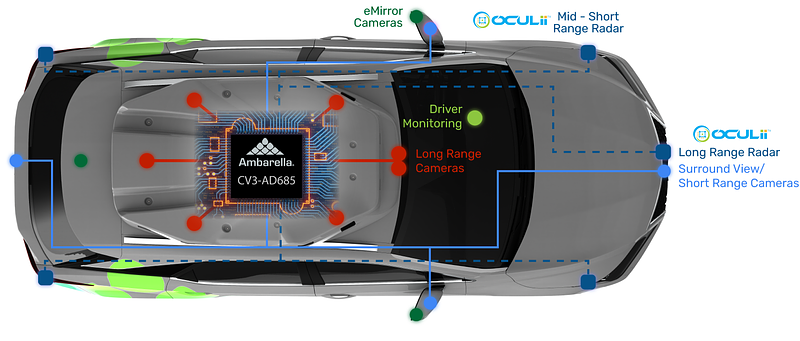
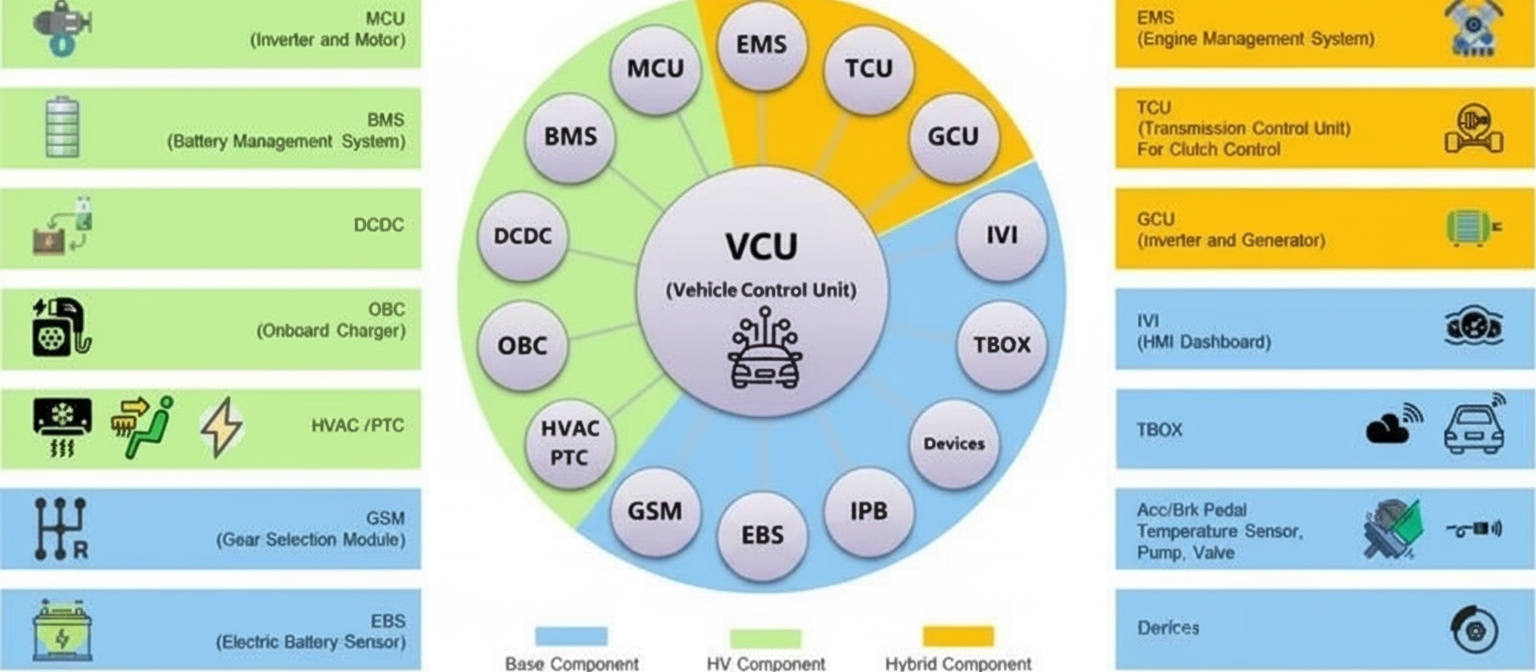
Overview
P3 released "Autonomous Driving Market Insight", divided into MaaS, freight transport, and private ownership. This article is the first part and focuses on MaaS across the U.S., China and European core markets.
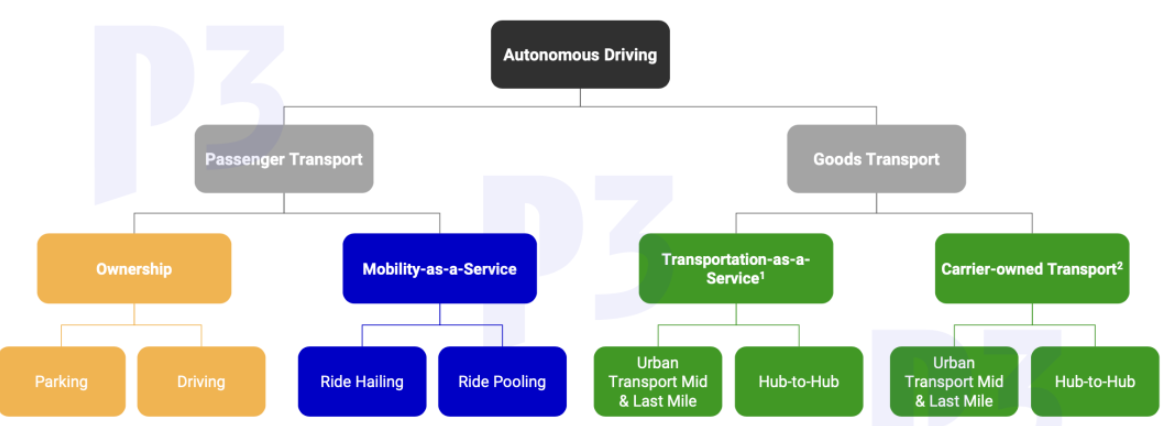
MaaS mainly includes ride-hailing, low-speed services and ride-pooling.
Platform Stack
Layer 1 and Layer 2
Autonomous driving system software and hardware represent the complete set of systems required to achieve SAE driving levels. Main functions include sensor data fusion, object detection, localization, prediction, environment interpretation, trajectory planning and actuator control. Self-driving vehicles (SDVs) are considered L4-ready vehicles that integrate and validate SDS (sensors, compute hardware and software) and operate within specific ODDs (operational design domains).
Layer 3
Fleet operations: fleet operators may own, operate and maintain a number of autonomous vehicles. Fleet operators may be responsible for fleet intelligence and technical oversight. Layer 3 therefore covers both physical and digital fleet operations.
Layer 4
Mobility and platform providers: mobility providers own the user front end. They are the point of sale and provide the primary communication and interaction channels with users. They handle pricing, ride planning and ride execution, and are critical to the overall user experience.
Layer 5
Passenger experience and content providers: these providers own middleware software platforms as service partners. Digital content (for example media), digital products (for example productivity tools), and digital services are part of this platform.
Layer 6
Infrastructure: service areas and their infrastructure are core elements enabling autonomous driving services. Infrastructure includes vehicle IT infrastructure, especially cloud services and back-end systems, V2X technologies, and considerations for human behavior prediction in specific scenarios.
United States
- Waymo: continues active, steady deployment.
- Cruise: operations have contracted following safety-related incidents.
- Aurora: high cash burn; scaling back robotaxi efforts.
- Mobileye: development stage.
- Motional (Hyundai and Aptiv): Hyundai plans further deployment.
- Zoox: limited recent public activity.
- Mobileye: development stage.
- Motional: Hyundai intends to promote deployment.
- Zoox: limited recent public activity.
Company Notes
- Waymo: Achieved L4 driving in Phoenix in 2020, operating fully driverless I-PACE and Pacifica fleets there.
- Cruise: Achieved L4 driving in San Francisco in 2022; however, operations are currently contracting following accidents.
- Aurora: High cash burn; released open autonomous driving datasets to support industry progress and is currently focusing on autonomous trucks.
- Mobileye: Testing autonomous fleets globally, including in complex traffic regions in Europe. Running pilot projects in Norway and Germany.
- Hyundai and Aptiv (Motional):
- By 2022 accumulated more than 2 million miles on public roads in Las Vegas.
- Planned to offer robotaxi services via Uber and Lyft in major U.S. cities in 2023.
- Zoox: Tested robotaxis in Las Vegas and in 2020 introduced a vehicle specifically designed for SDVs.
- Toyota: Focusing on partnerships, investments and acquisitions, for example Lyft Level 5, Momenta, Pony.ai and May Mobility.
- Perrone: Developing autonomous vehicle solutions since 2003, offering low-speed shuttles and stating retrofit kits are available for more than 30 vehicle models.
- IonQ and Hyundai: Expanding partnerships to improve quantum computing and, according to reports, jointly established Motional to develop robotaxis.
- May Mobility: Autonomous fleets have been available to the public in several cities. The SDS is designed for multiple vehicle platforms, including the Toyota Sienna Autono-MaaS autonomous vehicle.
- COAST Autonomous: Provides MaaS solutions for cities, theme parks, campuses, airports and rail yards. Positioned relatively weakly, lacking strong partners and clear future prospects.
- ADASTEC: Developing SDS for shuttle buses with a distinct value proposition, though SDS performance remains to be proven.
- AECOM: Advancing autonomous vehicle capabilities, including the AV-Readi routing tool and collaboration with ADASTEC Corp.