What is PCB Panelization and Why is it Important?
PCB panelization refers to the strategic arrangement of multiple individual printed circuit boards onto a single, larger manufacturing panel. This process is fundamental in modern electronics production, significantly enhancing efficiency, controlling PCB board cost, and maintaining consistent product quality during mass fabrication. By consolidating several boards into one panel, manufacturers can streamline automated assembly processes, simplify material handling, and ultimately reduce overall production expenditures. Following the assembly phase, these grouped boards undergo a separation process, known as depanelization, which is performed using mechanical methods tailored to the specific panelization technique initially chosen.
Related Reading: Depanelization Techniques: Stamp Holes vs. V-Scoring for PCBs
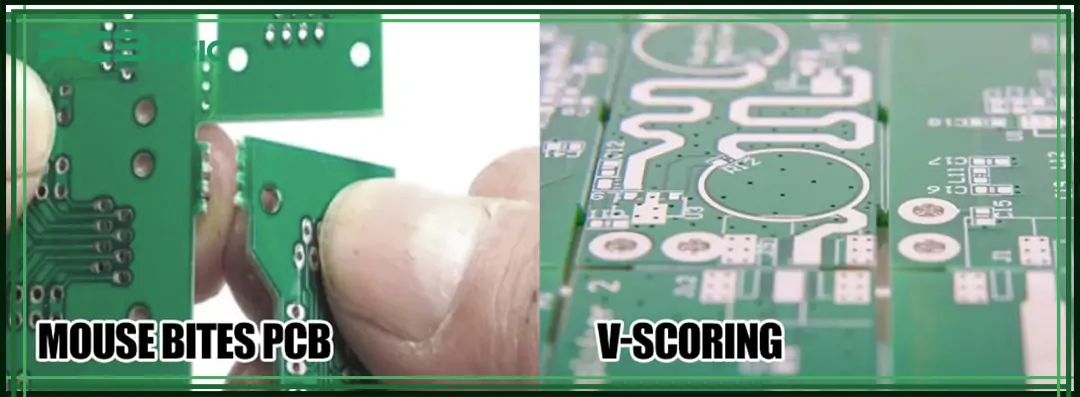
How Does V-Cut (V-Scoring) Work in PCB Manufacturing?
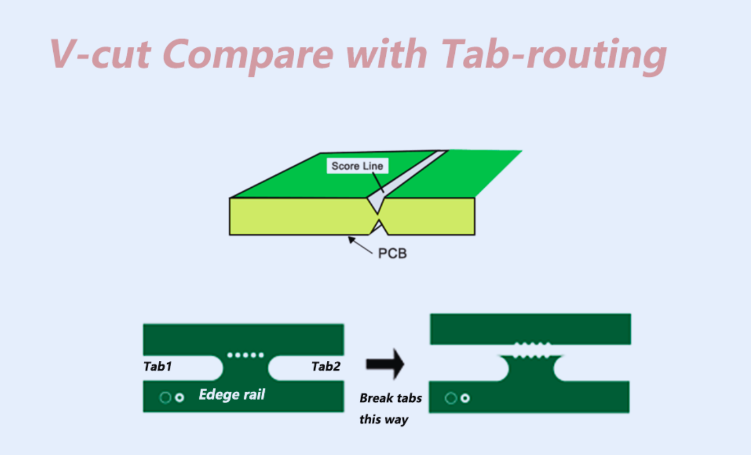
V-Cut, also widely known as V-Scoring, is a common panelization technique where V-shaped grooves are precisely cut along both the top and bottom surfaces of a PCB panel. These grooves are strategically placed to leave a very thin, consistent layer of board material in the middle. These scored lines function as predetermined break points, allowing for straightforward and clean separation of individual circuit boards once assembly is complete. The cuts are typically linear, running either vertically or horizontally across the panel, and the boards are separated by applying uniform pressure along these score lines.
Advantages of V-Cut Panelization
● Optimized Panel Density: V-Cut methods do not require additional space for connecting tabs between boards, which allows for closer placement of individual PCBs. This maximizes the utilization of the available panel area, leading to more boards per panel.
● Cost-Effectiveness: This technique is generally more economical due to its simpler tooling requirements and the faster processing times involved in creating the V-grooves.
● Rapid Depanelization: Boards can be separated very quickly and efficiently, requiring minimal mechanical force. This speeds up the post-assembly process significantly.
● Suitability for Straight Edges: V-Cut is ideally suited for boards with simple, rectilinear shapes such as rectangles or squares that have exclusively straight edges.
Limitations of V-Cut Panelization
● Design Constraints: V-Cut is strictly limited to straight-line separations, making it unsuitable for boards with irregular, curved, or complex outlines.
● Potential for Mechanical Stress: The act of breaking boards along V-score lines can introduce mechanical stress to the board edges. This poses a risk of damaging sensitive electronic components located too close to the separation path.
● Edge Quality Concerns: The resulting break lines may exhibit slight roughness or unevenness. For applications where aesthetics or a perfectly smooth edge finish is critical, additional post-processing might be necessary.
Related Reading: Optimizing Breakaway Tabs: Minimizing Stress in PCB Depanelization
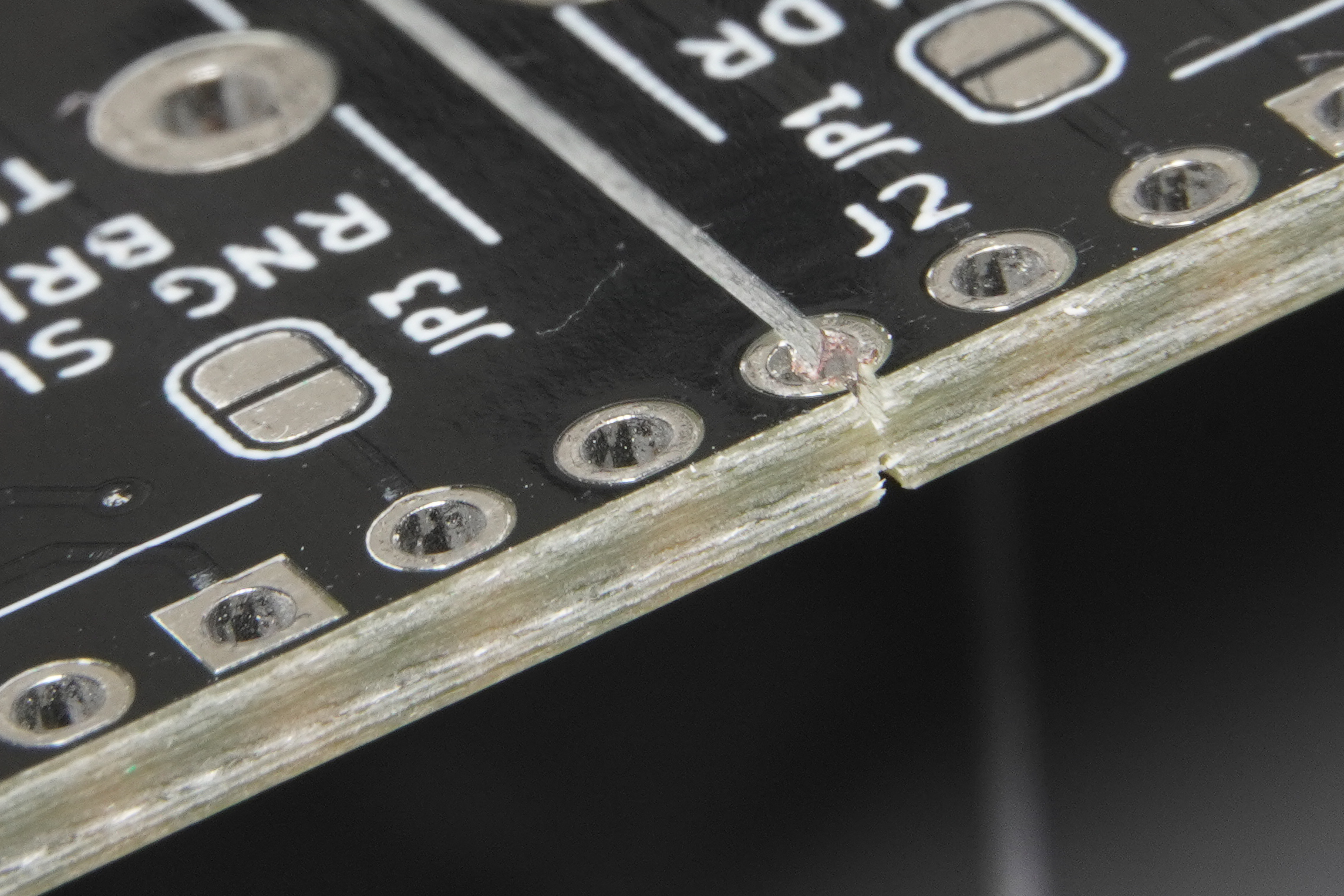
What is Tab-Routing in PCB Panelization?
Tab-Routing is a panelization method that involves creating small, narrow connecting tabs between individual PCBs within a larger panel. These tabs often incorporate perforated holes, commonly referred to as "mouse bites," which are designed to facilitate an easier and cleaner separation process. During manufacturing, a routing bit precisely cuts around the complete outline of each individual PCB, with these strategically placed tabs acting as temporary anchors to hold the boards securely within the panel until they are ready for final depanelization.
Advantages of Tab-Routing Panelization
● Flexibility for Complex Shapes: Tab-Routing is exceptionally versatile, accommodating non-rectangular, circular, and other highly irregular PCB outlines that cannot be separated by straight cuts.
● Reduced Mechanical Stress: This method generally provides a more controlled and cleaner break during depanelization, significantly reducing the risk of stress-induced damage to sensitive components or the board itself.
● Superior Edge Quality: The edges of the separated boards are typically smoother and cleaner, making Tab-Routing the preferred choice for high-precision applications or designs where an aesthetic finish is paramount.
Limitations of Tab-Routing Panelization
● Less Efficient Panel Utilization: The required routing paths and the physical presence of the tabs necessitate additional clearance space between individual boards, which reduces the overall density of PCBs that can be fitted onto a single panel.
● Increased Manufacturing Costs: Tab-Routing involves more complex tooling and longer machine routing times compared to V-Cutting, which inherently increases the custom PCB production cost.
● Slower Depanelization Process: Separating boards connected by tabs typically requires more time and can involve specialized manual or semi-automated tools, such as depaneling routers or punching machines, making the process slower than V-Cut separation.
Related Reading: Understanding Mouse Bites: A Key to Efficient PCB Manufacturing
How to Choose the Optimal Panelization Method
The decision between V-Cut and Tab-Routing hinges on a careful evaluation of your project's specific mechanical, aesthetic, and financial requirements. Each method offers distinct advantages that cater to different design and production goals.
Key Decision Factors
● Board Geometry: Opt for V-Cut if your design features simple, straight-edged boards. Choose Tab-Routing for complex, irregular, or non-linear board outlines.
● Component Proximity: With V-Cut, avoid placing components too close to the score lines due to potential stress during breaking. Tab-Routing offers better protection for densely populated PCBs.
● Production Volume: For high-volume manufacturing, V-Cut is often preferred due to its inherent speed and cost-efficiency.
● Required Edge Finish: If the smoothness and aesthetic quality of the board edges are critical, Tab-Routing generally delivers a superior finish.
● Panel Space Utilization Efficiency: When maximizing the number of boards on a panel is a primary concern, V-Cut provides superior panel utilization due to its minimal space requirements between individual units.
Exploring a Hybrid Panelization Approach
In certain advanced manufacturing scenarios, a hybrid panelization strategy may be employed. This approach combines the strengths of both V-Cut and Tab-Routing techniques to achieve an optimized balance. For instance, straight sections of a PCB panel might utilize V-Cut for efficiency, while intricate or curved areas are supported by Tab-Routing to maintain shape integrity and edge quality. This blended strategy offers a flexible solution, providing a balance among production cost, desired edge quality, and the geometric complexities of the board design.
Final Considerations for PCB Panelization
Both V-Cut and Tab-Routing stand as robust and reliable techniques for PCB panelization, each possessing its own set of strengths and weaknesses. A clear understanding of your product’s specific mechanical, aesthetic, and financial requirements is paramount for selecting the most appropriate method. By fostering close collaboration with your PCB manufacturer, you can develop a panelization strategy that not only ensures a streamlined production process but also delivers high-quality final products.