How Do "Mouse Bites" Function in PCB Manufacturing?
In a typical "mouse bite" design, a series of small holes (commonly ranging from 0.3 mm to 0.5 mm in diameter) is meticulously drilled along the designated tab area. These holes are spaced closely together, usually between 0.5 mm to 1 mm apart. The residual material situated between these perforations acts as a deliberate weak point, allowing the PCB to cleanly separate when an appropriate force is applied. The precise number and spacing of these holes can be calibrated based on the desired mechanical strength of the breakaway tab.
Benefits of Utilizing Mouse Bites
● Design Flexibility: Mouse bites are exceptionally well-suited for types of PCBs with irregular shapes or when V-scoring is impractical due to specific design constraints.
● Cost-Effectiveness: This method often proves more economical to implement, particularly for smaller production batches, as it does not necessitate specialized cutting tools during the manufacturing process.
● Manual Separation: Boards can frequently be separated by hand without requiring advanced equipment, making it an ideal choice for prototypes or low-volume projects.
Drawbacks Associated with Mouse Bites
● Rough Edges: The act of breaking the board can result in rough or jagged edges, which may necessitate additional finishing if aesthetic appeal or safety considerations are important.
● Risk of Stress: The force required to snap the board apart can introduce localized mechanical stress, potentially causing damage to nearby components or fine traces.
● Limited Strength: Breakaway tabs created with mouse bites are generally less robust than those formed by other methods, which might make them unsuitable for rigorous assembly processes where greater structural integrity is needed.
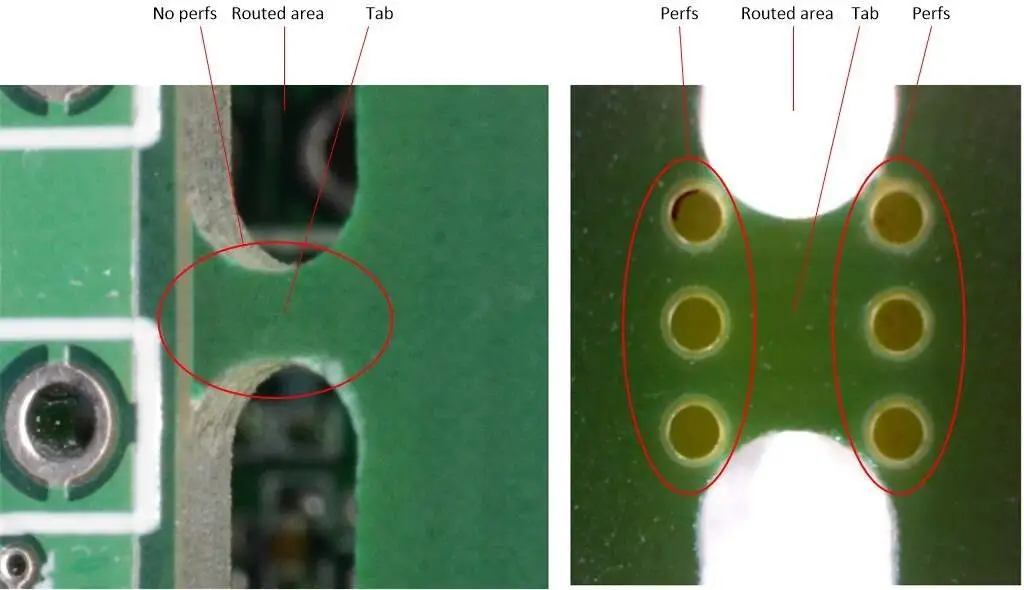
Exploring PCB V-Score Design Rules (V-Groove)
V-scoring, also known as V-groove, is a widely used depanelization technique where a V-shaped cut is precisely made along the separation line on both the top and bottom sides of the PCB panel. This is achieved using a specialized cutting tool. This process creates a thin, intentionally weakened section of material that allows the board to be snapped apart with high precision.
How V-Scoring Operates
During V-scoring, a blade typically angled at either 30 or 45 degrees incises the PCB from both the top and bottom surfaces. This leaves a small, controlled amount of material (usually between 0.3 mm to 0.5 mm thick) in the exact center. This residual material, termed the "web," maintains the panel's integrity throughout the manufacturing stages but is sufficiently weakened to allow for a clean break when required. The precise depth and angle of these V-cuts are critical parameters, ensuring both adequate structural stability and effortless separation.
Key V-Score Design Guidelines
● Board Thickness Compatibility: V-scoring achieves optimal results on boards ranging from 0.6 mm to 2.0 mm in thickness. Boards outside this range, whether significantly thinner or thicker, may not score consistently or could be prone to unpredictable cracking.
● Precision Alignment: It is imperative that the top and bottom V-cuts are perfectly aligned to prevent uneven stress distribution during the separation process. Misalignment can lead to incomplete breaks or damage to the board.
● Component Clearance: Maintain a minimum clearance of 1.0 mm between all components and traces and the V-score line. This precaution prevents potential damage from mechanical stress during separation or accidental cutting errors.
● Panel Layout Suitability: V-scoring is most effective for straight-line separations. This method is generally unsuitable for curved or highly irregular panel designs.
Advantages of V-Scoring
● Clean Edges: V-scoring consistently produces much smoother edges compared to the rougher finish often left by mouse bites, thereby reducing or eliminating the need for post-separation finishing work.
● High Precision: The highly controlled nature of the cutting process ensures uniform results, making V-scoring an ideal method for high-volume production environments.
● Enhanced Strength: V-scored tabs generally offer superior structural integrity during the manufacturing phase, providing better support and stability during PCB assembly process compared to perforated designs.
Drawbacks of V-Scoring
● Limited Flexibility: V-scoring is strictly confined to straight-line separations, which restricts its applicability for more complex panel designs that require curved or non-linear breaks.
● Equipment Requirements: This method necessitates specialized machinery, which can potentially increase manufacturing costs, particularly for low-volume production runs.
● Potential Stress Issues: Although generally less prone to stress damage than mouse bites, an incorrectly executed V-scoring depth can still induce stress cracks during the depanelization process.
Mouse Bite vs. V-Score: A Comparative Analysis for Selection
The decision between utilizing mouse bites and V-scoring is fundamentally driven by the specific demands of your project. Let’s conduct a comprehensive mouse bite vs. V-score comparison across several critical factors.
Ease of Separation
Mouse bites are often simpler to separate by hand, requiring minimal force or tools. However, this ease can sometimes lead to inconsistent results. V-scoring, while potentially requiring a slight bending force or a dedicated depaneling tool, consistently delivers more predictable and uniform separations.
Edge Quality Outcome
V-scoring demonstrably excels in terms of edge quality. Its precise cuts yield clean, smooth edges, whereas mouse bites frequently result in rough or uneven edges that may necessitate additional sanding or finishing steps.
Design Flexibility
For PCB panels featuring irregular shapes or curved contours, mouse bites emerge as the more suitable option, given that V-scoring is strictly limited to straight-line separations. For designs involving rectangular or square boards arranged in a grid-like panel, V-scoring offers superior efficiency.
Manufacturing Cost Implications
Mouse bites are generally more cost-effective for small production runs or prototypes due to their inherent simplicity. V-scoring, despite its higher initial cost attributable to the requirement for specialized tools, becomes a more economical choice at scale, particularly in high-volume production environments.

Breakaway Tab Strength Comparison: Mouse Bites vs. V-Score
In a direct breakaway tab strength comparison, V-scoring typically provides significantly greater structural integrity throughout the manufacturing process. The residual web of material left by a V-score (commonly between 0.3 mm and 0.5 mm thick) offers substantially more resistance to accidental breakage compared to the slender bridges between perforations in a mouse bite design. For instance, a V-scored tab might reliably withstand forces up to 10-15 Newtons (N) during routine handling, whereas a mouse bite tab might fail at forces ranging from 5-8 N, depending on the hole spacing and specific material thickness.
However, this enhanced strength comes with a trade-off. A more robust V-score tab may necessitate greater force for separation, which could potentially introduce undesirable stress if the design parameters are not precisely optimized. Mouse bites, while inherently weaker, offer the advantage of being highly customizable; by adjusting the number and size of holes, designers can fine-tune the balance between structural strength and ease of separation.
Other Notable PCB Depanelization Methods
Beyond the prevalent mouse bites and V-scoring, several other PCB depanelization methods are worth considering, depending on the unique requirements of your project.
Routing (Tab Routing)
Routing involves precisely cutting out the majority of the material surrounding individual PCBs, intentionally leaving small tabs to secure them within the panel. These tabs are subsequently broken or cut during the final depanelization stage. This method offers the advantage of producing very clean edges and is highly versatile for complex board shapes, but it can be more time-consuming and costly due to the high precision required.
Laser Cutting
Laser depanelization employs a highly focused laser beam to accurately cut through the PCB material with extreme precision. This technique is ideal for exceptionally delicate or high-density boards where any mechanical stress must be rigorously avoided. However, it is a significantly more expensive and slower process compared to traditional mechanical methods.
Manual Cutting Tools
For extremely small production runs or initial prototypes, basic manual tools such as shears or rotary cutters can be employed. This method is generally not recommended for production-scale quantities due to its inherent inconsistency in results and high associated labor costs.
Best Practices for Designing Effective Breakaway Tabs
Regardless of whether you ultimately opt for a perforation (mouse bite) or V-score design, adhering to these best practices will contribute significantly to a successful and robust breakaway tab design.
● Consider Board Material Properties: FR-4, the most common PCB substrate, performs well with both methods. However, more flexible or exceptionally thin materials may necessitate specific adjustments in design parameters to prevent cracking or delamination.
● Optimize Tab Placement: Strategically position tabs away from any sensitive components or areas prone to high mechanical stress. Typically, using 2-3 tabs per side provides sufficient support for most designs.
● Rigorous Prototype Testing: Prior to committing to full-scale production, thoroughly test your breakaway tab design on a prototype panel. This critical step allows for early identification of potential issues related to tab strength or the ease and cleanliness of separation.
● Consult Manufacturer Guidelines: Be aware that different PCB fabrication houses may have specific requirements or inherent limitations regarding the implementation of mouse bites or V-scoring. Always confirm compatibility and specific design rules with your chosen manufacturer before finalizing your design.
Conclusion: Making Informed Choices for Your PCB Design
The ultimate choice between a PCB breakaway tab perforation design and PCB V-score design rules hinges on a careful balance of manufacturing cost, design complexity, and anticipated production volume. Mouse bites offer a compelling combination of flexibility and affordability, making them an excellent choice for prototypes or boards with irregular geometries. In contrast, V-scoring delivers superior edge quality and greater structural strength, positioning it as the ideal method for high-volume production involving straight-line separations.
By thoroughly understanding the intricacies of the mouse bite vs. V-score comparison, conducting a precise breakaway tab strength comparison, and exploring the full spectrum of available PCB depanelization methods, you are empowered to design panels that not only streamline the manufacturing process but also actively safeguard the integrity of your finished circuit boards. Dedicate the necessary time to meticulously evaluate your project's unique requirements, and you will ensure a seamless and efficient transition from raw panel to polished product.
With an expertly executed breakaway tab design, you will not only significantly enhance manufacturing efficiency but also deliver high-quality PCBs that consistently meet the rigorous demands of your application. Keep these invaluable insights at the forefront as you approach your next design challenge.