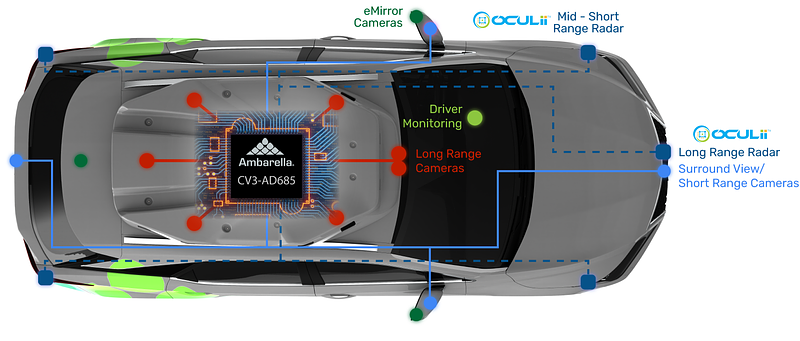
Overview
Avita was launched as a joint effort by Changan Auto, CATL, and Huawei. Huawei provides the vehicle's intelligent solutions, including mechanical, high-voltage electrical systems, intelligent vehicle software, and the electronic architecture. The following summarizes key technical aspects observed on the Avita 11.
Electronic architecture
Huawei proposed a distributed Ethernet gateway plus domain controllers architecture (cockpit CDC, vehicle control VDC, intelligent driving MDC) as a compute and communication architecture. The illustration below shows that concept from Huawei in 2021.
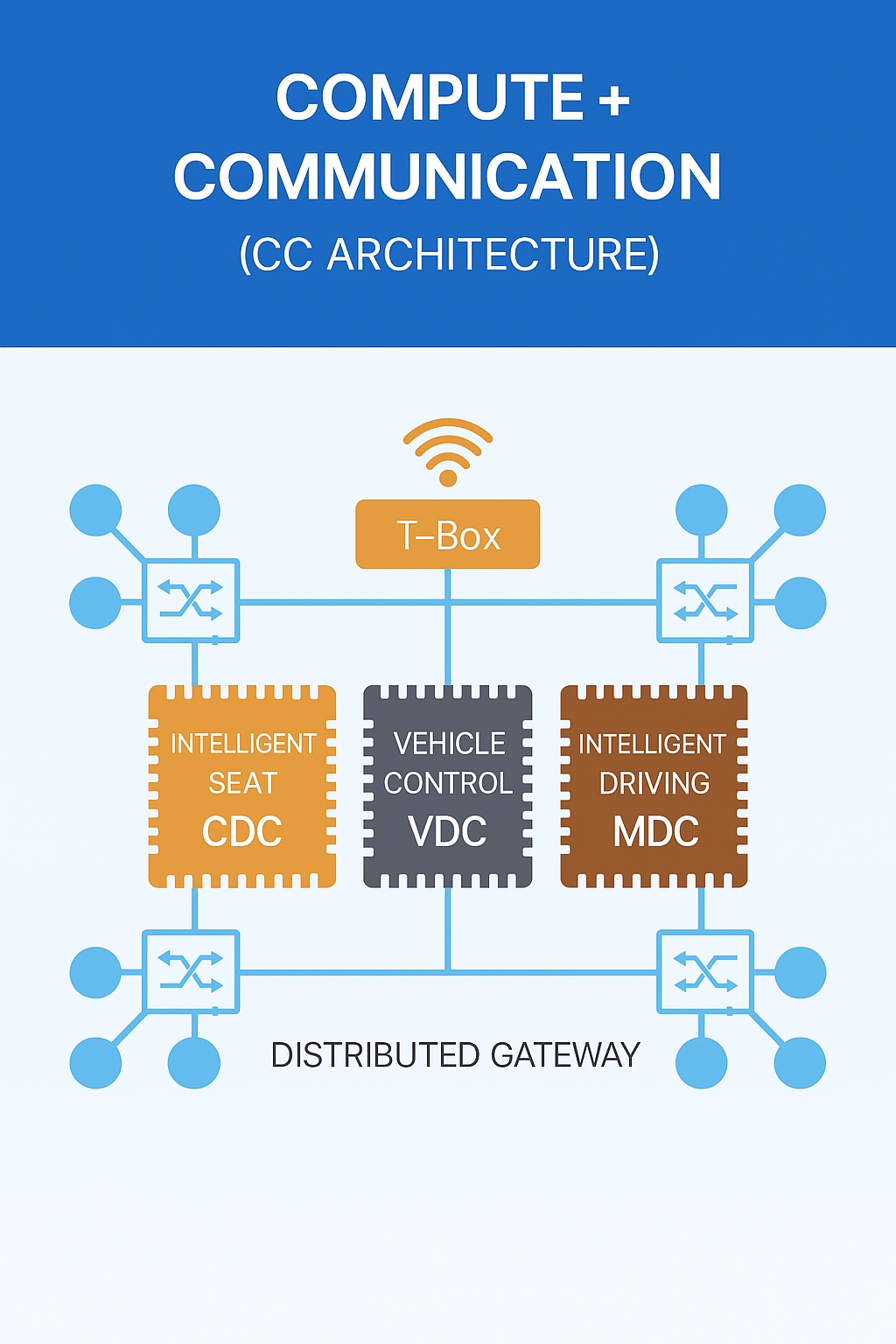
Figure 1 Huawei 2021 proposed domain controller architecture
The Avita 11 implementation follows this domain controller approach. The simplified electronic architecture diagram shows the cockpit domain controller (CDC), intelligent driving domain controller (MDC), and vehicle controller (VCU) arranged consistent with the referenced architecture.
The gateway connects to multiple CAN/CAN-FD buses including PTCANFD, PTS CANFD, CHDAND, TCANFD, RCANFD, ICANFD, and BCAN. It also supports 100Base-T1, 100Base-Tx, and 1000Base-T1. The gateway-to-MDC, gateway-to-T-Box, and gateway-to-CDC links are gigabit Ethernet, while gateway connections to body domain controllers, VCU, and the OBD port are 100 Mbps.
Intelligent cockpit domain
The cockpit runs HarmonyOS and is powered by a Kirin 990A-series SoC manufactured on a 7 nm process. The CPU uses an 8-core 4+4 configuration with a maximum frequency up to 2.86 GHz. The AI performance is listed as 3.5 TOPS. The unit is equipped with 8 GB of RAM and 128 GB of storage. The diagram below shows the cockpit domain controller and its connected peripherals.
Intelligent driving domain
Avita 11's intelligent driving hardware includes an MDC platform combined with multiple sensors: three lidar units, six millimeter-wave radars, 13 cameras, and 12 ultrasonic sensors. The overall hardware configuration is shown below.
The central compute is the MDC platform. The manufacturer did not specify whether the platform is MDC610 or MDC810 in public materials, but the software architecture is unified across the MDC series to support rapid application development and platform-level compatibility, with series-wide uniform form factors to allow smooth upgrades and replacements.
Using MDC610 as an example, the main compute combines an Ascend 610 and an Infineon TC397. The MDC610 hardware architecture is shown below.
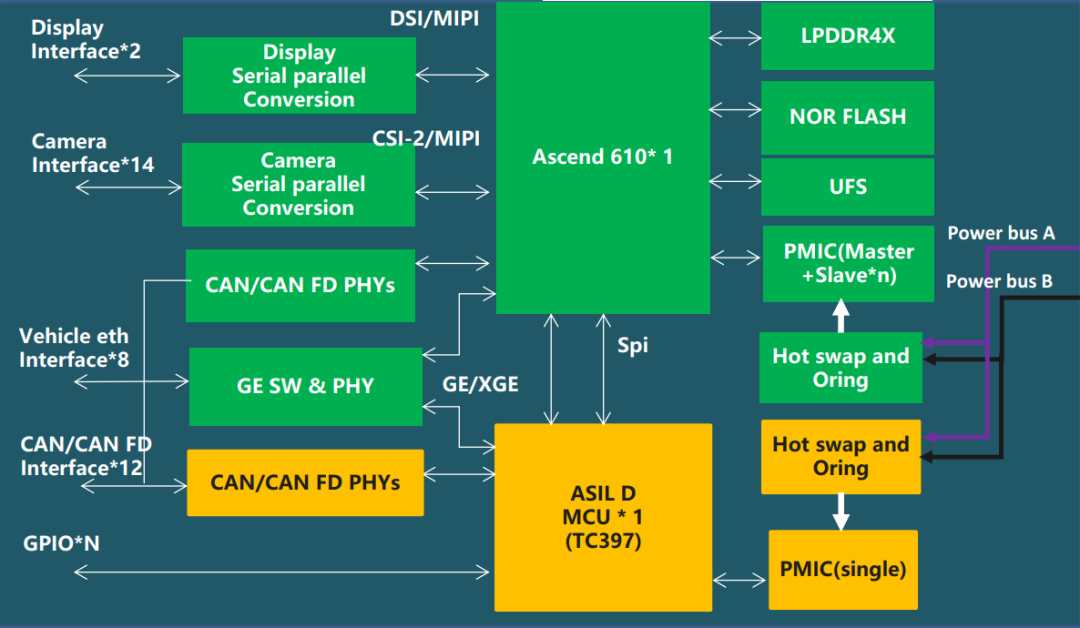
Figure 2 MDC 610 hardware architecture
Key specifications:
- AI performance: 200 TOPS (int8). ARM core integer performance: 220K DMIPs.
- Liquid-cooled power consumption: approximately 120 W.
- Sensor interfaces: 14 LVDS camera interfaces, 8 Ethernet interfaces, 12 CAN/CAN-FD interfaces, 6 in-vehicle Ethernet interfaces, and 1 PPS interface. External interface definitions are shown below.
- Ingress protection: IP67.
- EMC level: Class 3.
Acceleration capabilities include support for common AI operators and mainstream frameworks such as Caffe, TensorFlow, PyTorch, and ONNX, with a library of more than 400 operators. The platform provides configurable hardware accelerators and a Vector Core for vector acceleration and tightly coupled scalar execution, accelerating mixed-control and data-parallel code paths common in recursive computer vision algorithms. The hardware acceleration approach is illustrated below.
The MDC software architecture centers on Huawei-developed AP, CP, and OS layers, as shown below.
Huawei's Adaptive AUTOSAR implementation conforms to R19-11 and later, providing communication management, execution management, state management, upgrade management, health management, persistence, time synchronization, access control, encryption, diagnostic services, and network management, along with a configuration tool compatible with the Adaptive AUTOSAR specification.
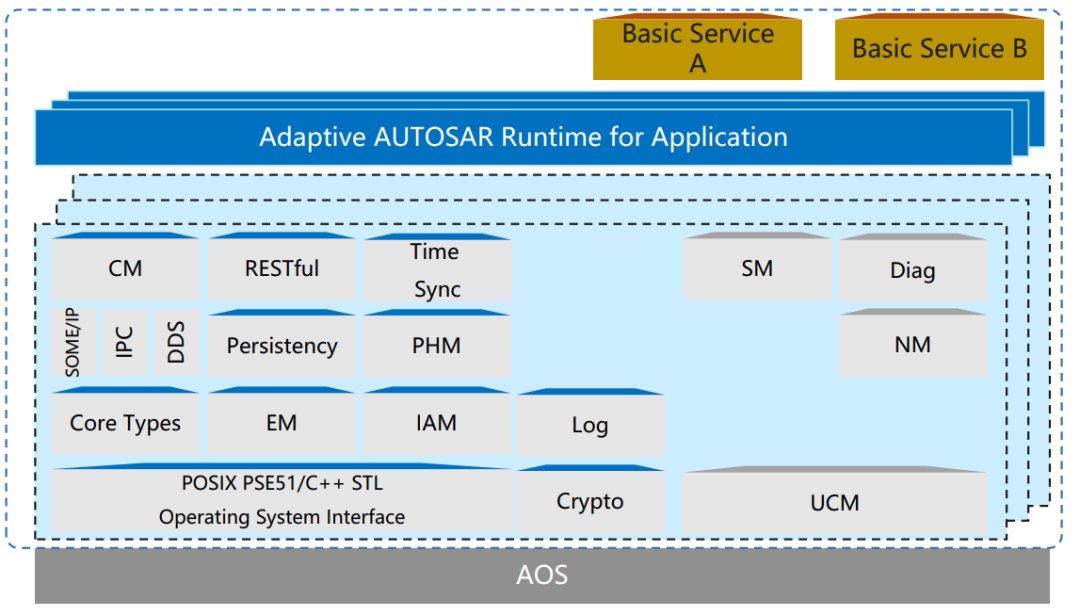
Figure 3 MDC Adaptive AUTOSAR features
The AOS real-time operating system is Huawei-developed, compatible with Linux interfaces, and provides deterministic scheduling, low latency, functional safety, and security features. It is compatible with Linux driver frameworks and third-party libraries. Regarding openness, it offers AUTOSAR compatibility. For safety and security, it supports isolation between Safety-Critical and Non-Critical applications, software-hardware co-design, a decentralized architecture to mitigate single-point failures, and deterministic latency approximately one tenth of general-purpose Linux, with kernel jitter below 10 microseconds. It also supports CC EAL4++ certification levels.
At the CP layer, VOS implements Classic AUTOSAR meeting AUTOSAR CP4.4 specifications. It provides full CAN/Ethernet protocol stacks, diagnostics, network management, calibration, and storage services, and offers a high functional safety runtime environment that supports development and deployment of ASIL-D applications. Like mainstream AUTOSAR tools, it includes graphical modeling and development tools for SWC development and BSW configuration.