Definition
With the development of autonomous driving technology, automated parking is evolving toward autonomous operation. Autonomous parking, also called valet parking or one-touch parking, allows a driver to summon a parked vehicle to a designated pickup point or to have the current vehicle park into a specified or an available parking space. Under normal conditions this process requires no human operation or supervision and corresponds to SAE Level 3.
Functions
The autonomous parking system includes two functions: parking and summoning.
Parking function
The user selects a parking spot within semi-enclosed areas such as business parks or residential complexes via the in-vehicle central display or a mobile phone app, or selects a parking lot covered by a high-definition map. The vehicle perceives lane markings, traffic signs, surrounding vehicles and other traffic participants, and controls throttle, steering, and braking to perform safe automated driving. It autonomously searches for available parking spaces or recognizes a user-selected space, performs automatic entry and parking, shifts to P, stops the engine, and locks the doors, while taking measures to prevent potential collisions.
Summon function
The user selects a pickup point within a semi-enclosed area via a smartphone app. The vehicle autonomously exits the parking space and performs low-speed automated driving to reach the pickup point, while preventing potential collisions.
Principles and Technical Approaches
According to the main technical routes, autonomous parking systems can be classified into:
- Vehicle-centric scheme
- Infrastructure-centric scheme
- Balanced vehicle-and-infrastructure scheme
Vehicle-centric autonomous parking scheme
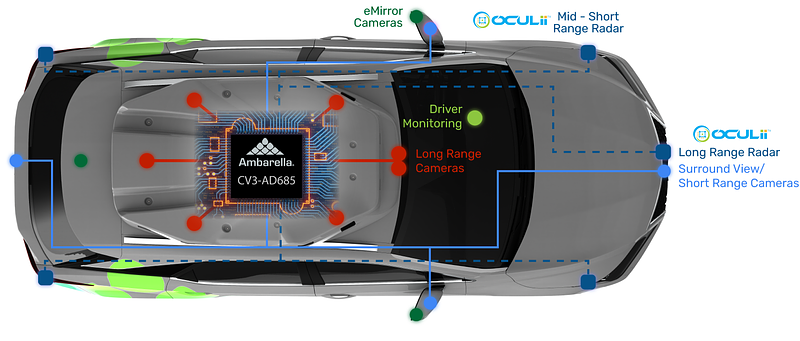
The system logic flow for the vehicle-centric scheme is shown in Figure 8. As illustrated, the vehicle-centric scheme mainly relies on onboard sensors to perceive the surrounding environment and the vehicle’s internal state for decision making and execution of vehicle maneuvers. These sensor signals are collected, conditioned, and processed through distributed electronic control units built on high-reliability automotive electronics PCB, ensuring robust signal integrity, real-time data processing, and stable operation under automotive environmental conditions. When system confidence is insufficient or boundary conditions are reached, the system prompts the user for in-cabin or remote takeover.
Infrastructure-centric autonomous parking scheme
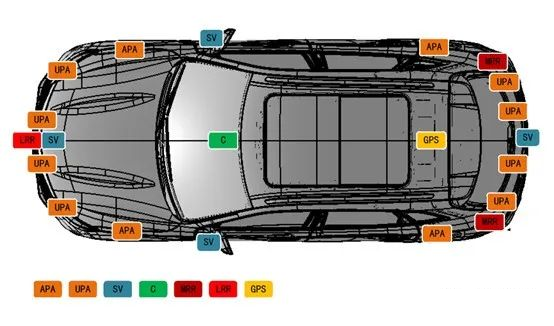
In the parking facility, lidar or stereo cameras are deployed to monitor vehicle status and the surrounding environment, and embedded parking sensors detect current occupancy. All sensor data are aggregated and analyzed in a data center. Based on stored meta-information such as parking space dimensions, fees, and special designations like disabled spaces, matching is performed. The data center generates parking maps in real time. Drivers receive this information via a smartphone app so they can always see nearby available parking spaces and related details such as distance and price. Vehicles only need communication capability with the parking facility and a controllable chassis actuator system to complete autonomous parking with support from the infrastructure.