Introduction
Designing an 8-layer PCB is a significant step for electronic hobbyists looking to create complex circuits with high performance. These multilayer boards offer enhanced signal integrity and space for intricate designs, but selecting electronic components for such projects can be daunting. From understanding SMD component guides to mastering resistor selection and capacitor types, each choice impacts the board’s functionality. Additionally, interpreting IC datasheets is crucial for compatibility. This guide aims to simplify the process, providing practical advice tailored for hobbyists venturing into advanced PCB design. Whether you are building a high-speed digital circuit or a compact prototype, knowing how to pick the right parts ensures reliability and efficiency in your project.
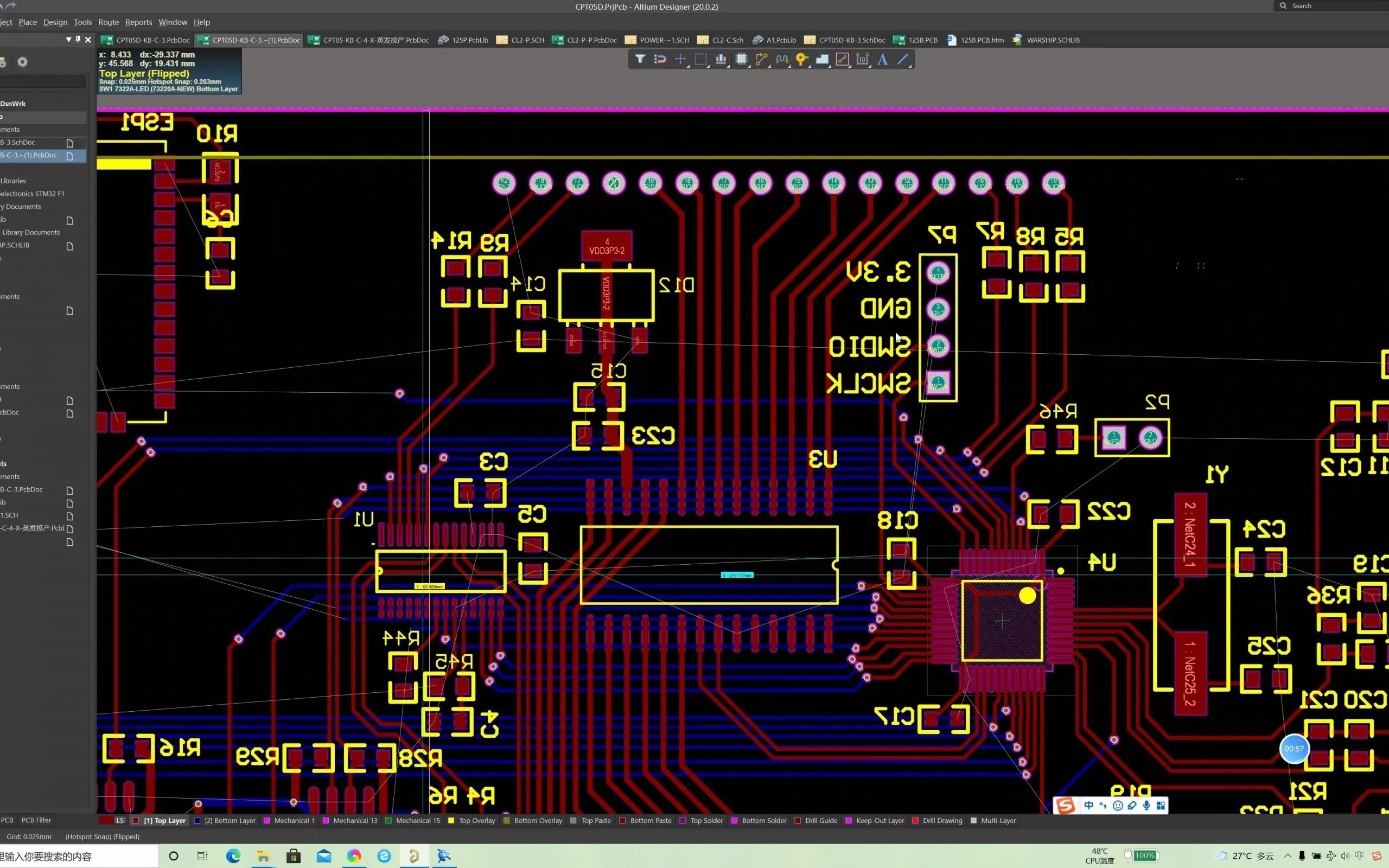
What Are 8-Layer PCBs and Why Component Selection Matters
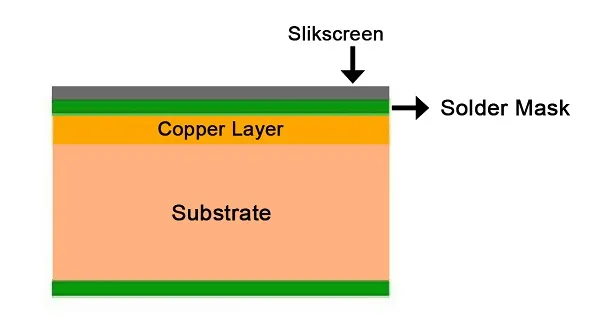
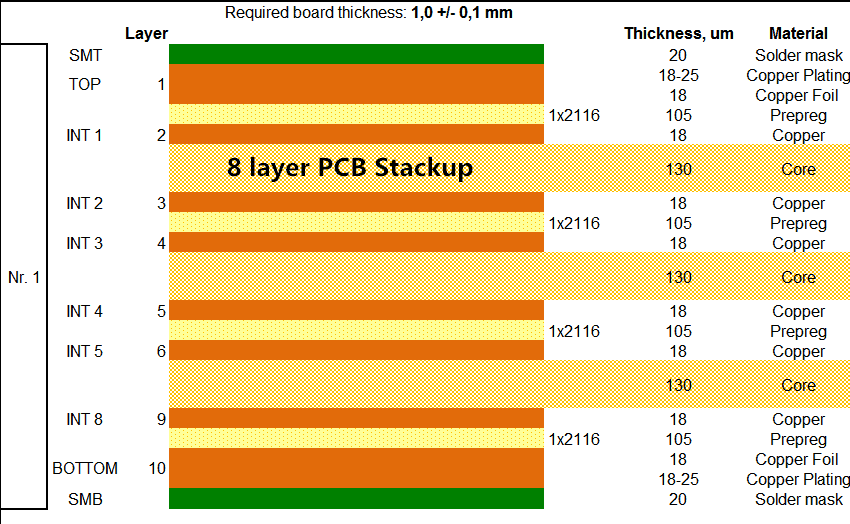
An 8-layer PCB consists of eight conductive layers stacked with insulating material between them. This structure allows for denser routing, improved power distribution, and better noise reduction compared to simpler boards. Such complexity is ideal for advanced applications like microcontrollers, RF designs, or high-speed data systems often tackled by hobbyists with growing expertise. However, the increased layer count demands precise component selection to avoid issues like signal interference or thermal stress. Choosing the wrong parts can lead to design failures, wasted time, and higher costs. Proper selection of electronic components ensures compatibility with the board’s electrical and physical constraints, making it a critical skill for successful project outcomes in multilayer designs.
Technical Principles of Component Selection for Multilayer PCBs
Understanding Electrical Requirements
Before selecting electronic components for an 8-layer PCB, hobbyists must analyze the circuit’s electrical needs. This includes voltage ratings, current demands, and frequency ranges. Components must match the power and signal requirements to prevent overheating or signal degradation. For instance, high-speed circuits require parts with low parasitic effects to maintain signal integrity across layers. Additionally, power distribution layers in an 8-layer design need components that can handle significant current without voltage drops. Always refer to circuit simulations or design specifications to guide your choices and avoid mismatches that could compromise performance.
Physical Constraints in Multilayer Designs
Physical space is a limiting factor in 8-layer PCBs due to their compact nature. Surface mount device (SMD) components are often preferred over through-hole parts because they occupy less space and suit high-density layouts. An SMD component guide can help identify package sizes like 0402 or 0603 for resistors and capacitors, ensuring they fit within the board’s footprint. Layer stacking also affects component placement, as internal layers may limit access for larger parts. Consider height restrictions and thermal dissipation needs when choosing components to avoid mechanical or heat-related failures.
Related Reading: Signal Integrity for Hobbyists: Simple Tips for Better 8 Layer PCB Designs
Signal Integrity and Noise Considerations
In an 8-layer PCB, signal integrity is paramount due to closely packed traces and multiple layers. Components must minimize electromagnetic interference and crosstalk. For high-frequency applications, select parts with low equivalent series resistance and inductance. Capacitor types, for example, play a role in decoupling noise from power lines. Choosing components with appropriate specifications reduces signal distortion and ensures reliable operation. Always prioritize parts designed for multilayer environments to maintain performance across complex routing paths.
Practical Tips for Selecting Electronic Components
Mastering Resistor Selection
Resistor selection is a foundational step in PCB design. Focus on resistance value, power rating, and tolerance when choosing resistors for an 8-layer board. For precision circuits, opt for resistors with tight tolerance values to ensure accuracy. Power rating is critical in high-current designs to prevent overheating. SMD resistors are commonly used in multilayer PCBs due to their small size. Check the operating temperature range, as multilayer boards can trap heat. Following guidelines from standards like IPC-6012E ensures resistors meet performance and reliability criteria for complex designs.
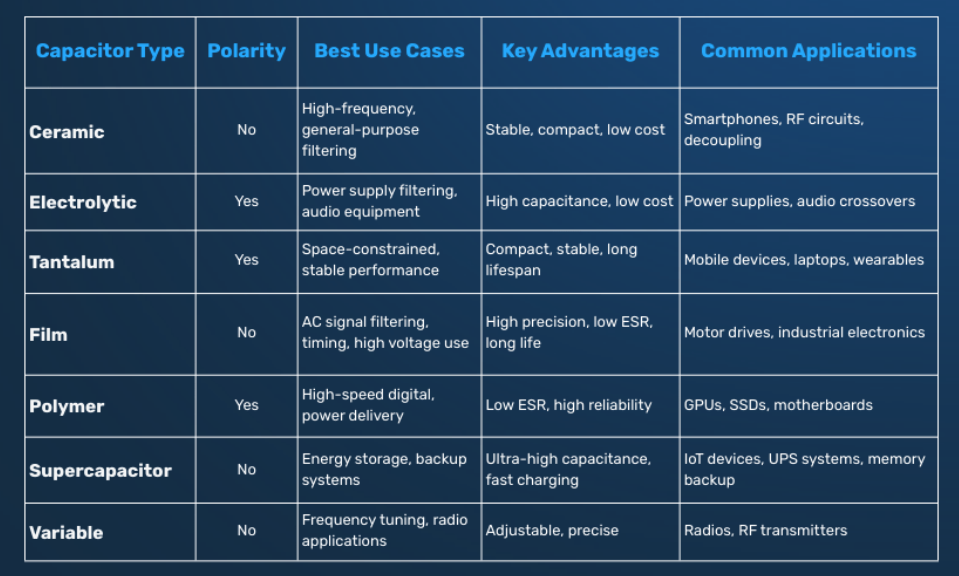
Choosing the Right Capacitor Types
Capacitors serve various roles, from decoupling to filtering, in an 8-layer PCB. Common capacitor types include ceramic, tantalum, and electrolytic, each with distinct properties. Ceramic capacitors are ideal for high-frequency decoupling due to low parasitic effects. Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance in small packages but are costlier. Electrolytic capacitors suit bulk energy storage but have limited frequency response. Match the capacitor type to the circuit’s needs, considering voltage rating and temperature stability. Standards like JEDEC J-STD-020E provide guidance on moisture sensitivity, crucial for SMD capacitors during assembly.
Navigating IC Datasheets for Compatibility
Integrated circuits (ICs) are often the heart of an 8-layer PCB project. Interpreting IC datasheets is essential to ensure compatibility with your design. Look for key parameters like supply voltage, input/output levels, and package type. Pay attention to pin configurations to match the PCB footprint. Thermal characteristics are vital, as multilayer boards may have limited heat dissipation. Datasheets also specify maximum operating frequencies, which must align with your circuit’s speed requirements. Taking time to review these details prevents costly redesigns and ensures seamless integration.
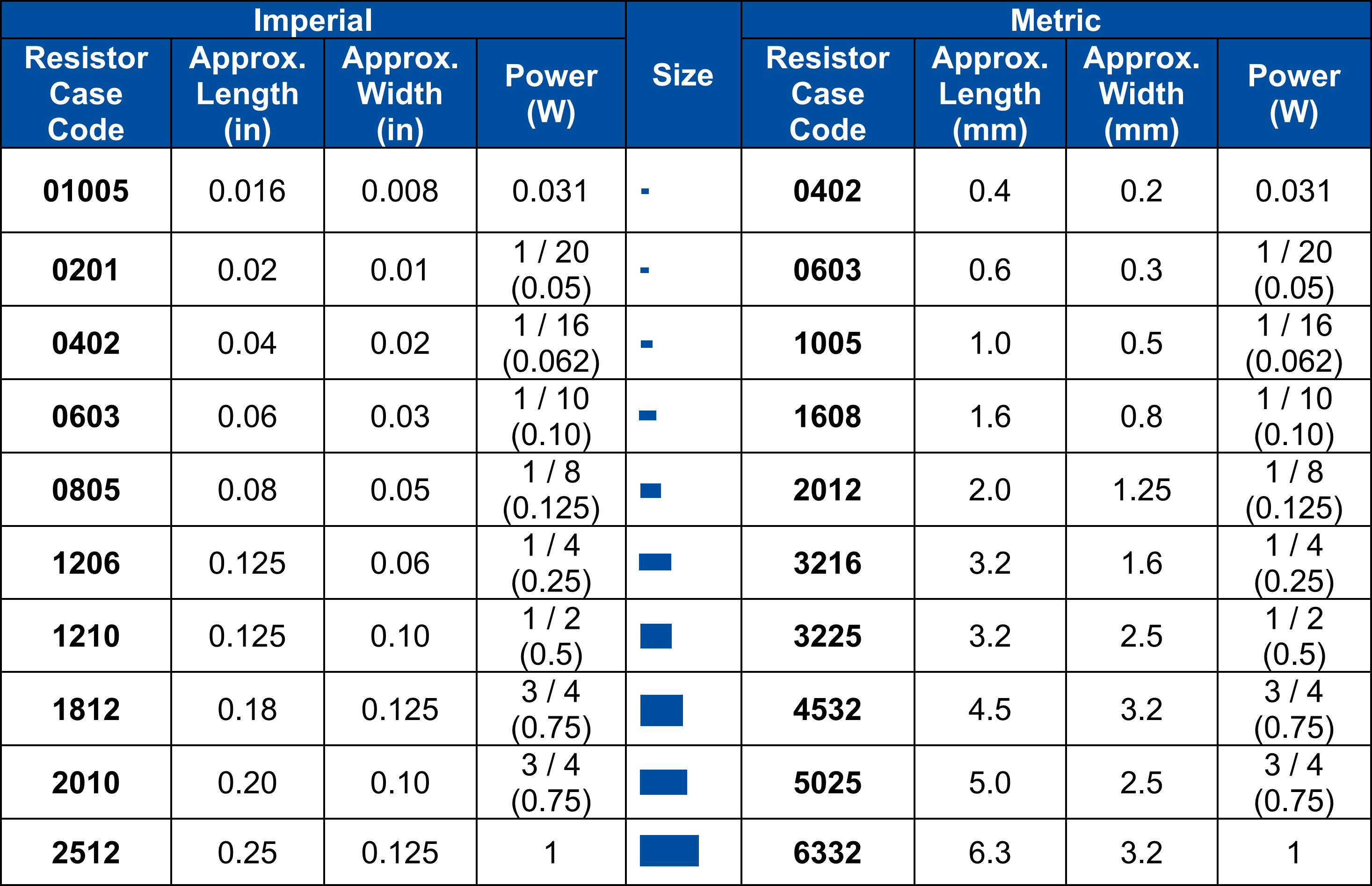
SMD Component Guide for Multilayer Boards
Surface mount devices dominate modern PCB designs due to their compact size and suitability for automation. An SMD component guide helps hobbyists understand package codes like 0805 or 1206, which indicate dimensions for resistors and capacitors. Smaller packages save space but can be harder to solder manually. Ensure the chosen SMD parts match the board’s pad sizes and layer constraints. Also, consider the reflow soldering process, as multilayer boards require precise thermal profiles to avoid damage. Standards like IPC-A-600K offer benchmarks for acceptable component placement and soldering quality.
Balancing Cost and Performance
Hobbyists often work within budget constraints, making cost a factor in component selection. While high-end parts may offer superior performance, affordable alternatives can suffice for many projects. Compare specifications to find components that meet design needs without unnecessary expense. Bulk purchasing of common values for resistors and capacitors can reduce costs. However, avoid compromising on quality for critical components like ICs or power regulators. A balanced approach ensures your 8-layer PCB performs reliably without exceeding financial limits.
Troubleshooting Common Component Issues in 8-Layer PCBs
Multilayer designs can present unique challenges during assembly and testing. One common issue is component mismatch, where parts do not meet electrical or physical requirements. Always double-check specifications before ordering to avoid delays. Thermal stress is another concern, as internal layers can trap heat, damaging sensitive components. Select parts with appropriate temperature ratings to mitigate this risk. Soldering defects, especially with SMD components, can occur due to improper heat profiles. Following assembly guidelines from standards like IPC-A-600K helps maintain quality. If issues arise, use a multimeter to test connections and verify component functionality.
Related Reading: Troubleshooting Common Issues in DIY 8 Layer PCBs
Conclusion
Selecting the right components for an 8-layer PCB project is a critical skill for electronic hobbyists aiming to build advanced circuits. By understanding electrical and physical constraints, mastering resistor selection, choosing appropriate capacitor types, and interpreting IC datasheets, you can ensure a successful design. An SMD component guide further aids in navigating the compact nature of multilayer boards. With practical tips and adherence to industry standards, hobbyists can tackle complex projects with confidence. Careful planning and attention to detail transform challenging designs into reliable, high-performing PCBs tailored to your vision.
FAQs
Q1: How do I start selecting electronic components for an 8-layer PCB as a beginner?
A1: Begin by defining your circuit’s requirements, such as voltage, current, and frequency. List the necessary components like resistors, capacitors, and ICs. Match their specifications to your design needs using datasheets. Prioritize SMD parts for space efficiency in multilayer boards. Refer to standards like IPC-6012E for performance guidelines. This structured approach ensures compatibility and reliability in your project.
Q2: What are the best capacitor types for high-frequency 8-layer PCB designs?
A2: Ceramic capacitors are often the best choice for high-frequency applications in 8-layer PCBs. They have low equivalent series resistance and inductance, making them effective for decoupling and filtering noise. Ensure the voltage rating and temperature stability suit your design. Standards like JEDEC J-STD-020E provide useful guidance on handling and selecting these components for optimal performance.
Q3: How can I use an SMD component guide to improve my PCB layout?
A3: An SMD component guide helps identify package sizes and footprints for resistors, capacitors, and other parts. Use it to select components that fit your 8-layer PCB’s pad dimensions and layer constraints. Smaller packages save space but require precise soldering. Following such a guide ensures better layout density and reduces assembly errors in compact designs.
Q4: Why are IC datasheets important for multilayer PCB projects?
A4: IC datasheets provide critical information like voltage ratings, pin configurations, and thermal limits. For 8-layer PCBs, ensuring compatibility with high-density layouts and heat constraints is vital. Datasheets help verify that the IC matches your circuit’s speed and power needs. Reviewing them prevents integration issues and supports reliable performance in complex designs.
References
IPC-6012E — Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
IPC-A-600K — Acceptability of Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
JEDEC J-STD-020E — Moisture/Reflow Sensitivity Classification. JEDEC, 2014.