Overview
With rapid advances in technology, human-machine interaction methods continue to evolve. After keyboards and touchscreens, voice recognition is increasingly used for interaction. Voice recognition can be implemented as online or offline processing. Unlike online voice recognition, which depends on network connectivity, offline voice recognition runs entirely locally without servers, offering lower cost and lower power consumption. This article describes an offline voice recognition solution based on a PT32Z192 Cortex-M3 MCU platform. The solution targets high recognition sensitivity, low cost, and convenient deployment. Recognition distance: up to 10 meters in a quiet environment.
1. MCU resources
Model: PT32Z192, Cortex-M3 core
Core frequency: 160 MHz
Flash: 512 KB, RAM: 128 KB
ADC: 12-bit high-precision ADC, maximum conversion rate 1 Msps
Advanced timers: configurable for up to 4 complementary PWM outputs
UART: 2 serial ports
I2C/SPI: available
Packages: QFN32 / LQFP64
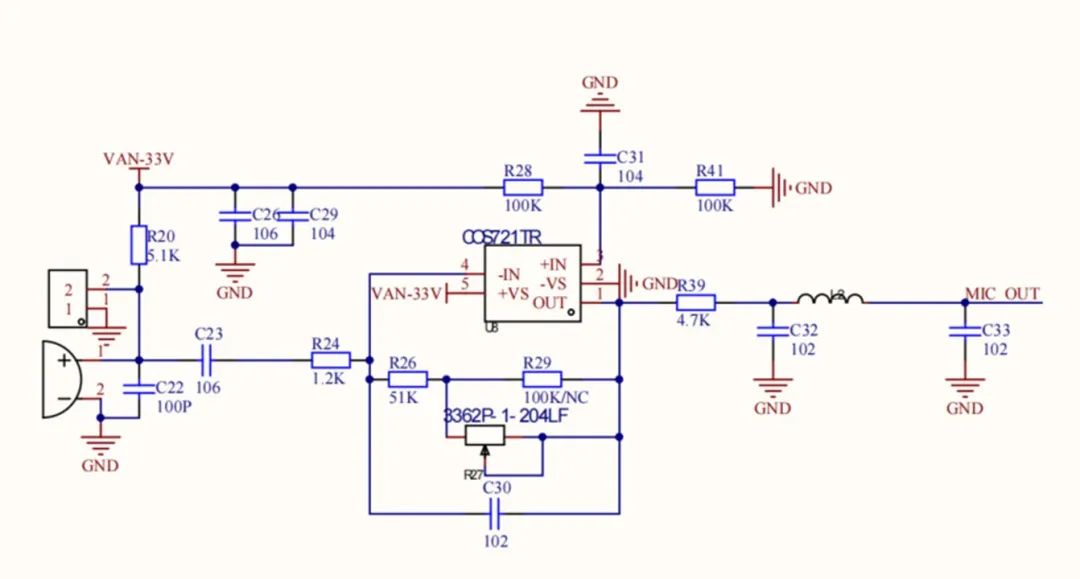
2. Microphone
A high-sensitivity microphone was selected, 30 dB or higher.
3. Display
A 2.8-inch TFT display is used with a 3-wire SPI interface. The LVGL graphics library was ported for UI interaction.
4. Communication interfaces
Two UART ports are reserved to support application expansion, for example connecting Bluetooth, NB-IoT, Zigbee, or other wireless modules.
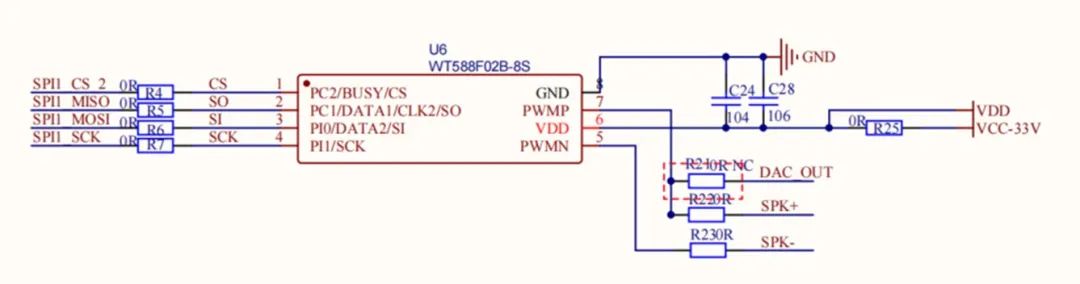
5. Voice playback
Two playback schemes are supported: a dedicated voice playback chip and a PWM-based playback solution.
1) Dedicated voice playback chip: Voice data is stored inside the voice chip, which can be customized or generated and programmed using vendor tools. The voice chip output is connected to a power amplifier (optional, for driving higher-power speakers) and a speaker. The MCU controls the voice chip via a serial interface. This approach simplifies control and software development because the main task is to implement the voice chip communication protocol.
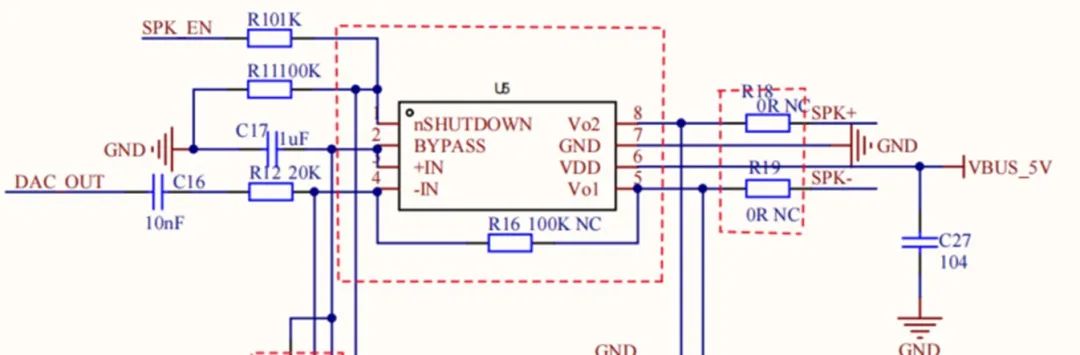
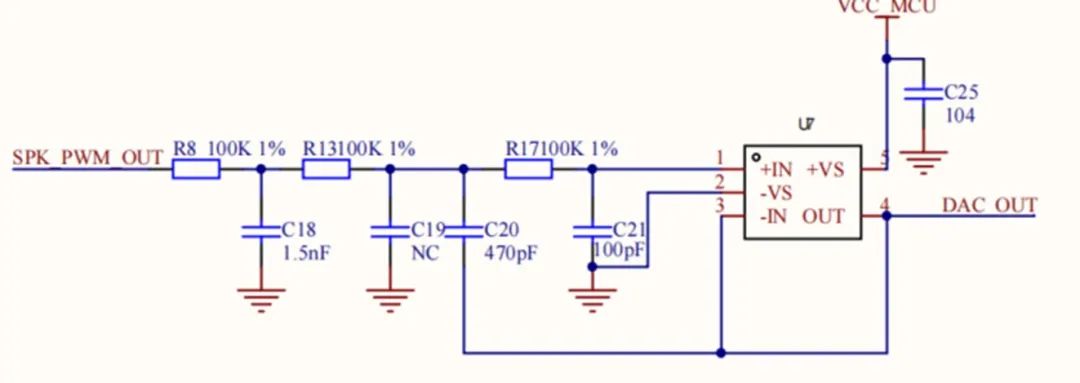
2) PWM voice playback: The MCU outputs recorded voice data via PWM. Large voice data can be stored in NOR flash. After power amplification, the signal drives a speaker. If no dedicated voice chip is used and playback volume requirements are modest, a PWM + power amp + NOR flash solution can replace a dedicated voice chip. This may reduce BOM cost depending on the application, but software processing is more complex and audio quality is not guaranteed without additional tuning and optimization.
6. AI voice recognition algorithm library
The MCU vendor provides a voice recognition algorithm library and reference demo applications. The interfaces are straightforward. Developers can retain the existing voice recognition framework in the demo and add their own application code to implement specific functionality.
Schematics
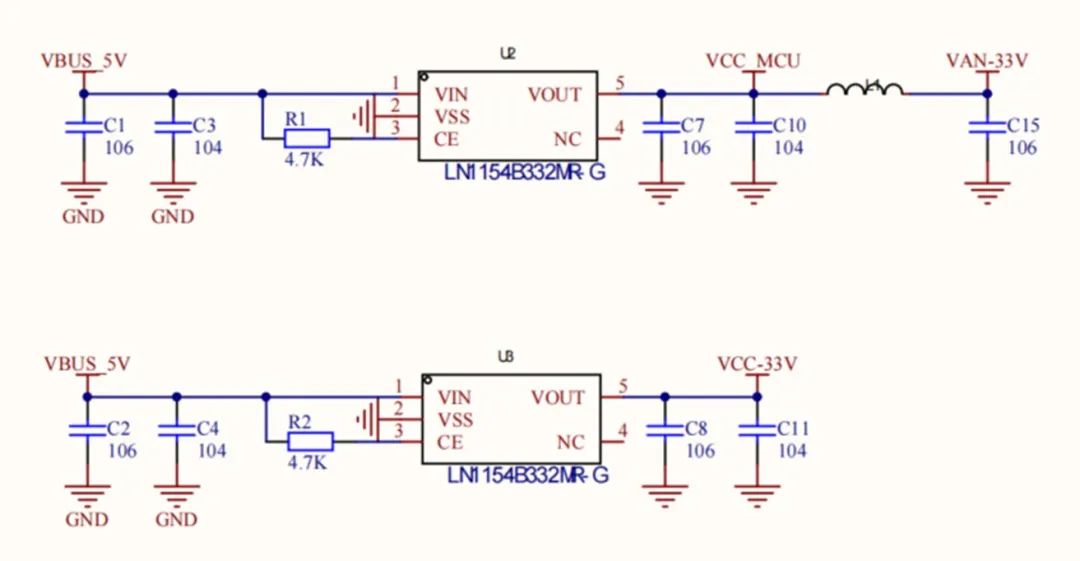
Power supply section
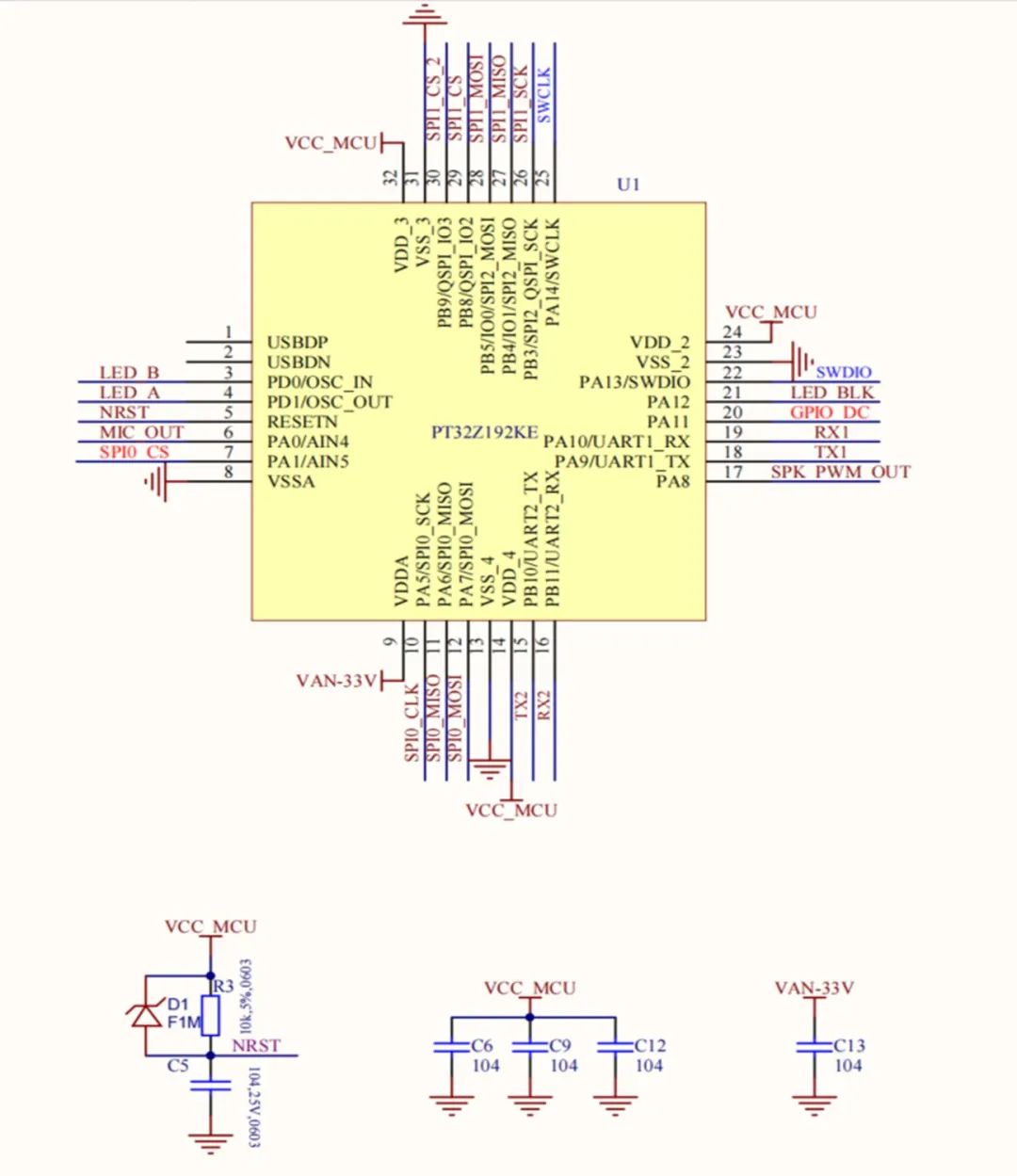
MCU main control section
Microphone circuit
Voice playback chip circuit
Power amplifier circuit
PWM voice playback circuit
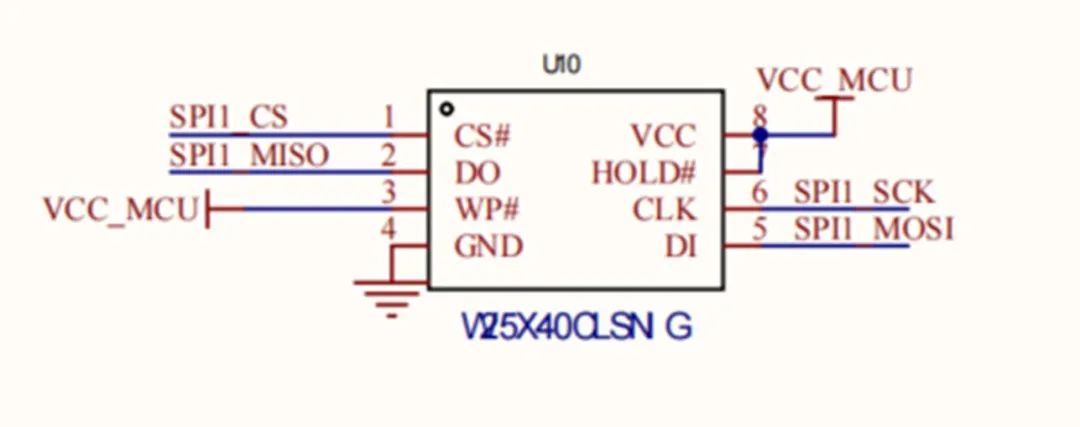
NOR flash circuit
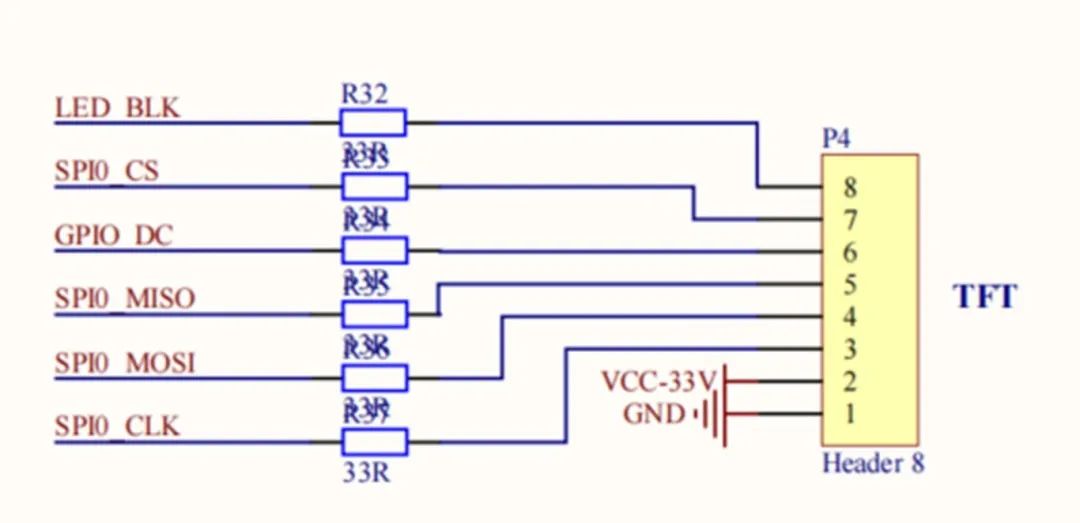
TFT display interface
Applications
This solution can be applied to various voice-controlled applications such as voice-controlled lights, voice fans, and automated curtains.
Voice recognition is increasingly integrated into smart home, automotive navigation, customer service, and voice assistant scenarios. As the technology matures, voice recognition will expand into more application areas and enable more convenient interaction models.