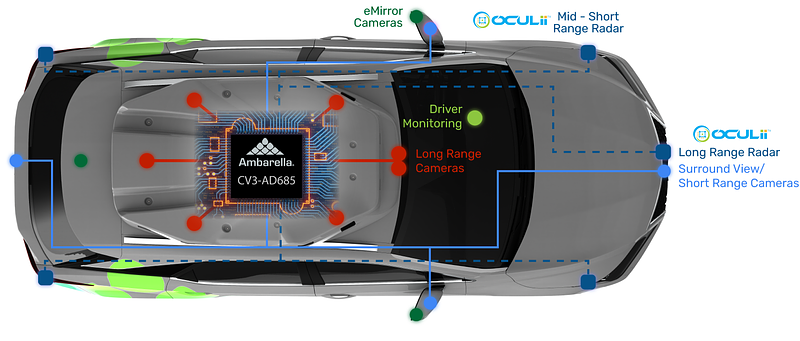
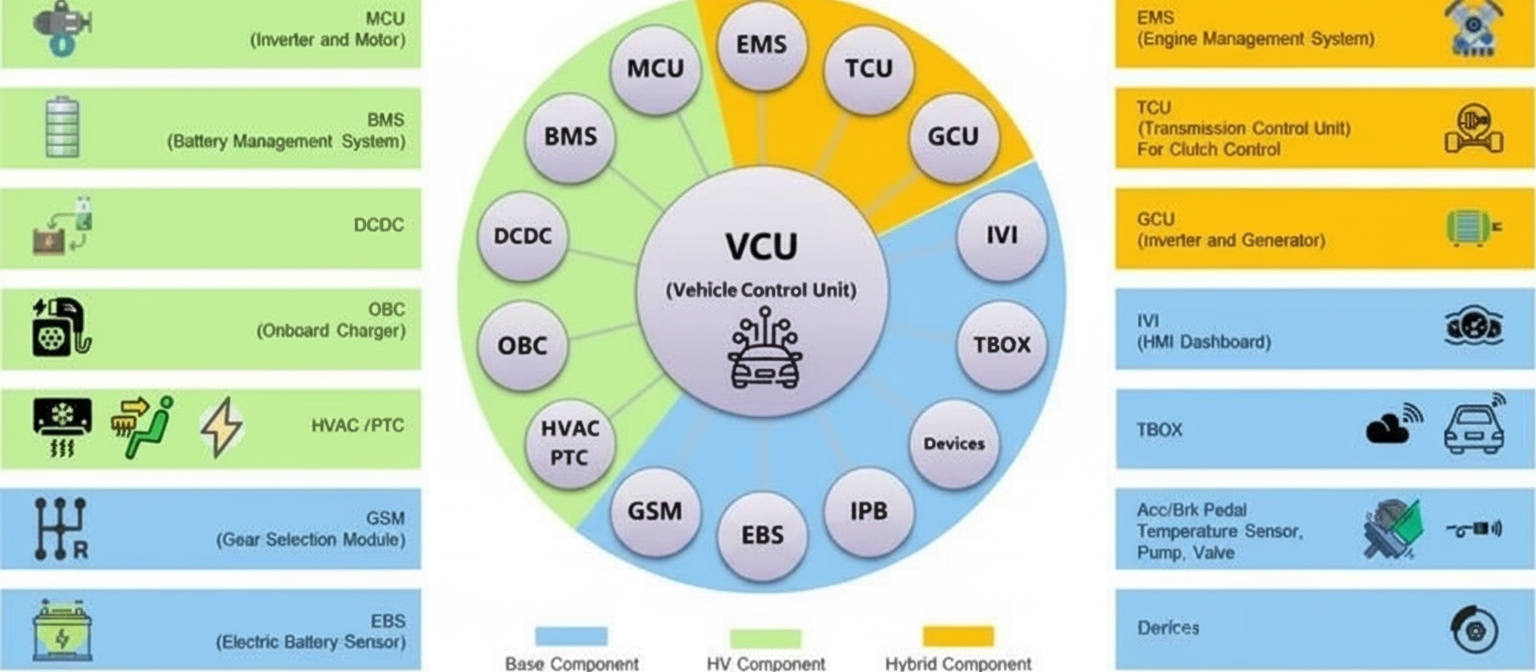
1. Overview of RISC-V
RISC-V is not only an open instruction set architecture (ISA); it also represents a fundamental shift in chip design philosophy. Unlike traditional closed architectures such as ARM and x86, RISC-V allows designers to innovate without patent restrictions. This openness is significant for the automotive industry because it enables manufacturers and suppliers to customize processors to meet specific goals, whether improving performance, reducing power consumption, or adding specialized functions.
2. RISC-V Compared with Traditional Architectures
ARM and x86 architectures have long dominated the market, but they are generally closed commercial products that require licensing fees and impose usage restrictions. In contrast, RISC-V’s openness and flexibility offer clear advantages. For example, RISC-V allows manufacturers to customize the instruction set for particular automotive applications. However, as a newer architecture, the RISC-V ecosystem and support libraries are still maturing compared with ARM and x86.
3. RISC-V Applications in the Automotive Sector
RISC-V has begun to appear across a range of automotive electronic systems, from basic in-vehicle control units to advanced autonomous driving and connected vehicle technologies. Because of its high customizability, RISC-V can be optimized for specific automotive tasks such as powertrain control, sensor data processing, and data encryption. In autonomous driving, RISC-V’s efficiency is attractive because it can handle large data volumes while keeping power consumption low, which helps extend the driving range of electric vehicles.
4. RISC-V Advantages
Open and flexible
RISC-V’s open-source nature removes expensive licensing fees and benefits from contributions from a large global community that continually improves the architecture. This collective development accelerates innovation, particularly for complex automotive requirements. Openness also reduces supply-chain dependency and single-vendor risks, which is important for automotive manufacturers.
Customizable and modular
RISC-V’s modular design lets manufacturers integrate only the functional modules they need. They can include only the instruction subsets critical to specific automotive tasks, optimizing performance and cost. RISC-V also permits adding accelerators or coprocessors for tasks like image processing or machine learning, enabling vehicle systems to handle complex workloads more efficiently.
Performance and energy efficiency
RISC-V’s efficiency comes from its streamlined instruction set and optimized core designs. These traits increase processing speed while reducing chip power consumption, which is crucial for battery-powered automotive systems. The architecture’s scalability also means it can adapt to growing performance demands, such as real-time processing requirements in autonomous systems.
5. Automotive Electronics and RISC-V
System requirements
Automotive electronic designs are becoming more complex, with higher data volumes and strict safety requirements. For instance, processors in autonomous systems must process camera, radar, and other sensor data in real time while maintaining high reliability and responsiveness. RISC-V’s configurability enables tailored solutions that meet these complex needs.
Role in key automotive applications
RISC-V is applicable across a spectrum of vehicle systems, from simple vehicle monitoring to advanced autonomous driving and connected services. It can provide the compute capacity needed for in-vehicle cameras and sensors while maintaining low energy consumption, which is important for preserving electric vehicle range. Its customizability also makes it suitable for infotainment and telematics systems, supporting richer multimedia capabilities.
Safety and reliability
Security and reliability are critical in automotive processors. RISC-V allows integration of advanced safety features such as fault detection, error correction, and secure boot mechanisms. These capabilities help meet automotive safety standards and protect vehicles from security threats. The open nature of RISC-V also enables community-driven verification and improvement of security features.
6. Case Studies
Real-world automotive deployments
For example, a well-known electric vehicle manufacturer is using RISC-V–based processors in its autonomous driving systems, with processors customized for high-throughput data processing and low power consumption. Some infotainment system vendors also choose RISC-V for more efficient multimedia processing and improved user experience.
RISC-V driven innovation
Automotive electronics vendors adopting RISC-V can adapt more quickly to market changes and deliver competitive products. This faster iteration and innovation contribute to RISC-V’s growing influence in the automotive sector. RISC-V’s openness also facilitates cross-industry collaboration, accelerating development of automotive electronics technologies.
7. Market Trends and Challenges
As demand grows for smarter, more connected vehicles, RISC-V’s market share is expected to expand, particularly in autonomous driving and connected vehicle domains where flexibility and efficiency are valued. With support from the open-source community, the RISC-V ecosystem is maturing rapidly, which should further boost automotive adoption.
Despite its advantages, RISC-V faces challenges when competing with established ARM and x86 ecosystems. RISC-V requires broader software and hardware support, including wider operating system and middleware support, and more optimization and validation for specific automotive use cases. For manufacturers and suppliers deeply invested in ARM or x86, migration to RISC-V could require significant time and resources.
8. Technical Overview
Key technical characteristics
The RISC-V instruction set emphasizes simplicity and efficiency. It follows reduced instruction set computing principles, meaning each instruction is optimized for fast execution. By contrast, ARM and x86 include more complex instructions that may deliver higher performance in certain scenarios but often at the cost of higher power consumption and increased design complexity. RISC-V’s modular approach lets designers keep the core simple while adding extensions such as vector processing or floating-point units for specific workloads.
Core design and instruction set
RISC-V cores can be configured in many ways, enabling use from low-power microcontrollers to high-performance processors. A basic RISC-V core may only implement integer instructions, while advanced configurations support floating-point and vector processing. This flexibility distinguishes RISC-V from ARM and x86, which typically provide fixed core configurations that can be efficient for some applications but less adaptable when deep customization is required.
9. Conclusion and Outlook
RISC-V’s potential in the automotive sector lies not only in its technical merits but also in its ability to foster broader innovation and collaboration. As the technology and ecosystem mature, RISC-V is likely to play an increasing role in automotive electronics. It offers automakers more design freedom and potential cost advantages while enabling faster innovation and wider collaboration. With ongoing advances in autonomous driving, electric vehicles, and connected vehicle technologies, RISC-V is positioned to become an important enabling technology in these areas.