Introduction
Conformal coating plays a vital role in protecting printed circuit boards (PCBs) from environmental stressors such as moisture, dust, and temperature fluctuations. For electrical engineers, understanding conformal coating failure analysis is essential to ensure the reliability and longevity of electronic assemblies. Failures like conformal coating delamination, cracking, discoloration, and corrosion can lead to catastrophic malfunctions in critical applications. This guide explores the root causes of these issues and offers practical prevention strategies. By addressing conformal coating failure analysis, engineers can enhance design and manufacturing processes to meet stringent industry standards. The following sections will break down the mechanisms behind failures such as conformal coating cracking and corrosion, providing actionable insights for robust PCB protection.
What Is Conformal Coating and Why It Matters
Conformal coating is a thin polymeric layer applied to types of PCBs to shield electronic components from environmental hazards. It acts as a barrier against moisture, chemicals, and mechanical stress, ensuring operational integrity in harsh conditions. For electrical engineers, conformal coating is critical in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices where reliability is non-negotiable. Without proper coating, PCBs are vulnerable to failures that can compromise functionality or safety.
The importance of conformal coating lies in its ability to extend the lifespan of electronic assemblies. It prevents short circuits, corrosion, and insulation breakdown. However, when failures occur, such as conformal coating delamination or discoloration, they can signal underlying issues in material selection or application. Understanding these failures through detailed analysis helps engineers mitigate risks and maintain performance standards.
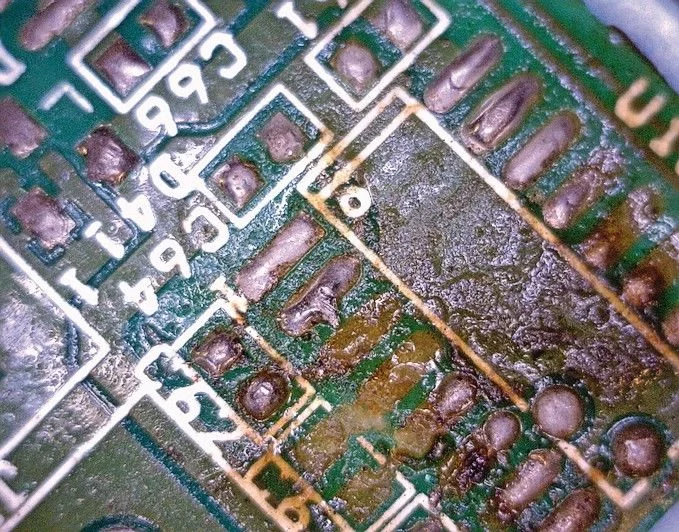
Root Causes of Conformal Coating Failures
Conformal coating failures manifest in various forms, each tied to specific causes. This section examines the mechanisms behind common issues like conformal coating cracking, delamination, discoloration, and corrosion, providing a foundation for effective failure analysis.
Conformal Coating Delamination Causes
Delamination occurs when the coating separates from the PCB surface, exposing components to environmental threats. This failure often results from poor adhesion due to surface contamination. Residues from flux, oils, or dirt prevent proper bonding during application. Inadequate surface preparation, such as insufficient cleaning, exacerbates this issue.
Another cause is mismatched thermal expansion between the coating and substrate. During temperature cycling, stress builds at the interface, leading to separation. Material incompatibility, where the coating's properties do not align with the PCB's base material, also contributes to delamination. Engineers must prioritize thorough cleaning and material testing to address these conformal coating delamination causes.
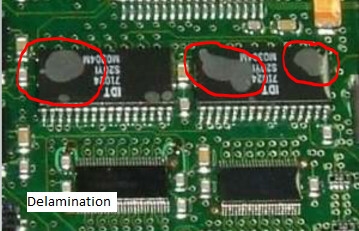
Conformal Coating Cracking
Cracking appears as fractures in the coating layer, often caused by mechanical stress or thermal shock. Excessive vibration or flexing of the PCB can exceed the coating's elasticity, leading to cracks. This is common in applications with frequent handling or dynamic environments.
Thermal stress from rapid temperature changes is another factor. If the coating cannot withstand expansion and contraction, it develops fissures. Improper curing, where the coating is not fully hardened, also weakens its structure, making it prone to conformal coating cracking. Selecting coatings with suitable flexibility and thermal resistance is crucial for prevention.
Conformal Coating Discoloration
Discoloration indicates chemical or thermal degradation of the coating material. Exposure to ultraviolet light often causes yellowing or darkening, especially in coatings lacking UV resistance. High operating temperatures can accelerate this aging process, altering the coating's appearance.
Chemical interactions with environmental contaminants, such as solvents or pollutants, also trigger conformal coating discoloration. This aesthetic change may not always affect performance, but it can signal early material breakdown. Engineers should evaluate the operating environment and choose coatings with appropriate chemical and thermal stability to avoid this issue.
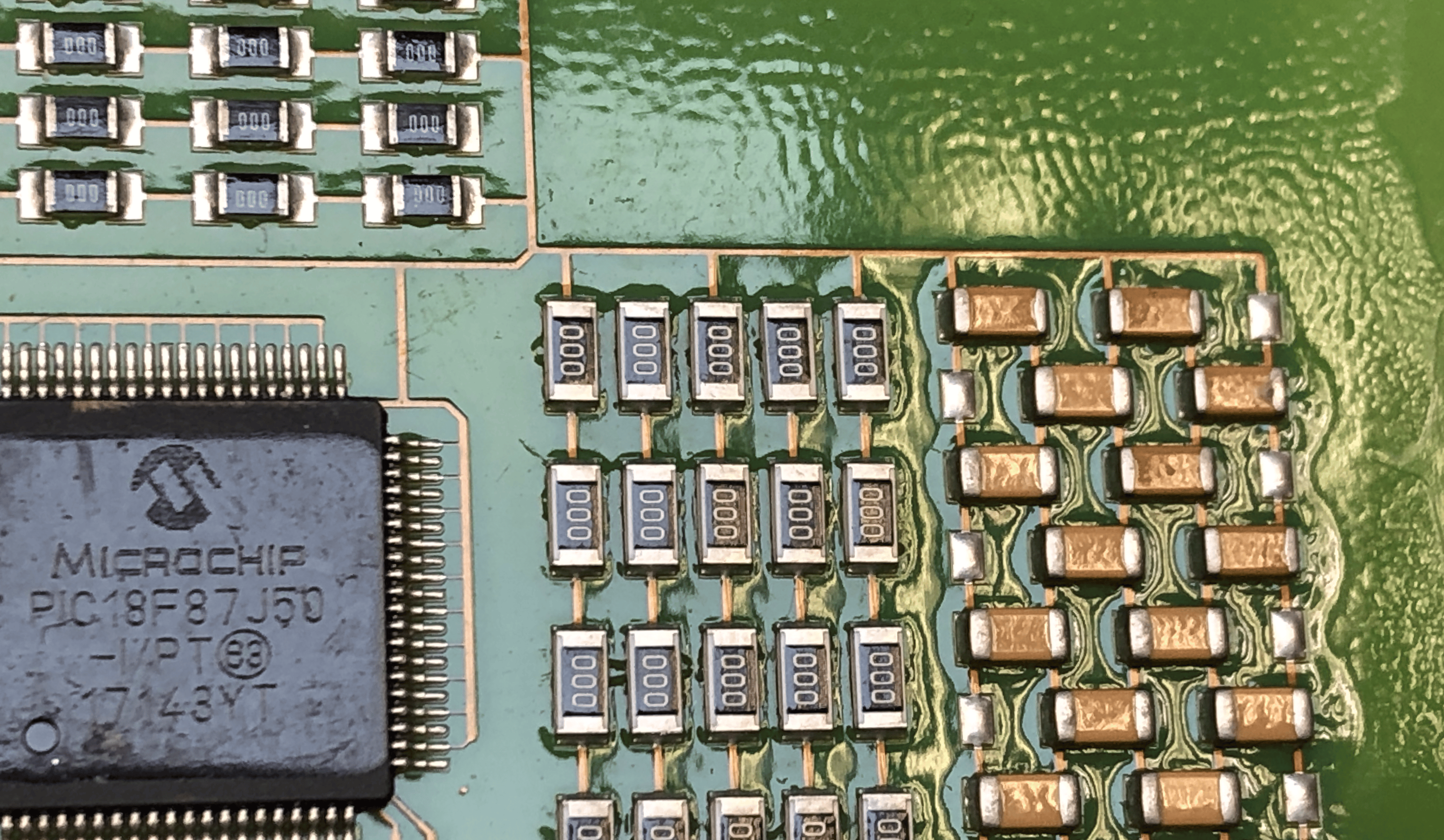
Conformal Coating Corrosion
Corrosion under conformal coating occurs when moisture or contaminants penetrate the layer, attacking metallic components. This failure often results from pinholes or defects in the coating that allow ingress of water vapor. High humidity environments worsen this problem, especially if the coating lacks sufficient barrier properties.
Improper application, such as uneven thickness, creates weak spots vulnerable to breach. Additionally, ionic contamination on the PCB surface can initiate electrochemical reactions, leading to conformal coating corrosion. Rigorous inspection and environmental testing are essential to detect and prevent such failures.
Practical Solutions for Preventing Conformal Coating Failures
Preventing conformal coating failures requires a systematic approach to material selection, application, and testing. This section outlines best practices for electrical engineers to address issues like conformal coating delamination causes and corrosion.
Material Selection Based on Environment
Choosing the right coating material is the first step in failure prevention. Acrylic coatings offer good moisture resistance and are easy to apply, suitable for moderate environments. Silicone coatings excel in high-temperature applications due to their flexibility. Polyurethane provides robust chemical resistance, ideal for harsh conditions. Parylene, applied via vapor deposition, ensures uniform coverage for critical applications.
Engineers must match the coating to the expected environmental stressors. Testing materials under simulated conditions, as outlined in standards like IPC-CC-830C, helps validate performance. This standard specifies qualification requirements for conformal coatings, ensuring reliability against failures like conformal coating cracking.
Surface Preparation and Cleaning
Surface cleanliness directly impacts coating adhesion. Contaminants must be removed using appropriate cleaning methods before application. Standards such as IPC-CH-65B provide guidelines for cleaning electronic assemblies to eliminate residues that cause delamination. Solvent or aqueous cleaning, followed by drying, prepares the surface for optimal bonding.
Inspection after cleaning ensures no residues remain. Techniques like ionic contamination testing can detect invisible impurities. Thorough preparation reduces the risk of conformal coating delamination causes and enhances overall protection.
Application Techniques for Uniform Coverage
Uniform application prevents defects like pinholes or uneven thickness that lead to conformal coating corrosion. Methods include brushing, spraying, dipping, or selective robotic coating. Each technique requires precise control to achieve consistent results. For instance, spraying must maintain a steady distance and angle to avoid overspray or pooling.
Curing conditions are equally important. Insufficient curing time or temperature can weaken the coating, causing issues like conformal coating cracking. Adhering to manufacturer guidelines and standards such as IPC-HDBK-830 ensures proper application and curing processes for long-term reliability.
Testing and Inspection Protocols
Regular testing identifies potential failures before they escalate. Visual inspection under magnification detects defects like cracks or discoloration. Environmental testing, including humidity and thermal cycling, evaluates coating performance under stress. Standards like IPC-A-610 provide criteria for acceptable coating appearance and coverage on electronic assemblies.
Advanced techniques, such as cross-sectional analysis, reveal internal defects or adhesion issues. Implementing these protocols as part of conformal coating failure analysis ensures early detection of problems like conformal coating discoloration or corrosion.
Suggested Reading: Implementing Automated Conformal Coating for Improved PCB Reliability
Insights from Industry Standards
Industry standards offer a framework for consistent quality in conformal coating processes. IPC-CC-830C defines material requirements and test methods for coatings, ensuring they withstand environmental challenges. IPC-HDBK-830 serves as a handbook for design, selection, and application, providing detailed guidance on avoiding failures.
IPC-A-610 sets acceptability criteria for electronic assemblies, including coating thickness and coverage. These standards collectively help engineers address root causes of failures through systematic approaches. By aligning with such guidelines, conformal coating failure analysis becomes a structured process, improving outcomes in design and manufacturing.
Conclusion
Conformal coating failure analysis is a critical skill for electrical engineers aiming to enhance PCB reliability. Issues like conformal coating delamination, cracking, discoloration, and corrosion stem from specific root causes such as poor adhesion, thermal stress, and environmental exposure. By understanding these mechanisms, engineers can implement prevention strategies through proper material selection, surface preparation, application techniques, and rigorous testing. Adherence to industry standards ensures consistency and performance in challenging conditions. This guide equips professionals with the knowledge to identify and mitigate conformal coating failures, safeguarding electronic assemblies for long-term functionality.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main conformal coating delamination causes in PCB assemblies?
A1: Delamination often results from poor surface adhesion due to contamination like flux residues or oils. Inadequate cleaning and mismatched thermal expansion between the coating and PCB also contribute. Following cleaning guidelines from standards like IPC-CH-65B and selecting compatible materials can prevent this issue, ensuring the coating bonds effectively to the substrate.
Q2: How does conformal coating cracking impact PCB reliability?
A2: Conformal coating cracking compromises protection, exposing components to moisture and mechanical stress. Cracks form from thermal shock or excessive vibration if the coating lacks flexibility. This can lead to short circuits or component failure. Using flexible coatings and testing under thermal cycling conditions helps mitigate risks and maintain PCB integrity.
Q3: Why does conformal coating discoloration occur, and is it a concern?
A3: Conformal coating discoloration often results from UV exposure or high temperatures, causing chemical degradation. While it may not always affect performance, it can indicate early material breakdown. Choosing UV-resistant coatings and assessing environmental conditions during design prevents this issue. Regular inspection ensures discoloration does not progress to functional failure.
Q4: How can engineers prevent conformal coating corrosion in humid environments?
A4: Conformal coating corrosion happens when moisture penetrates through defects like pinholes. Applying uniform coatings using precise techniques and testing for barrier properties under standards like IPC-CC-830C reduces risks. Surface cleanliness and environmental testing also prevent ionic contamination, ensuring the coating remains an effective barrier against humidity.
References
IPC-CC-830C — Qualification and Performance Specification for Conformal Coatings. IPC, 2021.
IPC-HDBK-830 — Guidelines for Design, Selection, and Application of Conformal Coatings. IPC, 2002.
IPC-A-610 — Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies. IPC, 2021.
IPC-CH-65B — Guidelines for Cleaning of Printed Boards and Assemblies. IPC, 2011.