Introduction
High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCBs are integral to modern electronics, especially in applications demanding high-speed data transfer and compact designs. Selecting the right materials for HDI PCBs in high-frequency applications is critical to ensure signal integrity, minimize losses, and maintain performance under demanding conditions. This article explores the essential factors in choosing HDI PCB materials for frequency-sensitive projects, focusing on dielectric properties, thermal stability, and compliance with industry standards. Aimed at electrical engineers, the content provides a structured approach to material selection for HDI high-speed designs. Whether working on telecommunications, aerospace, or advanced computing, understanding these principles will optimize your HDI project outcomes. Let's dive into the technical aspects that govern material choices for high-frequency environments.
What Are HDI PCBs and Why Material Selection Matters
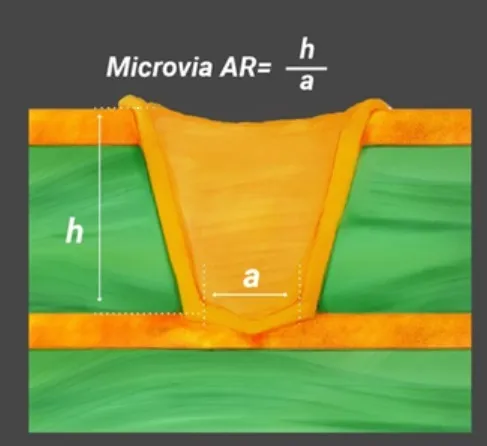
HDI PCBs are advanced circuit boards with higher wiring density per unit area compared to traditional boards. They utilize microvias, fine lines, and thin dielectric layers to achieve compactness and performance. In high-frequency applications, such as 5G networks or radar systems, these boards must handle rapid signal transitions without degradation. Material selection for HDI PCB materials frequency performance is pivotal because it directly impacts signal loss, impedance control, and thermal management.
Incorrect material choices can lead to signal attenuation, crosstalk, or board failure under high-speed conditions. For instance, materials with high dielectric constants may slow signal propagation, while those with poor thermal properties risk delamination during operation. Therefore, prioritizing materials that balance electrical, mechanical, and thermal characteristics is essential for any HDI project targeting high-frequency domains.
Technical Principles of Material Selection for High-Frequency HDI PCBs
Dielectric Constant and Loss Tangent
The dielectric constant (Dk) of a material determines how it affects the speed of signal propagation through the PCB. For high-frequency applications, a lower Dk is often preferred as it allows faster signal travel and reduces delay. Equally important is the dissipation factor (Df), or loss tangent, which indicates energy loss as heat during signal transmission. Materials with a low Df are critical for HDI high-speed designs to minimize insertion loss and maintain signal integrity.
Testing methods outlined in industry standards, such as IPC-TM-650, provide guidelines for measuring Dk and Df across specific frequencies. Engineers must select materials with stable Dk and low Df values over the operational frequency range to ensure consistent performance in an HDI project.
Thermal Stability and Glass Transition Temperature
High-frequency applications often generate significant heat due to rapid switching and power dissipation. Materials must withstand elevated temperatures without degrading. The glass transition temperature (Tg) is a key parameter, representing the point at which a material shifts from rigid to flexible. For HDI PCBs, a higher Tg ensures structural integrity during thermal cycling.
Additionally, the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) must be considered to prevent mismatches between layers, which can cause stress or cracking. Standards like IPC-4101 provide specifications for laminate materials, ensuring they meet thermal reliability requirements for high-frequency use.
Mechanical Properties and Laser Drilling Compatibility
HDI PCBs rely on microvias for interlayer connections, often created through laser drilling. Material selection must account for compatibility with this process. Some laminates are more prone to charring or uneven drilling, leading to defects. Mechanical strength is also vital to prevent board warpage or cracking during manufacturing and operation.
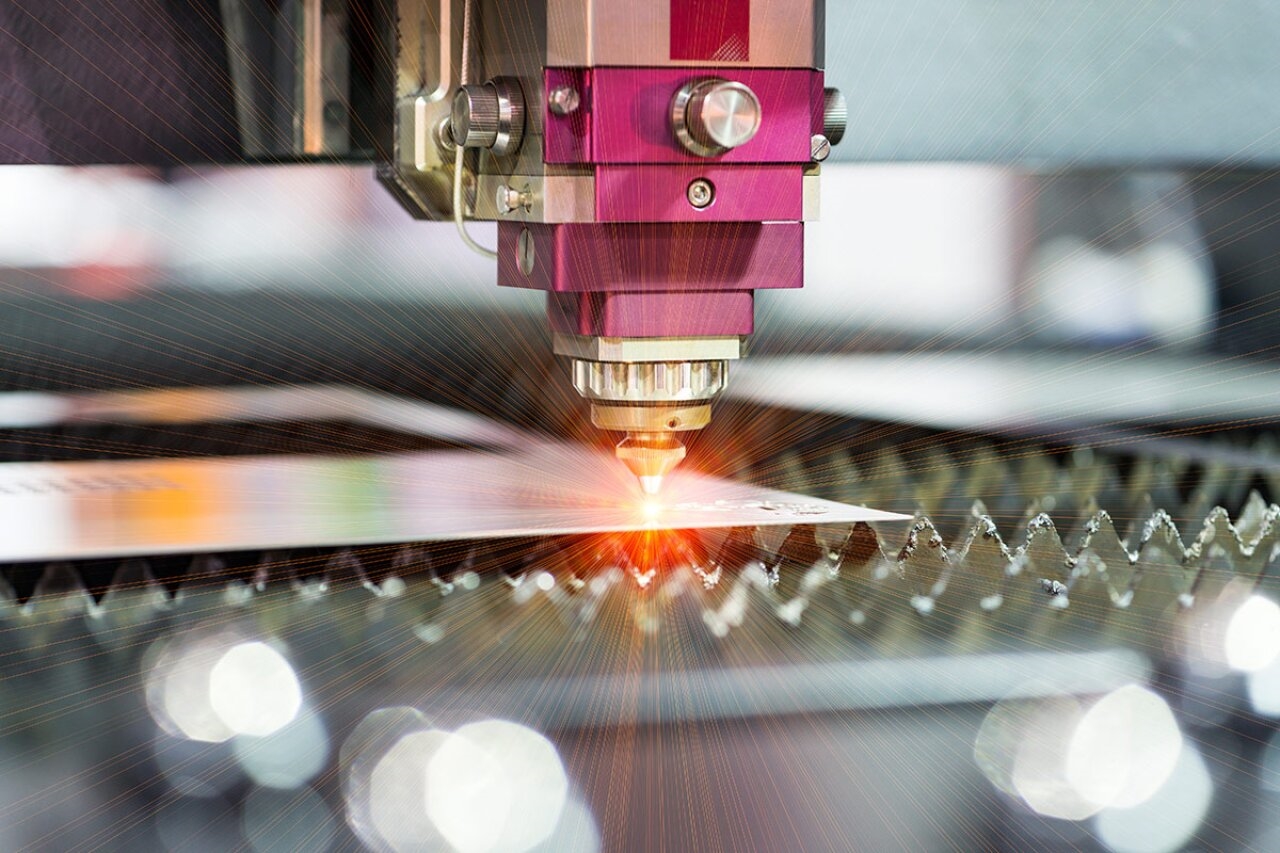

Guidelines from IPC-2226, which addresses HDI design and manufacturing, emphasize selecting materials that support fine feature formation without compromising structural integrity. This ensures reliability in high-density layouts for high-frequency applications.
Best Practices for Selecting HDI PCB Materials in High-Frequency Designs
Prioritize Low-Loss Laminates
For HDI high-speed applications, low-loss laminates are often the best choice. These materials are engineered to exhibit minimal signal loss at gigahertz frequencies. When evaluating options, refer to material datasheets for Dk and Df values tested under conditions matching your project's frequency range. Compliance with IPC-4103, which covers high-speed and high-frequency laminates, helps narrow down suitable choices.
Match Material to Frequency Range
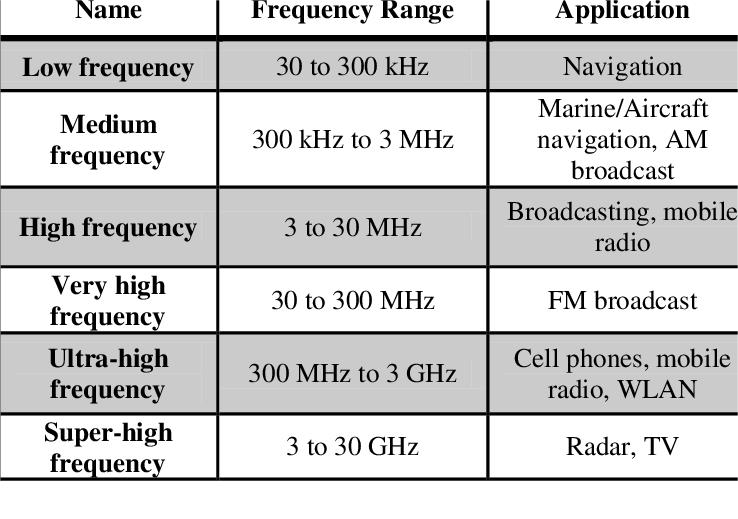
Different frequency bands impose unique demands on HDI PCB materials frequency performance. For instance, applications in the 1 to 10 GHz range, common in telecommunications, require materials with tightly controlled dielectric properties. Beyond 10 GHz, such as in automotive radar, even stricter control over loss tangent becomes necessary. Always align material specifications with the intended operational frequency to avoid performance issues.
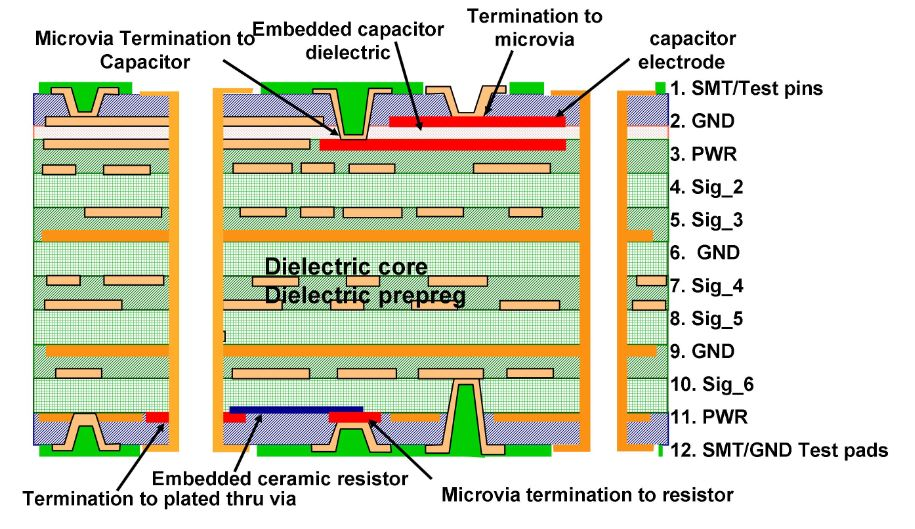
Consider Multilayer Stackup Design
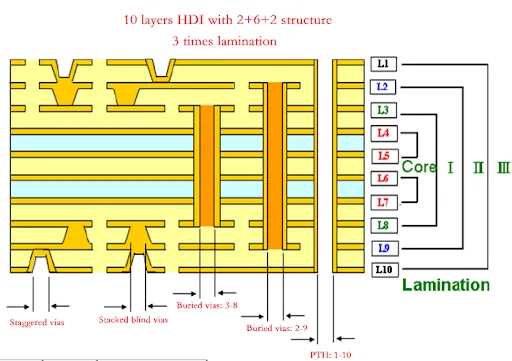
In HDI projects, multilayer stackups are common to achieve density and functionality. Material selection must ensure uniformity across layers to maintain impedance consistency. Mixing materials with differing dielectric constants can introduce signal reflection or delay. Following design rules from IPC-2226 ensures that stackup configurations support high-frequency signal paths without disruption.
Evaluate Environmental and Reliability Factors
The high-frequency PCB with HDI technology often operates in harsh environments, such as aerospace or industrial settings. Materials must resist moisture absorption, which can alter dielectric properties, and endure thermal shocks. Standards like IPC-6012E outline performance qualifications for rigid boards, including environmental testing protocols. Selecting materials that meet these criteria ensures long-term reliability.
Collaborate with Fabrication Experts
While not delving into specific entities, it's beneficial to work closely with fabrication teams during material selection. They can provide insights into process compatibility, such as lamination behavior or drilling precision. Adhering to guidelines in IPC-A-600K for board acceptability helps align material choices with manufacturing capabilities, reducing risks in HDI high-speed production.
Insight into Material Selection Challenges for HDI Projects
One common challenge in HDI projects is balancing cost with performance. High-frequency materials often come at a premium due to their specialized properties. Engineers must weigh the benefits of advanced laminates against budget constraints. A practical approach is to prioritize critical layers, such as those carrying high-speed signals, for low-loss materials while using standard laminates for less demanding sections.
Another issue is the limited availability of data for material behavior at extremely high frequencies. While standards like IPC-TM-650 offer testing methodologies, real-world performance may vary based on stackup or environmental factors. Iterative prototyping and simulation, guided by industry best practices, can help validate material choices before full-scale production.
Conclusion
Selecting materials for HDI PCBs in high-frequency applications requires a deep understanding of dielectric properties, thermal behavior, and mechanical compatibility. By focusing on low-loss laminates, aligning materials with frequency demands, and adhering to recognized standards, engineers can optimize performance in HDI high-speed designs. Challenges such as cost and data gaps can be mitigated through strategic planning and collaboration during the design phase. Ultimately, a methodical approach to HDI PCB materials frequency selection ensures signal integrity and reliability, paving the way for successful outcomes in any HDI project.
FAQs
Q1: What factors are most critical when selecting HDI PCB materials for frequency-sensitive applications?
A1: When choosing HDI PCB materials for frequency-sensitive applications, prioritize dielectric constant and loss tangent to minimize signal loss. Thermal stability, indicated by glass transition temperature, ensures durability under heat. Mechanical properties and laser drilling compatibility also matter for microvia formation. Following standards like IPC-4103 helps identify materials suited for high-frequency performance.
Q2: How does dielectric constant impact HDI high-speed PCB performance?
A2: Dielectric constant (Dk) affects signal propagation speed in HDI high-speed PCBs. A lower Dk allows faster signal travel, which is vital for high-frequency applications. Stability of Dk across frequencies prevents impedance mismatches. Testing per IPC-TM-650 ensures the material maintains consistent performance, reducing delays and signal distortion in critical designs.
Q3: What industry standards guide material selection for an HDI project?
A3: For an HDI project, key standards include IPC-2226 for design and manufacturing, IPC-4103 for high-speed laminates, and IPC-6012E for performance qualifications. IPC-A-600K addresses board acceptability, ensuring quality. These guidelines provide a framework for selecting materials that meet electrical, thermal, and mechanical requirements in high-frequency environments.
Q4: Why is thermal stability important for HDI PCB materials in high-frequency use?
A4: Thermal stability is crucial for HDI PCB materials in high-frequency use because rapid signal switching generates heat. A high glass transition temperature prevents material deformation. Low thermal expansion mismatch avoids stress or cracking. Standards like IPC-4101 specify thermal properties, ensuring reliability during operation in demanding conditions.
References
IPC-2226 — Sectional Design Standard for High Density Interconnect (HDI) Printed Boards. IPC, 2003.
IPC-4101 — Specification for Base Materials for Rigid and Multilayer Printed Boards. IPC, 2021.
IPC-4103 — Specification for Base Materials for High Speed/High Frequency Applications. IPC, 2017.
IPC-6012E — Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
IPC-A-600K — Acceptability of Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
IPC-TM-650 — Test Methods Manual. IPC, Current Version.