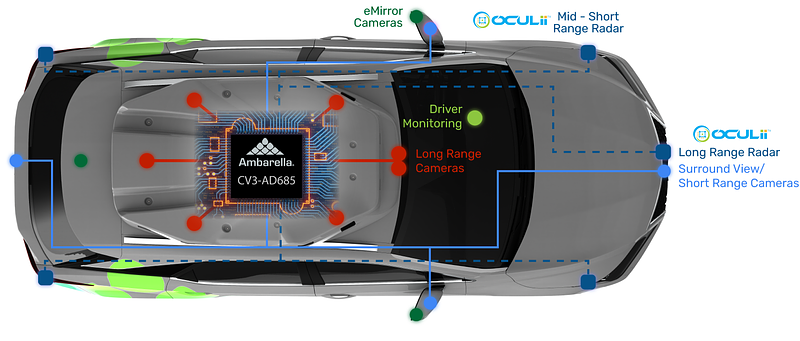
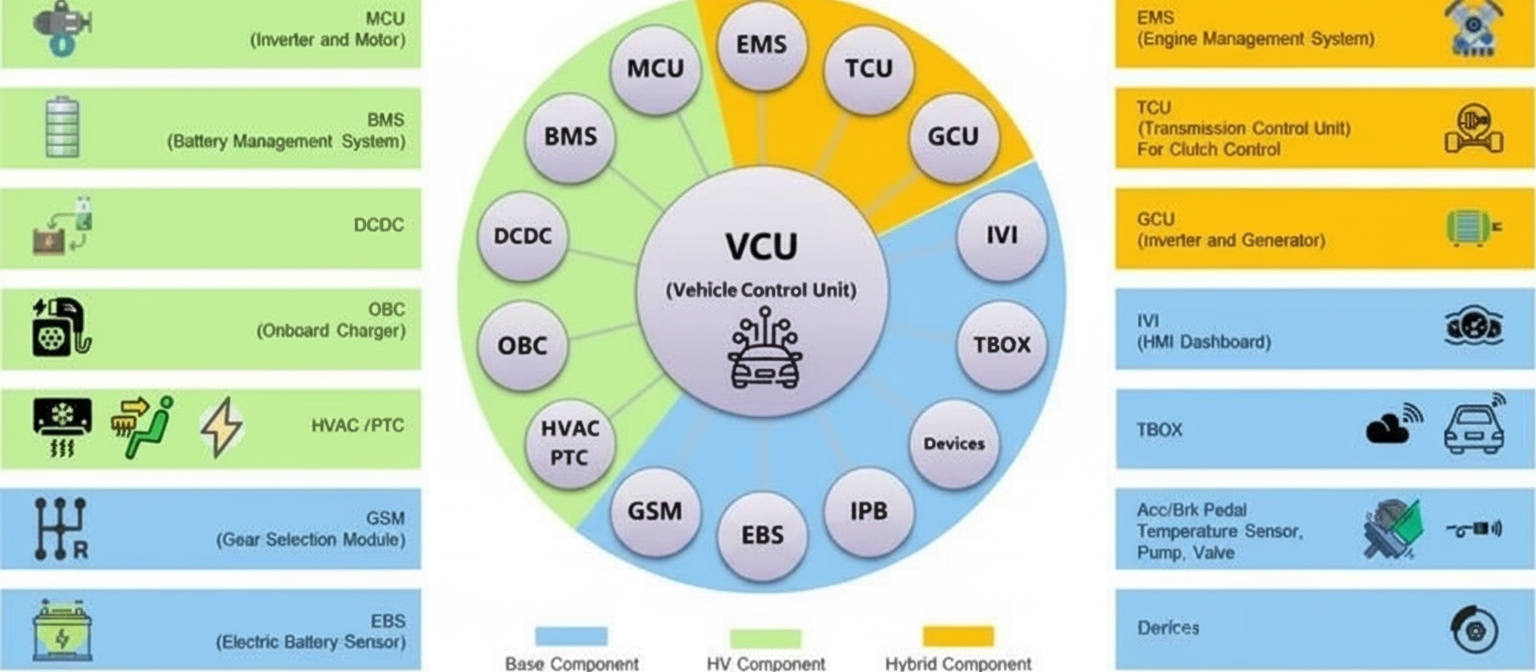
Overview
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are one approach to saving fuel, reducing CO2 and other harmful emissions, while improving driving enjoyment and ride comfort. HEVs combine an internal combustion engine with at least one electric motor for propulsion. A variety of configurations exist that follow different optimization strategies and different degrees of electric propulsion.
Principles
HEV designs generally pursue three objectives: fuel savings, emissions reduction, and improved torque and power output for better driving feel. Different hybrid architectures emphasize different objectives. Broadly, HEVs are classified as mild hybrids or full hybrids; some architectures also support pure electric driving.
Mild hybrids use an electric motor to assist the internal combustion engine, providing additional drive power and braking power in different operating states. Full hybrids combine an internal combustion engine with one or more electric motors so the vehicle can be driven by the engine, assisted by the motor, or driven in pure electric mode.
Both mild-hybrid and full-hybrid systems typically include a start/stop capability similar to conventional automatic start/stop systems. For example, the engine can be switched off when stopped at a traffic light to avoid idling and save fuel. Conventional vehicles can also use automatic start/stop systems; that feature is not exclusive to hybrid architectures.
Both mild-hybrid and full-hybrid drivetrains require a battery to supply the electric motor. Typically, a relatively high-voltage traction battery is used as the energy storage device. Compared with conventional drivetrains, the combination of electric motor and engine in mild and full hybrids offers the following advantages:
- Electric motors provide sustained high torque at low speeds. This complements the internal combustion engine, whose torque typically increases only from mid-range speeds. Together, the motor and engine can deliver strong drive performance across all driving conditions.
- Motor assistance allows the internal combustion engine to operate within its optimal efficiency range or in an operating region with lower pollutant emissions, enabling operating-point optimization.
- The combination with an electric motor can allow use of a smaller internal combustion engine for the same total vehicle power, reducing overall engine size.
- Combining an engine with an electric motor can permit use of a transmission with a larger overall reduction ratio while maintaining the same total output, which can improve efficiency and drivability.
Regenerative Braking
Another method for saving fuel is recovery of braking energy. When the electric motor operates in generator mode (or when an auxiliary generator is used), part of the vehicle's kinetic energy is converted into electrical energy during braking. The recovered energy is stored in the energy storage device and can be reused for propulsion.