1. Overview
1. Ethernet open communication means the communication protocol is defined by the user.
2. It is a software communication protocol based on the TCP or UDP transport layer.
3. PLCs can use Ethernet open communication to exchange data with other PLCs or third-party devices.
4. Each PLC requires separate programming to implement Ethernet open communication.
2. Main instructions by PLC brand
Different PLC brands use different names and instructions for Ethernet open communication:
- Rockwell Micro800 series: referred to as socket communication; sending data typically uses the SOCKET_WRITE instruction.
- Siemens S7-1200 series: referred to as Ethernet open communication; sending data typically uses the TSEND instruction.
- Siemens S7-200 Smart series: referred to as Ethernet open communication; sending data typically uses the TSEND instruction.
- Schneider M241/M251/M258 series: referred to as socket communication; sending data typically uses instructions such as TCP_Client_Send and TCP_Server_Send.
- Mitsubishi FX5U/FX5UCFX5UJ/FX5S series: referred to as socket communication; sending data typically uses the SP.SOCSEND instruction.
- Omron CP1H/CP1L/CP2E series: referred to as socket communication; sending data is typically implemented by writing data into special register areas and enabling special bits.
- Panasonic FPXH/FP0H series: referred to as general communication; sending data typically uses the MTRN and UNITSEL instructions.
- Delta DVP-ES3 series: referred to as socket communication; sending data typically uses the SSEND instruction.
3. Standardizing send-data programming across PLC brands
Different PLC brands use different instructions and programming methods for Ethernet open communication. To simplify use, the open communication implementations can be encapsulated into function blocks or instruction libraries that expose the same input and output parameters. This standardization makes it easier and faster to use PLC Ethernet open communication across multiple brands.
4. Client connection function block parameters
The packaged send-data function blocks for various PLC brands follow a common parameter structure. Example images of the function blocks are shown below.
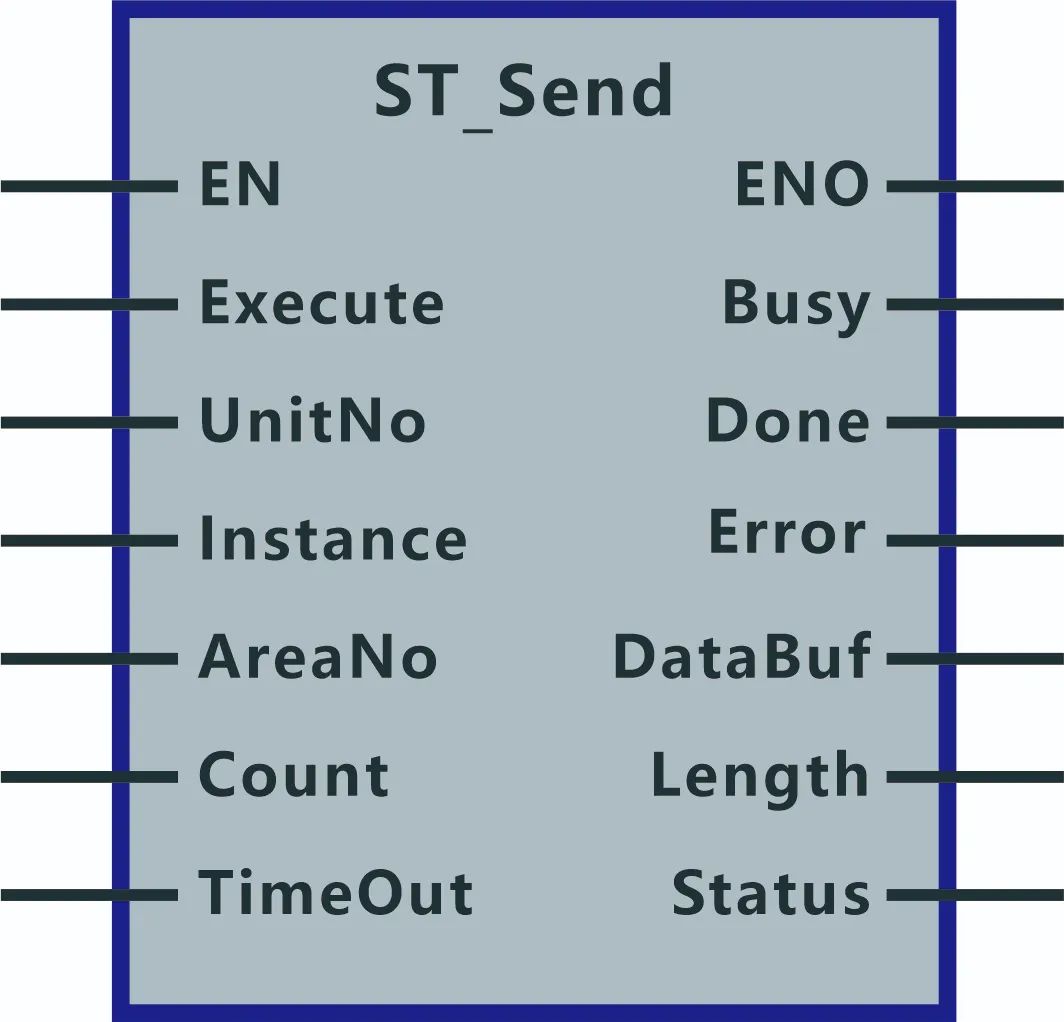
1. Input parameters:
- EN: Function block enable input. Typically enabled by a logic-true signal.
- Execute: Command switch. When 1, the data send operation is executed.
- UnitNo: Unit selection. Enter hex values such as FFF0, FFF1, FFF2 to select different PLC models.
- Instance: Socket handle, provided by the connection function block output.
- AreaNo: Start address of the send buffer, used to set the send buffer.
- Count: Preset number of bytes to send.
- TimeOut: Send timeout, in units of 100 ms.
2. Output parameters:
- ENO: Function block output indicator.
- Busy: Busy flag. 1 indicates sending is in progress; 0 indicates sending is not in progress.
- Done: Completion flag. 1 indicates data was sent successfully.
- Error: Error flag. 1 indicates an error occurred during sending.
- DataBuf: Start address of the temporary send buffer.
- Length: Actual number of bytes sent.
- Status: Error code for send operation.