Introduction
In the realm of consumer electronics, selecting the right printed circuit board material is crucial for balancing performance, cost, and reliability. Among various options, CEM-1, a composite epoxy material, stands out as a widely used choice for many applications. This material, known for its cost-effective nature, is particularly favored in devices like calculators and remote controls where high performance is not always the primary concern. Its unique properties make it suitable for single-layer boards in less demanding environments, ensuring functionality without inflating production costs. For electric engineers, understanding the advantages of CEM-1 consumer electronics applications provides insight into optimizing designs for both efficiency and economy. This article explores the technical aspects of CEM-1, its benefits, and why it remains a popular pick in specific consumer electronic products.
What Is CEM-1 and Why It Matters
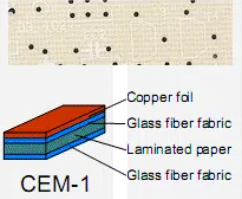
CEM-1, or Composite Epoxy Material-1, is a laminate used in the fabrication of printed circuit boards. It consists of a paper core impregnated with epoxy resin, often reinforced with woven glass fabric on the surface. This construction offers a blend of mechanical strength and electrical insulation at a lower cost compared to higher-grade materials like FR-4. In the electronics industry, CEM-1 is primarily utilized for single-sided PCBs due to its limitations in thermal and mechanical performance under extreme conditions.
The significance of CEM-1 lies in its ability to meet the needs of cost-sensitive projects. For electric engineers working on consumer electronics, selecting a cost-effective PCB material like CEM-1 can significantly reduce overall expenses without compromising essential functionality. Its relevance is most apparent in mass-produced items where budget constraints are a priority over advanced performance requirements. Understanding its properties helps engineers make informed decisions for applications such as remote controls and calculators, where reliability of CEM-1 PCBs is sufficient for the intended use.
Technical Properties of CEM-1 Material
CEM-1 material exhibits specific characteristics that define its suitability for consumer electronics. It offers adequate dielectric strength for low-voltage applications, ensuring stable electrical performance in simple circuits. The material also provides reasonable mechanical durability for single-layer designs, though it falls short in multi-layer configurations due to its lower thermal resistance and strength compared to alternatives.
From a standards perspective, CEM-1 complies with industry benchmarks for basic PCB manufacturing. According to IPC-6012E, which outlines performance specifications for rigid printed boards, materials like CEM-1 must meet minimum requirements for dielectric breakdown and dimensional stability under specified conditions. Its thermal performance is limited, making it unsuitable for high-temperature environments, but it performs well within the typical operating range of consumer devices.
Moisture absorption is another consideration. CEM-1 has a higher tendency to absorb moisture compared to glass-epoxy laminates, which can affect long-term reliability in humid conditions. However, for indoor applications like remote controls CEM-1 PCBs offer acceptable performance. Engineers must evaluate these properties to ensure the material aligns with the environmental and operational demands of their designs.
Advantages of CEM-1 in Consumer Electronics
CEM-1 holds several advantages that make it a preferred choice for specific consumer electronics applications. These benefits cater directly to the needs of electric engineers designing products with tight budget constraints and moderate performance requirements.
Cost Efficiency
One of the primary CEM-1 advantages in calculators and other low-cost devices is its affordability. The use of a paper-based core reduces material expenses compared to glass-reinforced alternatives. This cost-effective PCB material allows manufacturers to produce large volumes of electronics at a lower price point, which is critical for competitive markets.
Adequate Performance for Simple Circuits
CEM-1 provides sufficient electrical insulation and mechanical stability for single-sided boards used in basic devices. Its dielectric properties support the operation of low-power circuits found in remote controls CEM-1 PCBs, ensuring reliable signal transmission without the need for advanced materials.
Ease of Manufacturing
The material’s composition simplifies the fabrication process for single-layer designs. It can be easily punched or drilled, reducing production complexity and time. This characteristic aligns with standards like IPC-A-600K, which defines acceptability criteria for printed boards, ensuring that CEM-1 meets basic manufacturing quality benchmarks.
Lightweight Construction
CEM-1’s lightweight nature is beneficial for portable consumer electronics. Devices such as handheld calculators benefit from reduced weight, improving user comfort without sacrificing essential functionality. This aspect enhances the practicality of using CEM-1 in everyday products.
Applications of CEM-1 in Consumer Electronics
CEM-1 consumer electronics applications are predominantly in devices where simplicity and cost take precedence over high performance. Two common examples are calculators and remote controls, both of which utilize single-layer PCBs to manage basic functions.
Calculators
In calculators, CEM-1 advantages shine through due to the minimalistic circuit requirements. These devices typically operate with low power and do not generate significant heat, making CEM-1 a suitable choice. The material supports the keypad matrix and display driver circuits effectively, ensuring the reliability of CEM-1 PCBs in prolonged use. Its cost efficiency also aligns with the need to keep production expenses low for educational and office tools.
Remote Controls
Remote controls CEM-1 PCBs are another area where this material excels. These devices rely on simple infrared or radio frequency circuits to transmit signals, requiring only basic electrical performance. CEM-1 provides the necessary insulation and structural integrity for button contacts and small components. Its ability to withstand typical indoor conditions further solidifies its position as a practical option for such applications.
Other Low-Power Devices
Beyond calculators and remote controls, CEM-1 finds use in other low-power consumer electronics such as digital clocks, small toys, and basic LED displays. These products benefit from the material’s affordability and adequate performance, allowing manufacturers to cater to budget-conscious markets without over-engineering the PCB substrate.
Limitations of CEM-1 and Design Considerations
While CEM-1 offers notable benefits, it is not without limitations. Electric engineers must consider these constraints when integrating this material into their designs to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Thermal and Mechanical Constraints
CEM-1 has lower thermal resistance and mechanical strength compared to higher-grade laminates. It is not suited for applications involving high temperatures or significant physical stress. As per IPC-6012E standards, the material’s performance under thermal cycling is limited, restricting its use to environments with stable conditions.
Moisture Sensitivity
The paper core in CEM-1 makes it more susceptible to moisture absorption. This can lead to dimensional changes or degradation over time in humid settings. Engineers should account for environmental exposure when selecting CEM-1 for a project, ensuring it aligns with the expected usage conditions.
Single-Layer Restriction
CEM-1 is generally unsuitable for multi-layer PCBs due to its structural properties. This restricts its application to simpler designs, which is why it is prevalent in consumer electronics with basic circuitry. Design layouts must accommodate this limitation by minimizing complexity.
Best Practices for Using CEM-1 in PCB Design
To maximize the reliability of CEM-1 PCBs, electric engineers can follow several best practices during the design and manufacturing phases. These guidelines ensure that the material’s strengths are leveraged while mitigating its weaknesses.
Optimize for Single-Layer Configurations
Design circuits to fit within a single-layer format, avoiding the need for complex routing or vias. This approach aligns with CEM-1’s inherent capabilities and reduces potential failure points in the board structure.
Control Environmental Exposure
Limit the use of CEM-1 to indoor or controlled environments to minimize moisture and temperature fluctuations. Protective coatings can be applied to enhance resistance to humidity, adhering to acceptability criteria outlined in IPC-A-600K.
Adhere to Manufacturing Standards
Ensure that fabrication processes comply with recognized standards such as IPC-6012E. This includes proper handling during lamination and drilling to prevent delamination or damage to the material’s core.
Test for Reliability
Conduct thorough testing under simulated operating conditions to verify the reliability of CEM-1 PCBs. This includes assessing dielectric strength and mechanical stability to confirm that the board meets design specifications.
Conclusion
CEM-1 remains a popular choice in consumer electronics due to its balance of cost and performance for specific applications. Its role as a cost-effective PCB material is evident in devices like calculators and remote controls, where simplicity and affordability are paramount. While it has limitations in thermal resistance and multi-layer suitability, the advantages of CEM-1 in calculators and similar products make it a viable option for electric engineers. By understanding its properties and adhering to best practices, designers can ensure the reliability of CEM-1 PCBs in targeted use cases. This material continues to support the production of accessible electronics, proving its enduring value in the industry.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main CEM-1 consumer electronics applications?
A1: CEM-1 is widely used in devices like calculators, remote controls, and digital clocks. Its cost efficiency and adequate performance for single-layer circuits make it ideal for these low-power applications. Electric engineers select CEM-1 to keep production costs low while ensuring basic functionality in consumer products designed for everyday use.
Q2: Why is CEM-1 considered a cost-effective PCB material?
A2: CEM-1 uses a paper-based core with epoxy resin, which lowers material costs compared to glass-reinforced laminates. This affordability allows manufacturers to produce large volumes of consumer electronics at reduced expenses. For engineers, it provides a practical solution for projects where high performance is not a primary requirement.
Q3: How does the reliability of CEM-1 PCBs hold up in remote controls?
A3: The reliability of CEM-1 PCBs in remote controls is sufficient for typical indoor use. It supports simple circuits and withstands moderate conditions without significant degradation. However, engineers must consider moisture sensitivity and limit exposure to humid environments to maintain consistent performance over time.
Q4: What are the key CEM-1 advantages in calculators?
A4: CEM-1 advantages in calculators include low cost and suitability for single-layer designs. It handles basic keypad and display circuits effectively, meeting the needs of low-power devices. Its lightweight nature also contributes to portability, making it a practical choice for educational and office tools.
References
IPC-6012E — Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
IPC-A-600K — Acceptability of Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.