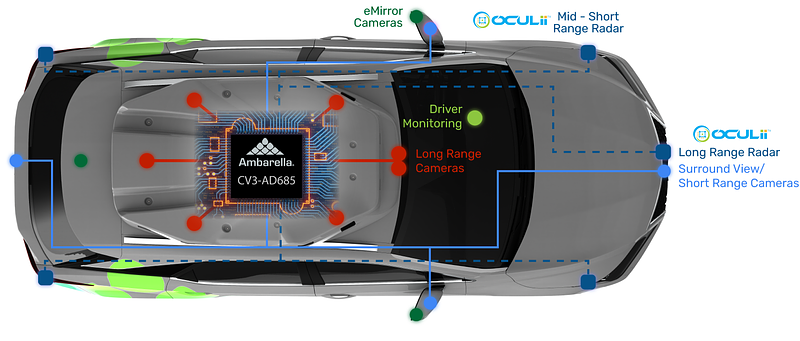
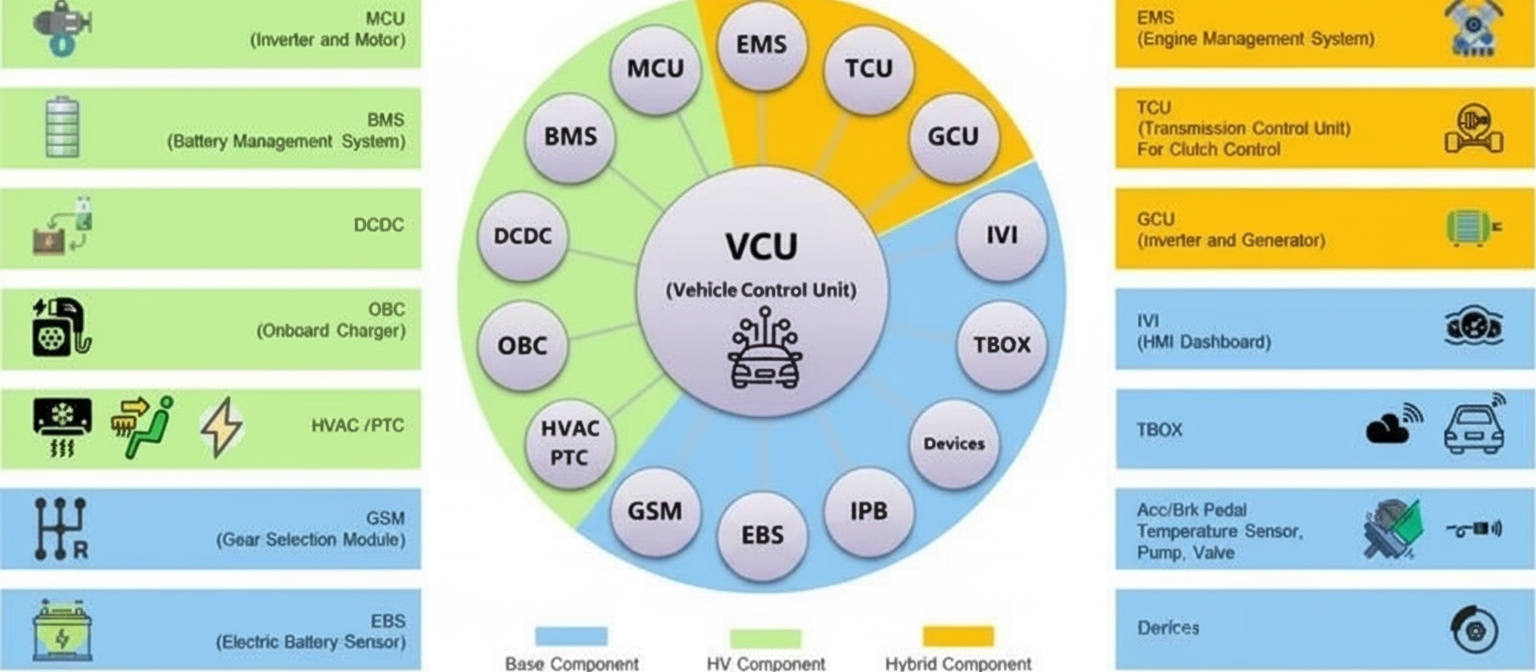
Overview
The high-voltage battery modules are placed inside a sealed and shielded high-voltage battery enclosure. The battery system connects to the vehicle via reliable high- and low-voltage connectors. Typical module installation positions are shown below.
Figure: High-voltage battery module installation position
The battery management system (BMS) continuously measures individual cell voltages, temperatures from temperature sensors, the total pack voltage and current, insulation resistance and other data. It evaluates system status against configured thresholds and performs real-time fault monitoring. The BMS communicates with the vehicle control unit (VCU) or the charger via CAN and manages charging and discharging of the high-voltage battery system.
The high-voltage battery system receives and stores high-voltage DC supplied by the onboard charger, the motor, regenerative braking devices and external charging equipment. It supplies high-voltage DC to the motor controller, DC/DC converter, electric air conditioning and PTC heater, among other high-voltage components.
Main Components
The high-voltage battery system mainly consists of high-voltage battery modules, the battery management system, the high-voltage battery enclosure and auxiliary components, as illustrated below.
Figure: High-voltage battery system composition (BAIC E150EV)
Individual cells are the smallest units of a battery module and are typically composed of a positive electrode, negative electrode, electrolyte and enclosure, enabling direct conversion between chemical and electrical energy. A cell group is a set of parallel-connected cells whose nominal voltage equals the nominal voltage of a single cell; it is the smallest replaceable physical and electrical grouping. A module consists of multiple cell groups or cells connected in series, forming a combined unit, as shown below.
Figure: High-voltage battery module structure (JAC EV models)
The battery enclosure supports, secures and surrounds the battery system. It typically includes an upper cover, a lower tray and various auxiliary parts such as transition pieces, skid plates and bolts. The enclosure provides structural support and protection for the battery pack and electrical components.
The battery enclosure is bolted to the vehicle floor and has an IP67 protection rating. Bolt tightening torque is specified at 80 to 100 N·m. During vehicle maintenance, inspect the enclosure bolts for looseness, check for damage or severe deformation, and verify the integrity of sealing flanges to ensure normal operation of the high-voltage battery. Externally, the enclosure is typically matte silver-gray or black. The surface must be free of scratches, sharp edges, burrs and residual oil; welded areas must be smoothed.
Auxiliary components for battery modules mainly include the electrical parts inside the high-voltage battery system, such as fuses, relays, shunts, connectors, service switches and smoke sensors, as well as sealing strips and insulating materials.
Figure: High-voltage battery module internal auxiliary components
High-Voltage Battery Management System
The battery management system, or Battery Management System (BMS), is the core component for battery protection and management. A BMS module example is shown below.
Figure: BMS module (BAIC E150EV)
1. Role of the BMS
The BMS is the central controller for battery protection and management. It ensures safe and reliable battery operation, optimizes battery performance and extends service life. Acting as the communication bridge between the battery and the vehicle controller (VCU) and the driver, the BMS controls contactors to manage pack charging and discharging and reports key battery parameters and fault information to the VCU.
2. BMS Functions
The BMS implements overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, overtemperature and undertemperature protection through voltage, current and temperature monitoring. It controls relays, estimates state of charge (SOC), manages charge and discharge, performs cell balancing, generates alarms and handles faults, and communicates with other controllers. Additionally, the BMS performs insulation monitoring of the high-voltage circuit and can provide heating for the battery system.
3. BMS Composition
The BMS can be categorized by nature into hardware and software, and by function into a data acquisition unit and a control unit.
4. BMS Hardware
Typical hardware components include the main board, slave boards and the high-voltage module, along with electronic devices for sensing voltage, current and temperature.
5. BMS Software
The software monitors cell voltages, current, SOC, insulation resistance and temperatures, and controls charging and discharging of the high-voltage battery system through communication with the VCU and the charger.