Introduction
Aluminum PCBs have gained attention in the field of electronics design due to their unique properties and performance benefits. Unlike traditional FR4 PCBs, which use fiberglass as the base material, aluminum PCBs incorporate a metal substrate that offers distinct advantages for specific applications. For electronic hobbyists exploring electronics components and PCB for beginners, understanding the strengths and limitations of aluminum PCBs can guide better project decisions. This article dives into the technical aspects of aluminum versus FR4 PCBs, focusing on their role in CAD design and practical use. Whether you are designing a simple circuit or tackling complex electronics design projects, knowing when to choose aluminum PCBs can impact performance and cost. Let’s explore the key pros and cons to help you make informed choices for your next build.
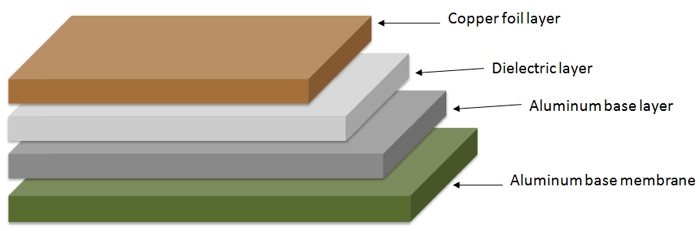
What Are Aluminum PCBs and Why Do They Matter
Aluminum PCBs, often referred to as metal core PCBs, consist of a thin layer of thermally conductive dielectric material sandwiched between a copper circuit layer and an aluminum base. This structure sets them apart from standard FR4 PCBs, which rely on fiberglass and epoxy resin for their core. The aluminum base provides excellent heat dissipation, making these boards ideal for applications where thermal management is critical. For electronic hobbyists, this can mean better reliability in projects involving high power electronics components like LEDs or power supplies.
The importance of aluminum PCBs lies in their ability to handle heat effectively while maintaining structural integrity. In electronics design, overheating can degrade components and reduce lifespan. Aluminum PCBs address this by transferring heat away from sensitive areas, ensuring stable operation. As hobbyists often experiment with compact designs using CAD design tools, understanding when to opt for aluminum over FR4 PCBs can enhance project outcomes. Their growing use in industries like lighting and automotive also highlights their relevance for learning and experimentation.
Technical Advantages of Aluminum PCBs
Aluminum PCBs offer several technical benefits that make them a compelling choice for specific electronics design needs. Below are the primary advantages that hobbyists should consider when selecting materials for their projects.
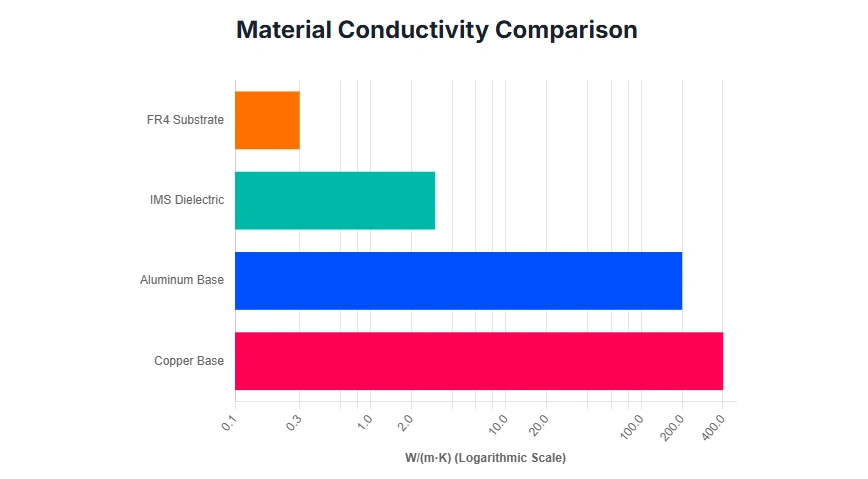
Superior Thermal Conductivity
One of the standout features of aluminum PCBs is their ability to dissipate heat efficiently. The aluminum base acts as a heat sink, drawing thermal energy away from critical electronics components. This property is especially useful in high power applications where components generate significant heat. For hobbyists working on LED circuits or motor drivers, this can prevent thermal runaway and extend component life.
Lightweight and Durable
Aluminum is lighter than many other metal substrates, which can be a benefit when designing portable or compact devices. Additionally, it offers good mechanical strength, resisting bending and warping under stress. This durability makes aluminum PCBs suitable for projects that require robust physical performance, a factor often overlooked by beginners using PCB for beginners resources.
Environmental Benefits
Aluminum is a recyclable material with a lower environmental impact compared to some other substrates. For hobbyists conscious of sustainability in electronics design, choosing aluminum PCBs aligns with eco friendly practices. Its non toxic nature further supports safer handling during experimentation and prototyping.
Cost Effectiveness in Specific Applications
While not always cheaper than FR4 PCBs, aluminum PCBs can be cost effective for designs where thermal management is a priority. Avoiding the need for additional heat sinks or cooling mechanisms can reduce overall project expenses. Hobbyists using CAD design software can simulate thermal performance to justify material selection based on long term savings.
Limitations of Aluminum PCBs
Despite their advantages, aluminum PCBs are not a universal solution. Hobbyists must weigh their drawbacks to ensure compatibility with project goals. Here are the key limitations to consider.
Higher Initial Cost
Aluminum PCBs generally come with a higher upfront cost compared to standard FR4 PCBs. For electronic hobbyists on a tight budget, this can be a barrier, especially for small scale or experimental projects. The price difference may not always be justified if thermal management is not a critical concern.
Limited Flexibility
Unlike FR4 PCBs, which can be produced in flexible variants, aluminum PCBs are rigid due to their metal core. This lack of flexibility limits their use in applications requiring bending or dynamic movement. Hobbyists designing wearable electronics or foldable circuits may find aluminum unsuitable for such needs.
Design Constraints
The metal core of aluminum PCBs can introduce challenges in multi layer designs. Signal integrity and electromagnetic interference can become issues in complex electronics design projects. For beginners using PCB for beginners guides, working around these constraints in CAD design might require additional learning or adjustments.
Weight Considerations
Although lighter than some metals, aluminum is still heavier than fiberglass based FR4 PCBs. In projects where weight is a critical factor, such as drones or miniature devices, this added mass could be a disadvantage. Hobbyists must evaluate whether thermal benefits outweigh the impact of increased weight.

Aluminum vs FR4 PCBs: A Practical Comparison
When choosing between aluminum and FR4 PCBs, hobbyists must consider project requirements and constraints. Below is a comparison to aid decision making in electronics design.
- Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum PCBs — High, ideal for heat dissipation; FR4 PCBs — Moderate, may need external cooling.
- Cost: Aluminum PCBs — Higher initial investment; FR4 PCBs — Generally more affordable.
- Weight: Aluminum PCBs — Heavier than FR4; FR4 PCBs — Lighter, better for portable builds.
- Flexibility: Aluminum PCBs — Rigid, no flex options; FR4 PCBs — Available in rigid and flex types.
- Durability: Aluminum PCBs — Strong, resists mechanical stress; FR4 PCBs — Less durable under physical stress.
For projects involving high heat generating electronics components, aluminum PCBs often outperform FR4. However, for low cost, lightweight, or flexible designs, FR4 remains the go to choice. Using CAD design tools, hobbyists can model both options to predict performance before committing to a material.
Suggested Reading: Aluminum vs FR4 PCB Material Which One is Better for Your Design?
Best Practices for Using Aluminum PCBs as a Hobbyist
To maximize the benefits of aluminum PCBs, electronic hobbyists should follow practical guidelines tailored to their skill level and project scope. These tips focus on effective integration into electronics design workflows.
Assess Thermal Needs Early
Before selecting aluminum PCBs, evaluate whether your project involves significant heat generation. Components like power transistors or high intensity LEDs often benefit from the thermal conductivity of aluminum. Use CAD design software to simulate heat distribution and confirm if aluminum is necessary over the FR4 PCB.
Optimize Layout for Heat Dissipation
When designing with aluminum PCBs, place heat generating components strategically to leverage the metal core’s properties. Ensure direct thermal pathways to the aluminum base by minimizing insulating barriers. This approach enhances cooling efficiency and protects sensitive electronics components from damage.
Start with Simple Designs
For those new to PCB for beginners resources, begin with single layer aluminum PCB designs to understand their behavior. Complex multi layer setups can introduce challenges like signal interference. Gain experience with basic circuits before scaling up to intricate projects.
Balance Cost and Performance
While aluminum PCBs offer thermal advantages, they are not always the most economical choice. Compare costs against FR4 PCBs for your specific application. If heat dissipation is not a primary concern, standard materials might suffice, saving resources for other project aspects.
Conclusion
Aluminum PCBs present a valuable option for electronic hobbyists tackling projects with high thermal demands. Their superior heat dissipation, durability, and environmental benefits make them suitable for specific electronics design challenges, particularly in high power applications. However, limitations like higher cost, rigidity, and design constraints require careful consideration against alternatives like FR4 PCBs. By understanding these pros and cons, hobbyists can make informed decisions using CAD design tools to optimize outcomes. Whether you are a beginner exploring PCB for beginners materials or an experienced designer, weighing these factors ensures your electronics components perform reliably in any project.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main benefits of aluminum PCBs for electronics design?
A1: Aluminum PCBs excel in thermal management, making them ideal for high power electronics design projects. They efficiently dissipate heat, protecting components from damage. Their durability also suits robust applications. For hobbyists, this means longer lasting builds with high heat components like LEDs, ensuring reliability without complex cooling solutions.
Q2: How do aluminum vs FR4 PCBs compare for beginners?
A2: Aluminum offers better heat dissipation but at a higher cost and with a rigid structure. FR4 PCBs are cheaper, lighter, and available in flexible forms, making them easier for PCB for beginners to use. Beginners should choose based on thermal needs and budget constraints.
Q3: Can I use aluminum PCBs in CAD design software easily?
A3: Yes, most CAD design tools support aluminum PCB layouts by allowing material specifications for thermal simulation. Hobbyists can model heat distribution and component placement effectively. Ensure your software includes aluminum’s thermal conductivity properties to predict performance accurately before manufacturing your design.
Q4: Are aluminum PCBs suitable for all electronics components?
A4: Aluminum PCBs are not ideal for every project involving electronics components. They work best with high heat parts like power supplies or LEDs. However, their rigidity and cost make them less suitable for lightweight or flexible designs. Evaluate component needs before selecting this material.
References
IPC-6012E — Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
IPC-A-600K — Acceptability of Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
ISO 9001:2015 — Quality Management Systems. ISO, 2015.