system to identify heat sources and critical areas. Simulation tools can model heat flow and pinpoint where thermal pads will have the most impact. Once identified, pads should be placed directly between heat generating components and dissipation structures for optimal transfer.
Proper installation is crucial for performance. Ensure surfaces are clean and free of debris before applying the pad to avoid air gaps that hinder heat transfer. Apply uniform pressure during PCBA assembly to achieve consistent contact, adhering to assembly guidelines such as those in IPC-6012E for electronic board performance. If using adhesive backed pads, verify that the adhesive does not degrade thermal conductivity or long term reliability.
Regular testing and validation are also recommended. Standards like JEDEC J-STD-020E provide frameworks for assessing moisture and thermal stress on materials, which can help predict pad performance over time. By integrating these practices, engineers can enhance power supply reliability and maintain efficiency under varying operating conditions.
Suggested Reading: Beginner's Guide to Thermal Pads: Simple Steps for Effective Heat Dissipation
Impact on Power Supply Efficiency and Reliability
The use of thermal pads directly influences both power supply efficiency and reliability. Efficient heat dissipation reduces the operating temperature of components, which in turn minimizes power losses. For instance, lower junction temperatures in semiconductors lead to reduced on state resistance, improving overall energy conversion efficiency. This is particularly critical in high power applications where even small efficiency gains translate to significant energy savings.
Reliability benefits are equally important. Elevated temperatures accelerate wear mechanisms like thermal fatigue and material degradation in power electronics. By maintaining lower temperatures, thermal pads extend component lifespan and reduce failure rates. Standards such as IPC-A-600K outline acceptability criteria for electronic assemblies, emphasizing the need for robust thermal management to ensure long term performance.
Moreover, thermal pads contribute to system stability under dynamic loads. Power supplies often experience rapid changes in current draw, leading to thermal transients. Well designed pads mitigate these effects by providing consistent heat transfer, preventing thermal runaway scenarios. For engineers, integrating thermal pads into designs is a proactive step toward achieving durable and efficient power supply systems.
Troubleshooting Common Thermal Pad Issues
Even with careful design, challenges can arise when using thermal pads in power supplies. One common issue is insufficient heat transfer due to poor contact. This often results from surface irregularities or improper installation. To resolve this, inspect surfaces for flatness and cleanliness before assembly, ensuring the pad conforms fully to both interfaces.
Another issue is material degradation over time, especially in harsh environments. Exposure to high temperatures or humidity can cause pads to lose flexibility or conductivity. Selecting materials that comply with durability standards like JEDEC J-STD-020E can prevent such problems. If degradation occurs, replace the pad with a more suitable option for the operating conditions.
Finally, engineers may encounter challenges with pad sizing or placement. Pads that are too small fail to cover the heat source adequately, while oversized pads waste material and space. Accurate measurements and thermal simulations during the design phase can help avoid these issues, ensuring optimal performance in thermal management for power electronics.
Conclusion
Thermal pad design is a cornerstone of effective thermal management for power electronics, directly impacting power supply efficiency and reliability. By understanding the principles of heat transfer, selecting appropriate materials, and following best practices for implementation, electrical engineers can significantly enhance system performance. Thermal pads not only prevent overheating but also contribute to long term stability and energy savings in high power applications. As power supply designs continue to evolve, integrating robust thermal solutions remains essential for meeting the demands of modern electronics.
FAQs
Q1: How do thermal pads for power supplies improve system performance?
A1: Thermal pads for power supplies enhance heat dissipation by filling gaps between components and heat sinks. This reduces operating temperatures, minimizes power losses, and boosts efficiency. Lower temperatures also prevent thermal stress, extending component lifespan and ensuring consistent performance under load.
Q2: What factors affect power supply reliability when using thermal pads?
A2: Power supply reliability depends on thermal pad material quality, thickness, and installation. Poor contact or degraded materials can lead to overheating, reducing reliability. Selecting durable pads and adhering to standards like IPC-A-600K ensures consistent heat transfer and long term stability.
Q3: How can engineers optimize thermal management for power electronics with thermal pads?
A3: Engineers can optimize thermal management for power electronics by conducting thermal simulations to identify heat sources. Choose pads with high conductivity, ensure proper installation, and validate performance using standards like JEDEC J-STD-020E. Regular testing helps maintain efficiency over time.
Q4: What are common challenges in implementing high power thermal solutions?
A4: Challenges in high power thermal solutions include poor contact, material degradation, and incorrect sizing of thermal pads. Surface irregularities or harsh conditions can reduce effectiveness. Thorough design analysis and compliance with industry standards help address these issues effectively.
References
IPC-6012E - Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
IPC-A-600K - Acceptability of Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
JEDEC J-STD-020E - Moisture/Reflow Sensitivity Classification. JEDEC, 2014.