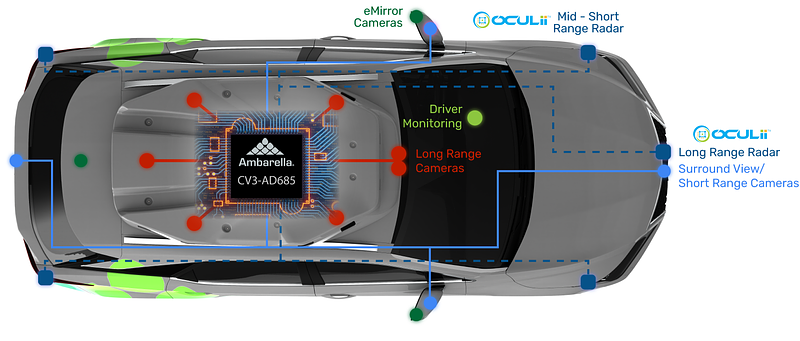
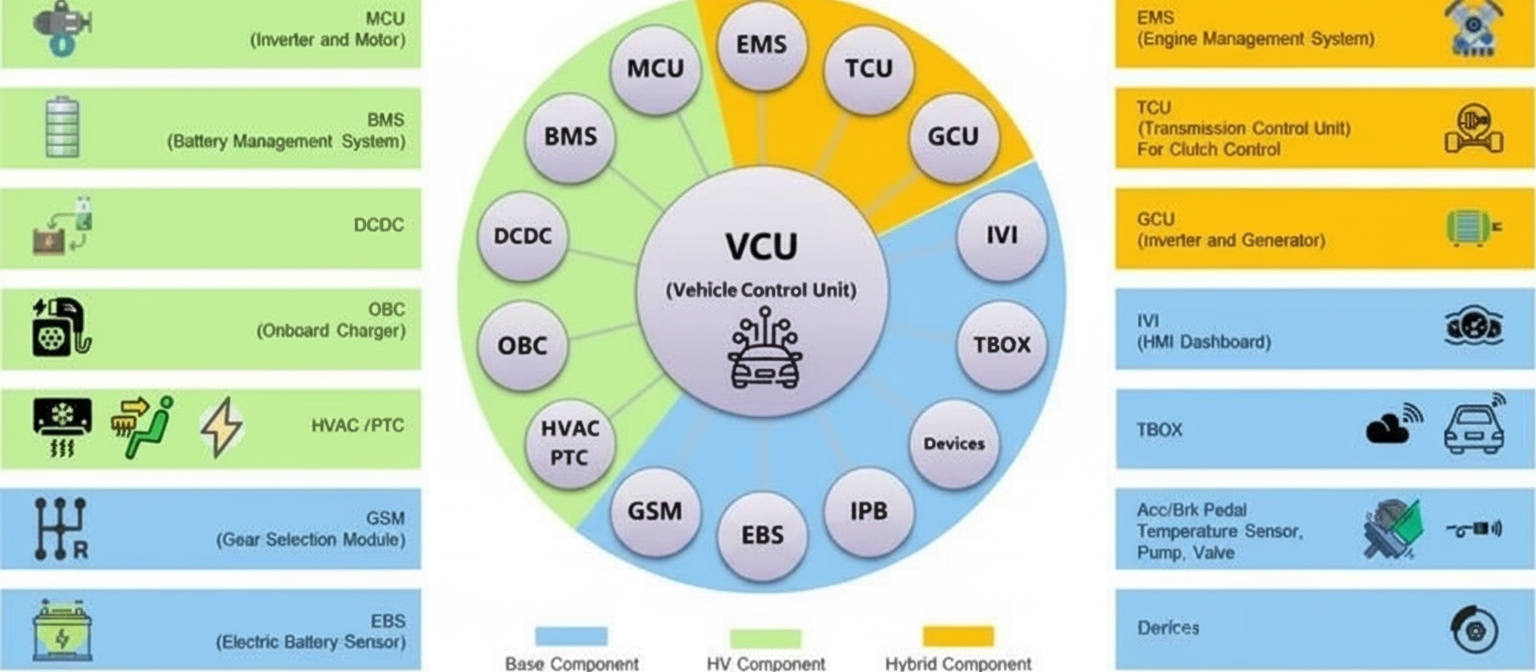
Overview
New-energy electric vehicles have been promoted in recent years as green, zero-emission transport. The drive motor, battery, and controller are the core components of these vehicles. Rolling bearings are rotating components within the drive motor. High speed, high temperature, frequent start-stop cycles, and shock loads are typical operating conditions for EV drive motors. Developing sealed deep-groove ball bearings optimized for these conditions enables use across hybrid buses, pure-electric buses, passenger cars, and microvehicles, and these bearings are widely applied in the market.
Design and Application Characteristics
Bearing designs for EV drive motors emphasize good sealing performance, high- and low-temperature capability, resistance to repeated start-stop cycles, and tolerance for certain axial shock loads. Internal structure, bearing materials, heat treatment, machining accuracy, lubricants, and assembly fits have been optimized to improve performance. The maximum permissible speed can exceed that of conventional bearings by more than 1.5 times under comparable conditions.
1. Speed
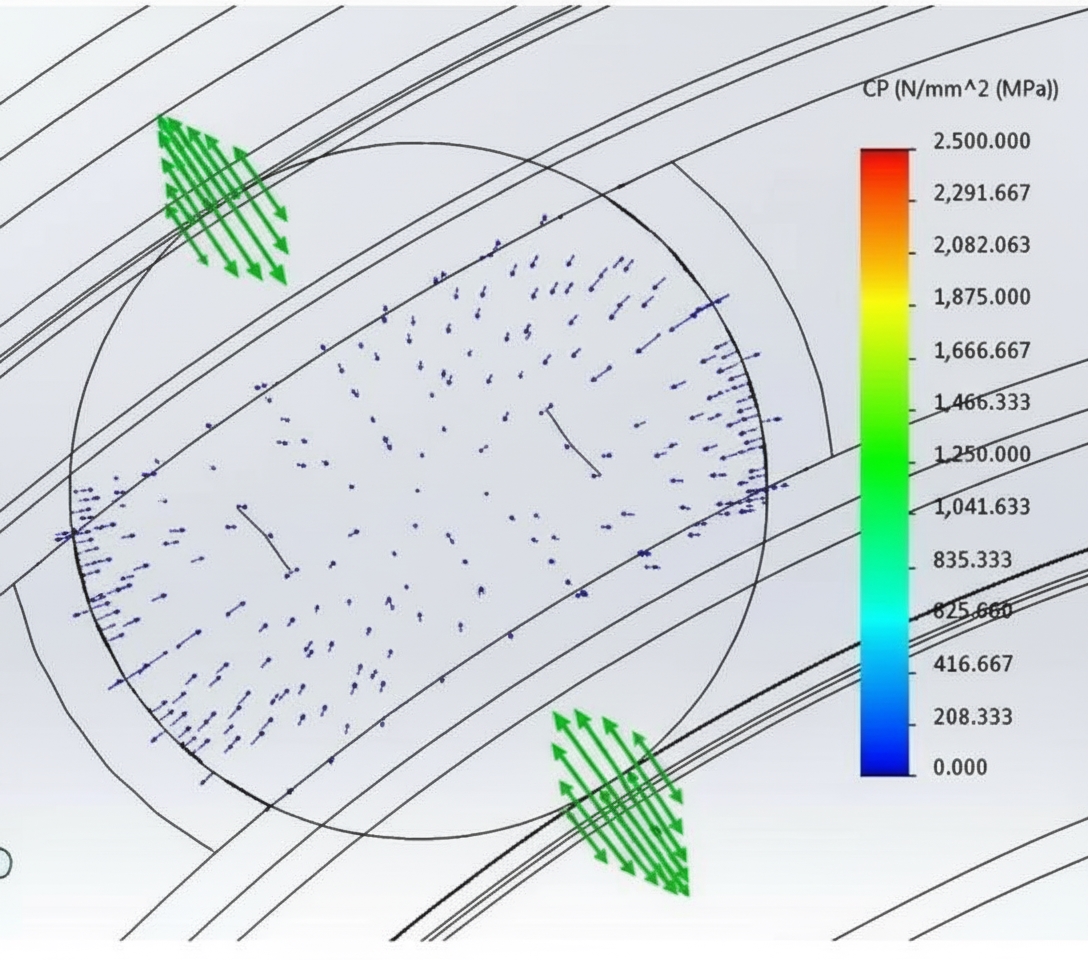
Operating speed affects both bearing life and lubricant life. When selecting a bearing, consider bearing size, cage type, lubrication method, internal clearance, and seal type. Speeds in EV drive motors can reach up to 18,000 rpm, with dmn values exceeding 800,000.
2. Shaft and Housing Materials
Thermal expansion and contraction are important when choosing shaft and housing materials. Thermal growth and shrinkage directly affect shaft-to-housing fits and thus bearing internal clearance. Shafts for EV drive motors commonly use medium carbon steel with quenching and tempering; housings commonly use cast aluminum or aluminum alloys to reduce motor weight and improve heat dissipation.
3. Operating Environment
In humid, low-temperature, high-temperature, or environments with significant water, mud, or dust ingress, the seal and seal material are critical. Considerations include preventing lubricant leakage that could contaminate the environment or the product, and preventing lubricant loss that would starve the bearing and reduce service life.
4. Temperature
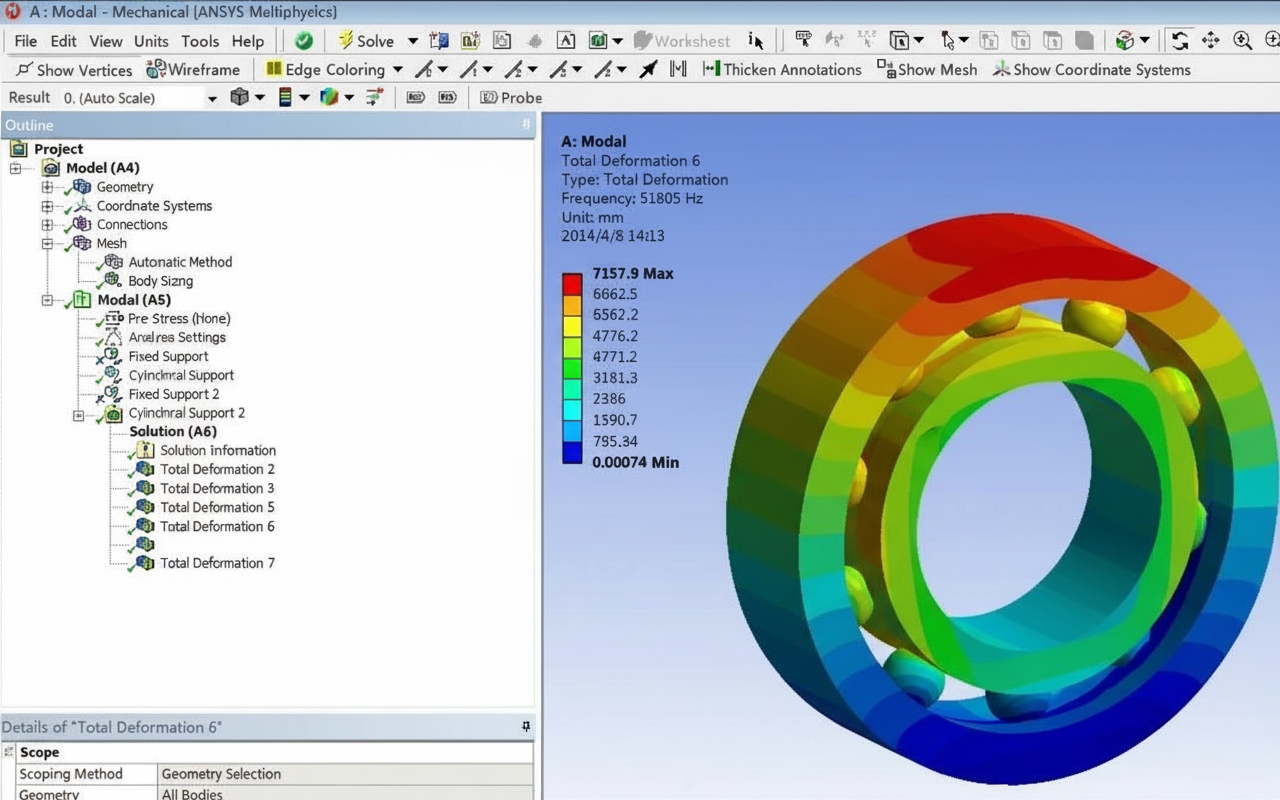
Bearing temperature is a major factor affecting machine life. Large differences between ambient temperature and bearing operating temperature create thermal gradients. If the thermal gradient is significant, check the bearing internal clearance to avoid unnecessary damage.
5. Cage
High-speed bearings for EV drive motors often use high-temperature-resistant engineering-plastic cages rated for ≥180°C. Medium- and low-speed bearings may use SPCC steel cages. These cage materials provide good high-speed performance and low noise.
6. Bearing Accuracy
Bearing accuracy grades for EV drive motors typically meet P6, with internal parameters reaching P5 in some cases. This yields high rotational stability and low noise (noise grade up to Z3 group).
7. Bearing Life
The rated life of a rolling bearing is defined as the number of revolutions, or the operating hours at a constant speed, that a group of identical bearings can sustain before the first signs of fatigue (pitting or fracture) appear on the races or rolling elements.
Laboratory tests and field experience show that bearings that appear identical on the surface can still have different service lives under the same operating conditions. In general, bearing life depends on the operating conditions, but installation and maintenance procedures also directly affect life. When premature failures occur, a thorough inspection and root cause analysis are required before corrective actions are taken.
Target life is a value specified by manufacturers based on ideal load and speed conditions. For example, a specified minimum life under the maximum allowable load might be 5,000 hours or approximately one year.
Under favorable operating conditions, bearings can achieve longer life than standard life calculations predict. Good conditions include an effective lubricant film that separates the rolling surfaces (raceways and rolling elements) and limited surface damage from contaminants.