Introduction
For electronic hobbyists venturing into robotics, the choice of components can significantly impact a project's success. Among these, the printed circuit board plays a critical role in ensuring reliability and performance. Heavy copper PCB in robotics stands out as a specialized solution for high power demands and thermal challenges often encountered in robotic systems. These boards, with thicker copper layers, offer unique advantages over standard PCBs, especially in applications requiring robust current handling and heat dissipation. This article explores the technical benefits of heavy copper usage, how it enhances robotic designs, and practical considerations for hobbyists. Whether you are building a small autonomous rover or a complex articulated arm, understanding enhanced PCB benefits in robotics can elevate your project to new levels of efficiency and durability.
What Is Heavy Copper PCB and Why It Matters in Robotics
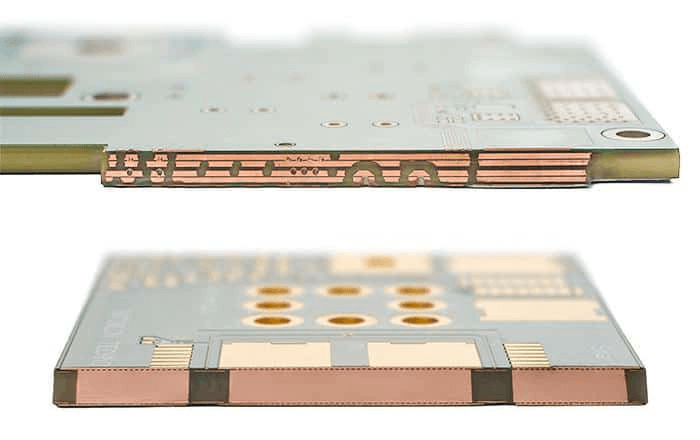
Heavy copper PCB refers to printed circuit boards with copper thicknesses exceeding the standard range, typically above 3 ounces per square foot. In contrast, standard PCBs often use 1 to 2 ounces of copper. This increased thickness allows heavy copper boards to handle higher currents and provide better thermal management, which are crucial in robotics. Robotic systems, even at the hobbyist level, often involve motors, servos, and sensors that draw significant power and generate heat during operation.
The relevance of heavy copper PCB in robotics lies in its ability to support these demanding components. For hobbyists, this means fewer failures due to overheating or electrical shorts, leading to more reliable robots. Additionally, these boards can withstand mechanical stress better, which is vital for robots with moving parts. By integrating heavy copper usage into designs, hobbyists can push the boundaries of their creations, achieving higher performance without compromising safety or longevity.
Technical Principles of Heavy Copper PCB in Robotics
Heavy copper PCBs operate on fundamental electrical and thermal principles that make them ideal for robotics. The thicker copper layers reduce electrical resistance, allowing the board to carry higher currents without significant voltage drops. This is particularly important for robotic systems where motors and actuators require consistent power delivery to maintain precise movements.
From a thermal perspective, copper is an excellent conductor of heat. In heavy copper PCBs, the increased mass of copper acts as a heat sink, dissipating thermal energy away from critical components. This prevents hotspots that could degrade performance or damage parts like microcontrollers and power transistors often used in robotic circuits. According to widely accepted industry standards such as IPC-6012E, the design and fabrication of such boards must account for thermal expansion and current density to ensure reliability under load.
Moreover, the structural integrity provided by thicker copper layers enhances durability. Robots built by hobbyists often operate in dynamic environments, experiencing vibrations and shocks. Heavy copper PCBs resist cracking and delamination better than standard boards, ensuring consistent operation. For hobbyists, this translates to a robust foundation for experimenting with complex designs without frequent board replacements.
PCB Benefits in Robotics: Why Heavy Copper Stands Out
The enhanced PCB benefits in robotics become evident when comparing heavy copper boards to standard alternatives. Below are key advantages tailored to the needs of electronic hobbyists working on robotic projects.
- Higher Current Capacity: Heavy copper usage allows boards to support the high current needs of robotic components like DC motors and stepper motors. This ensures smooth operation without the risk of trace burnout.
- Improved Heat Dissipation: The superior thermal conductivity of heavy copper prevents overheating, protecting sensitive electronics. Hobbyists can run their robots for extended periods without performance drops.
- Increased Mechanical Strength: The thicker layers add rigidity, making the PCB less prone to damage from vibrations or impacts during robotic movements.
- Longer Lifespan: With reduced wear from thermal and electrical stress, heavy copper PCBs offer durability, saving hobbyists time and cost on replacements.
- Design Flexibility: These boards support complex layouts with high power traces, enabling hobbyists to integrate more features into compact robotic designs.
These benefits collectively contribute to better robot performance, allowing hobbyists to focus on innovation rather than troubleshooting hardware failures. Standards like IPC-A-600K emphasize the importance of copper thickness and trace integrity in achieving such reliability, providing a benchmark for quality in quick turn PCB fabrication.
Practical Applications of Heavy Copper PCB in Robotics for Hobbyists
For electronic hobbyists, heavy copper PCB in robotics opens up a range of practical applications. One common use is in motor control circuits for wheeled robots or drones. These systems require sustained high current to drive motors, and heavy copper boards ensure stable power delivery without overheating. This is especially useful for projects involving rough terrains or prolonged operation times.
Another application lies in robotic arms, where precise servo control is essential. Heavy copper usage supports the power needs of multiple servos while managing heat generated during repetitive motions. Hobbyists can build more intricate mechanisms without worrying about circuit failures. Additionally, in sensor heavy designs like autonomous robots, these PCBs provide the necessary current for processing units and communication modules, ensuring seamless data handling.
When designing such projects, hobbyists should consider board layout to maximize the enhanced PCB benefits in robotics. Placing high current components closer to power traces and ensuring adequate spacing for heat dissipation can optimize performance. Following guidelines from standards like IPC-6012E during the design phase helps maintain quality and functionality.
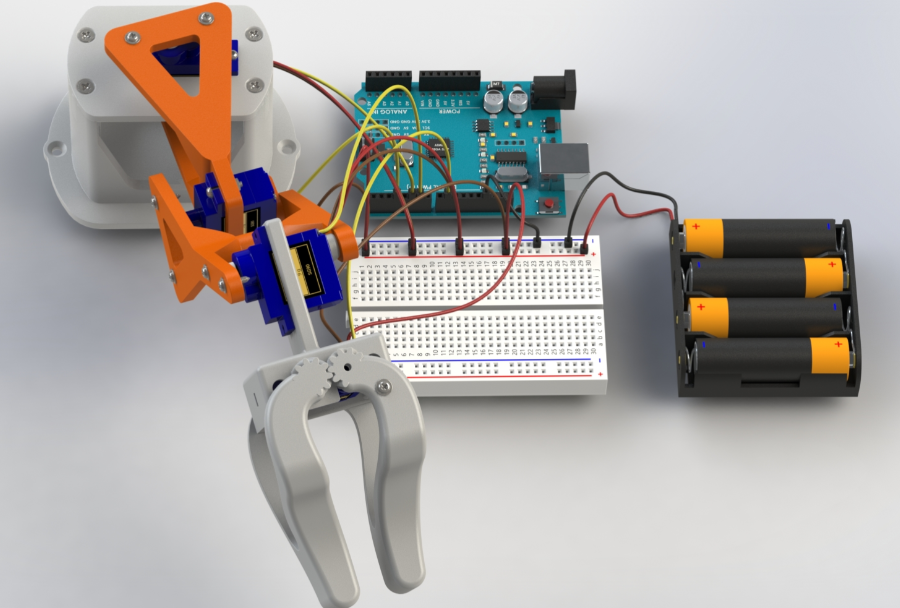
Best Practices for Using Heavy Copper PCB in Robotics Projects
Integrating heavy copper PCBs into robotics projects requires careful planning to fully leverage their advantages. Below are actionable tips for hobbyists to ensure successful implementation.
- Understand Power Requirements: Calculate the current draw of all components in your robot. This helps determine the necessary copper thickness to avoid overloading the board.
- Optimize Trace Widths: Wider traces on heavy copper PCBs can handle more current. Use design software to simulate current flow and adjust trace dimensions accordingly.
- Prioritize Thermal Management: Place heat generating components strategically to benefit from copper's heat sinking properties. Adding vias can further improve thermal conductivity.
- Test Under Load: Before final assembly, test the PCB with the robot's full operational load to identify potential weak points in current or heat handling.
- Adhere to Standards: Refer to industry benchmarks like IPC-A-600K for acceptability criteria on copper thickness and board quality to ensure reliability.
By following these practices, hobbyists can mitigate common issues like trace failure or thermal runaway, ensuring their robots operate efficiently. Additionally, documenting the design process can help refine future projects, building a knowledge base for complex builds.
Challenges and Considerations with Heavy Copper Usage
While heavy copper PCB in robotics offers significant benefits, hobbyists should be aware of certain challenges. One primary concern is the increased weight of the board due to thicker copper layers. In lightweight robots like drones, this can affect balance and energy efficiency. Careful design adjustments, such as minimizing board size, can help address this issue.
Another consideration is the cost. Heavy copper PCBs typically require specialized fabrication processes, which may be more expensive than standard boards. For hobbyists on a budget, balancing performance needs with cost constraints is essential. Planning the project scope and prioritizing critical areas for heavy copper usage can optimize expenses.
Lastly, soldering components on heavy copper boards can be trickier due to higher thermal mass. The copper absorbs more heat, potentially leading to cold solder joints if not handled correctly. Using a soldering iron with adequate power and preheating the board can ensure proper connections. Awareness of these factors allows hobbyists to make informed decisions, maximizing the enhanced PCB benefits in robotics.
Conclusion
Heavy copper PCB in robotics provides a powerful solution for electronic hobbyists aiming to enhance their robot's performance. With superior current handling, excellent thermal dissipation, and increased durability, these boards address the unique challenges of robotic systems. By understanding the technical principles and applying best practices, hobbyists can build more reliable and efficient robots, whether for simple educational projects or advanced autonomous designs. The PCB benefits in robotics, particularly through heavy copper usage, empower creators to push the limits of innovation. As you embark on your next robotic project, consider integrating these robust boards to achieve consistent, high quality results that stand the test of time.
FAQs
Q1: How does heavy copper PCB in robotics improve my project's performance?
A1: Heavy copper PCB enhances robotics projects by supporting higher currents for motors and servos, ensuring stable power delivery. It also dissipates heat effectively, preventing component damage during extended operation. This reliability allows hobbyists to build more complex robots without frequent failures, as outlined in standards like IPC-6012E for board performance.
Q2: What are the key PCB benefits in robotics when using heavy copper?
A2: The primary benefits include improved current capacity, better heat management, and increased mechanical strength. Heavy copper PCBs resist damage from vibrations in dynamic robotic systems and offer a longer lifespan. These advantages make them ideal for hobbyists experimenting with high power robotic designs.
Q3: Is heavy copper usage suitable for small scale robotics projects?
A3: Yes, heavy copper usage can benefit small scale robotics by providing durability and thermal stability, even if power needs are moderate. However, consider the added weight and cost. For lightweight or budget constrained projects, hobbyists should evaluate if standard PCBs might suffice for basic functionality.
Q4: How can I ensure proper design with heavy copper PCB in robotics?
A4: Focus on calculating power needs and optimizing trace widths for current flow. Strategically place components to manage heat and test the board under load before final integration. Following guidelines from standards like IPC-A-600K ensures quality and reliability in your robotic design.
References
IPC-6012E — Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
IPC-A-600K — Acceptability of Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.