Overview
OBU stands for On Board Unit, referring to the in-vehicle electronic tag used in ETC (Electronic Toll Collection) systems. Common commercial names include YueTong ETC, ETC Sutong, and similar. The OBU stores vehicle identification data and is typically mounted on the windshield. It communicates with the RSU (Road Side Unit) at toll plazas via dedicated short-range microwave communication (DSRC). When a vehicle approaches a toll barrier, the RSU recognizes the OBU signal and automatically opens the barrier, completing the toll transaction without requiring the driver to stop and thus improving traffic throughput.
RSU and OBU Roles
The RSU is installed on the toll lane gantry and functions as the roadside base station. It typically includes a transceiver, an antenna control board, patch antennas, and an RSU controller board to handle signal and data transmission/reception, modulation/demodulation, encoding/decoding, and encryption/decryption. This article focuses on chip-level and solution selection for the vehicle-mounted OBU.
Typical OBU Architecture
Common OBU architectures use an antenna unit to communicate with the gantry RSU in the 5.8 GHz band. A smartphone can connect to the OBU via Bluetooth in the 2.4 GHz band. A card reader unit connects user cards to the OBU using the 13.56 MHz band.
Key OBU Components
An OBU typically comprises an MCU, RF communication chip or module (5.8 GHz, 2.4 GHz, and Bluetooth), an RFID chip (13.56 MHz reader), a security chip (ESAM), a display, a photovoltaic solar module, batteries, and associated peripherals.
MCU and RF
MCU suppliers include Xiaohua, Nuvoton, Shanghai Beken (BEKEN), and STMicroelectronics. An industry estimate of market share placed Xiaohua at about 40%, Nuvoton about 30%, Shanghai Beken about 20%, and STMicroelectronics about 10%. Other MCU vendors seen in the market include Fuwei (FMSH), Unigroup Guoxin, Jiefa, Qipuwei, Texas Instruments (TI), Nations Technology, Lailins, Hangxin, Zhongkewei, and others. SoC chips that integrate 5.8 GHz RF communication often offer better cost-performance; Shanghai Beken, for example, offers highly integrated SoC solutions that combine RF communication and security functions.
Major RF chip or module vendors include Shanghai Beken, Scyrelli, Shengke, Texas Instruments, Analog Devices, Qualcomm, Microchip, Juxin Integration, Nordic, Yizhaowei, Telink, and Jielian Micro.
RFID and Security
Major RFID chip vendors include NXP, Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics, Fuwei (FMSH), Zhongkewei, Huada, Nations Technology, Weisheng, Shanghai Feiju, WeilinTong, Kedaoxin Guo, and Jielian Micro. Security chip vendors include Analog Devices, Nations Technology, Hongsi Electronics, Hangxin, and Unigroup Tongxin.
Batteries
Battery manufacturers observed in OBU designs include EVE (EVE Energy), Longsheng, VIMUN, Mottcell, Delip, and others.
Case Studies: Component Teardowns
The following sections summarize component-level findings from three OBU teardown examples.
1) ETC Sutong Card (teardown)
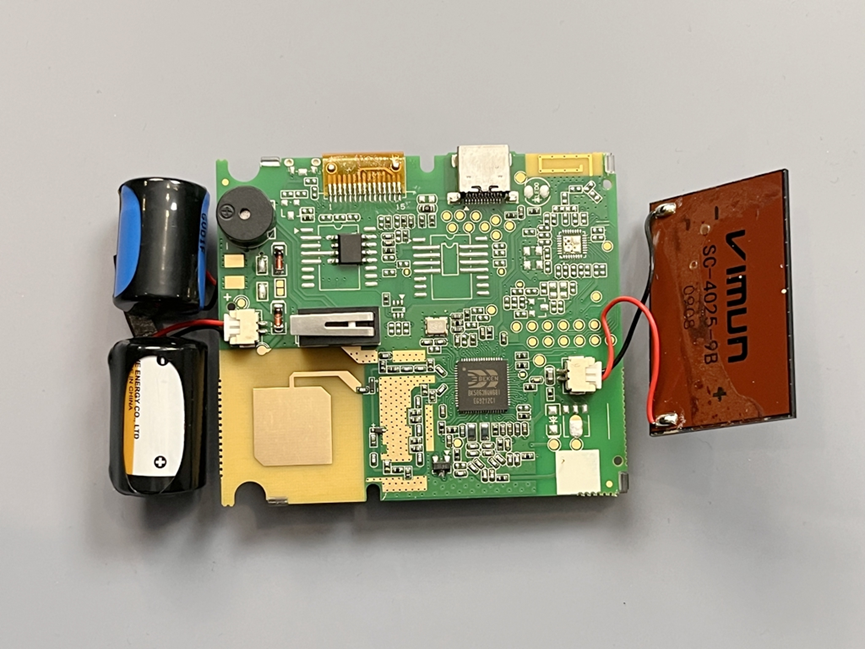
| Brand | Model | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Shanghai Beken (BEKEN) | BK5863N | Low-power SoC integrating an ARM9 processor, a contactless RF card reader, a 5.8 GHz RF transceiver, solar charging management, audio output, temperature sensor, flash, UART, SPI, I2C, and DES |
| EVE | ER14250 | Primary lithium battery, 3.6 V, 1200 mAh |
| Recovery | IFR14200 | Rechargeable battery, 3.2 V, 100 mAh |
| VIMUN | SC-4025-9B | Photovoltaic solar module |
| — | SSESAM08 (silkscreen) | ESAM security chip |
| — | — | Buzzer and an LCD screen |
| — | — | Contact mechanical switch, RC sensing, LED, connectors, interfaces, structural parts and fasteners, high-frequency ceramic antenna, etc. |
Table 1. Selected components from the ETC Sutong card
2) ETC Sutong (TUNA-C10)
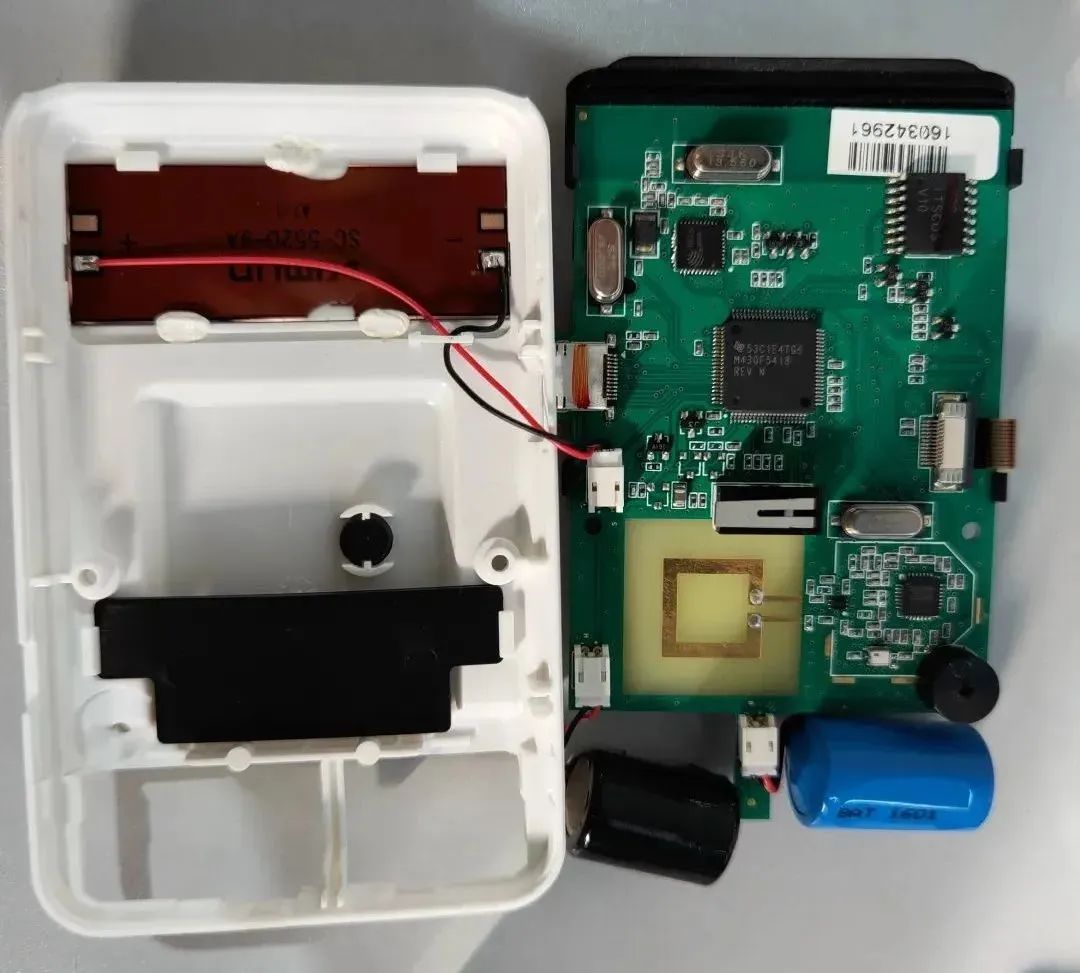

| Brand | Model | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Texas Instruments (TI) | M430F5418A | 16-bit low-power MCU |
| Shanghai Beken (BEKEN) | BK5863N | 5.8 GHz RF transceiver integrating all national-standard ETC RF functions including receive, transmit, and wake-up |
| VIMUN | SC-5520-9A | Weak-light amorphous silicon solar battery |
| FMSH | FM1702Q | 13.56 MHz contactless card reader chip |
| SJK | — | Two crystals: 32.768 MHz and 13.560 MHz |
| MUP | — | Card slot |
| — | YGG ITSCOS V10 (silkscreen) | ESAM security chip |
| — | 12832J 000097 (silkscreen) | 128x32 LCD display |
| — | BAT 1601 (silkscreen) | Rechargeable battery |
| — | — | Primary lithium battery |
| — | — | Buzzer |
| — | — | Contact mechanical switch, RC sensing, LED, connectors, interfaces, structural parts and fasteners, high-frequency ceramic antenna, etc. |
Table 2. Selected components from the ETC Sutong unit
3) ETC YueTong Card (Efsys T103)
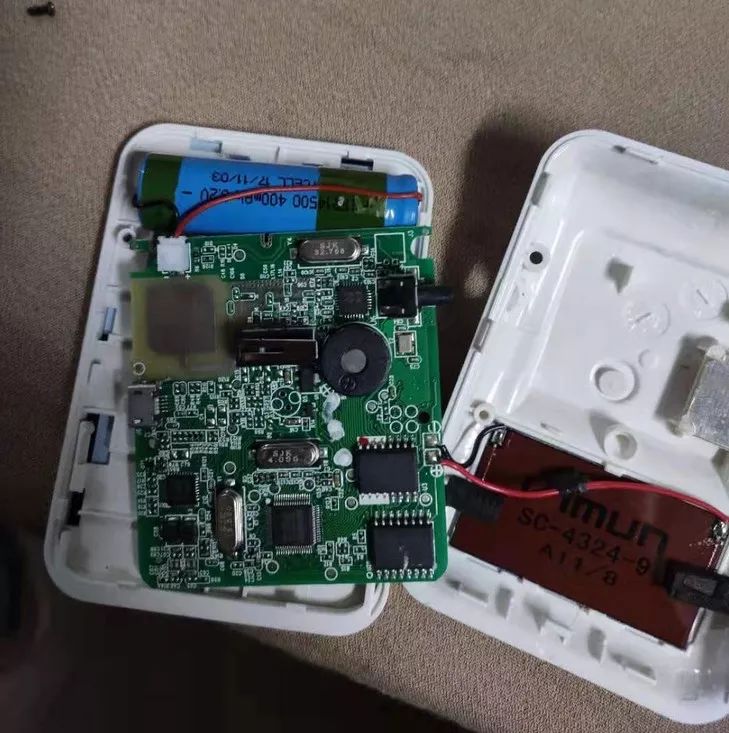

| Brand | Model | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Nuvoton | NANO100SD3BN | 32-bit low-power MCU (NuMicro Nano100 series). Features ultra-low power, 1.8 V to 3.6 V operation, -40 °C to 85 °C, built-in 12 MHz high-accuracy crystal (1% accuracy), and peripherals including timers, watchdog, RTC, DMA, UART, SPI, I2C, I2S, PWM, 12-bit ADC, 12-bit DAC, and ISO-7816 |
| Shanghai Beken (BEKEN) | BK5823 | 5.8 GHz RF transceiver integrating national-standard ETC RF functions including receive, transmit, and wake-up |
| MOTTCELL | IFR14500 | Rechargeable battery, 3.2 V, 400 mAh |
| VIMUN | SC-4324-9 | Weak-light amorphous silicon solar cell |
| Yizhaowei (MUP) | YC1021 | Multi-mode Bluetooth chip |
| Nations Technology | Z32HCD2S | 13.560 MHz contactless card reader chip |
| Nations Technology | Z8HM2 | ESAM security chip |
| Holtek | HT7136-1 | Power management chip |
| Puya | P25Q40H | NOR Flash |
| Jincai | — | LCD display |
| SJK | — | Three crystals: 32.768 MHz, 13.560 MHz, and 4.096 MHz |
| — | — | Buzzer |
| — | — | Contact mechanical switch, RC sensing, LED, connectors, interfaces, structural parts and fasteners, high-frequency ceramic antenna, etc. |
Table 3. Selected components from the Efsys T103
Summary
All three OBU teardowns show anti-tamper designs implemented with contact mechanical switches, and the security chip (ESAM) is mandatory. Devices that read and write bank contactless cards should be treated like POS terminals and therefore require financial-grade security.