What is PWM
PWM stands for pulse width modulation. Its operation essentially encodes an analog signal into a digital form by varying the width of pulses.
Frequency
Frequency is the number of times a signal goes from high to low and back to high in one second. In other words, it is how many PWM cycles occur per second. The unit is Hz.
Duty Cycle
Within one pulse period, the duty cycle is the ratio of the time the signal stays at the high level to the entire period.
Design
One common question is whether PWM is a digital signal or an analog signal. Any analog signal can be represented by a defined digital encoding. For example, when a sine wave is passed through a comparator, it becomes a square wave, which is a PWM-like signal.
When a sine wave is compared to a threshold, the output is a square wave. From a broad perspective, PWM is used to represent an analog waveform in a pulsed digital form: high level is interpreted as 1 and low level as 0.
Applications of PWM
PWM is widely used in many everyday applications.
Example 1: Servo control
In devices such as drones, steering and position control are often driven by PWM signals. Devices like a Raspberry Pi or a microcontroller can output PWM signals with different pulse widths to control servo angle.
For typical hobby servos, a pulse shorter than 1.5 ms will make the output shaft rotate a certain angle counterclockwise from the center position, while a pulse longer than 1.5 ms will rotate it in the opposite direction. Changing the PWM duty cycle controls the servo angle.
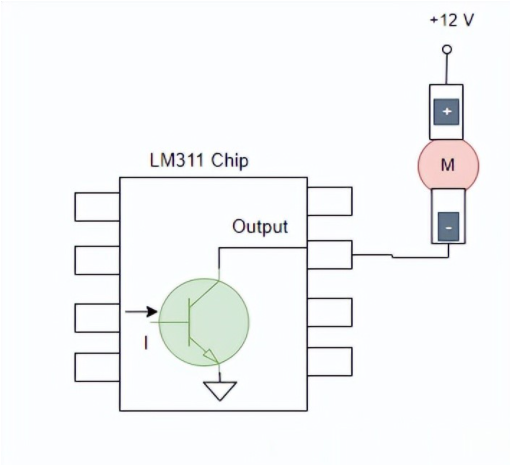
Example 2: Motor speed control
A square wave with adjustable duty cycle, i.e., a PWM signal, can change the effective voltage across a motor and thereby control motor speed.