Introduction
In the realm of LED PCB design and manufacturing, optimizing light reflection is crucial for enhancing efficiency and performance. The solder mask, a protective layer on printed circuit boards, plays a significant role in determining how light interacts with the PCB surface. Selecting the right solder mask material and color, such as white or black, impacts reflectivity and light absorption. This directly influences LED brightness and energy efficiency. For electrical engineers, understanding solder mask reflectivity and its effect on LED PCB manufacturing is vital. This article explores the technical aspects of solder mask material selection, compares white solder mask versus black solder mask, and offers practical guidance for improving light reflection to boost LED efficiency. Let us delve into the principles and best practices for achieving optimal results.

What Is Solder Mask and Why It Matters in LED PCBs
Solder mask is a thin polymer layer applied to the copper traces of a PCB to prevent oxidation and unintended solder bridges during assembly. Beyond its protective function, it influences the aesthetics and performance of the board. In LED PCB manufacturing, the solder mask affects how light emitted from LEDs interacts with the board surface. High reflectivity can amplify brightness, while high absorption can diminish it. This makes solder mask material selection a critical factor in enhancing LED efficiency.
The choice of solder mask color, particularly white versus black, alters light absorption and reflection properties. A well chosen solder mask can improve light output and thermal management, both essential for LED applications. Electrical engineers must consider these aspects to meet design specifications and performance goals in lighting systems.
Suggested Reading: Understanding Solder Mask: A Beginner's Guide to PCB Protection
Technical Principles of Solder Mask Reflectivity
Solder mask reflectivity refers to the ability of the mask layer to bounce light back rather than absorb it. This property is governed by the color and material composition of the solder mask. Lighter colors, such as white, reflect a higher percentage of incident light across the visible spectrum. Darker colors, like black, absorb more light, converting it into heat.
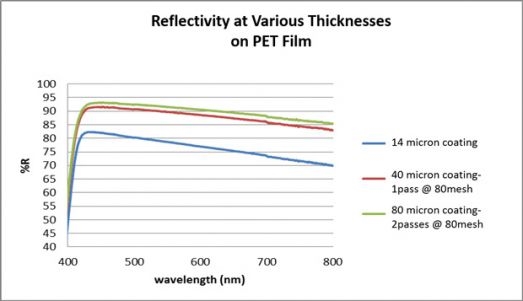
In this fast turn circuit board manufacturing, white solder mask materials are often formulated with pigments that maximize reflection. These masks can reflect up to 80 to 90 percent of visible light, depending on the specific formulation and surface finish. Conversely, black solder mask materials absorb a significant portion of light, reflecting only a small fraction. This absorption can lead to localized heating, potentially affecting LED performance and longevity.
The interaction between light and solder mask also depends on the PCB surface finish. A glossy finish can enhance specular reflection, directing light in specific angles, while a matte finish diffuses light more evenly. Engineers must balance these factors to optimize light reflection for specific LED applications.
White Solder Mask vs. Black Solder Mask: A Detailed Comparison
Choosing between white solder mask and black solder mask involves evaluating their impact on light absorption and reflection. Below is a detailed comparison tailored for LED PCB design considerations.
- Reflectivity and Light Output: White solder mask excels in reflecting light, making it ideal for applications where maximizing LED brightness is critical. It enhances overall light output by redirecting light that would otherwise be absorbed. Black solder mask, due to high light absorption, reduces stray light but at the cost of lower brightness.
- Thermal Performance: Black solder mask absorbs more light energy, converting it to heat. This can raise the PCB temperature, potentially impacting LED efficiency and lifespan. White solder mask minimizes heat absorption, aiding in thermal management.
- Contrast and Inspection: White solder mask provides high contrast against copper traces and components, facilitating automated optical inspection during manufacturing. Black solder mask offers less contrast, which can complicate visual checks.
- Application Suitability: White is preferred in general lighting and display applications for enhancing LED efficiency. Black is often used in automotive or high end electronics where controlling light scatter and aesthetics are priorities.
This comparison highlights why white solder mask is frequently chosen for LED PCB manufacturing when light reflection is a primary concern.
Practical Solutions for Enhancing LED Efficiency with Solder Mask
Optimizing solder mask for the LED PCB board requires a strategic approach to material selection and design. Below are actionable best practices for electrical engineers to improve light reflection and overall performance.
- Prioritize White Solder Mask for Reflectivity: Select a white solder mask with high reflectivity properties for applications requiring maximum light output. Ensure the mask meets industry standards for durability and adhesion, as outlined in IPC-A-600K.
- Consider PCB Surface Finish: Pair the solder mask with an appropriate surface finish to control light direction. A glossy finish can enhance directed reflection, while a matte finish offers diffuse reflection for uniform light distribution.
- Evaluate Thermal Impact: Assess the thermal implications of solder mask color. Use simulation tools to predict temperature rise with black solder mask in high power LED designs, and opt for white when heat dissipation is a concern.
- Test Reflectivity in Prototypes: During the design phase, prototype boards with different solder mask options. Measure light output and thermal performance to validate the choice for enhancing LED efficiency.
- Adhere to Manufacturing Standards: Follow guidelines from standards like IPC-6012E for solder mask application to ensure consistent quality and performance in LED PCB manufacturing.
Implementing these strategies can significantly improve light reflection and efficiency in LED systems.

Solder Mask Material Selection: Key Considerations
Beyond color, the composition of the solder mask material itself influences performance in LED PCBs. Common materials include epoxy based and polyimide based formulations, each with distinct properties.
Epoxy based solder masks are widely used due to their cost effectiveness and good adhesion to PCB substrates. They are available in various colors, including high reflectivity white options. However, their thermal resistance may be limited in high power LED applications.
Polyimide based masks offer superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, suitable for demanding environments. While they can be formulated for high reflectivity, their cost is often higher, requiring engineers to balance performance and budget.
When selecting a solder mask material, consider the operating conditions of the LED PCB. Ensure compatibility with the chosen PCB surface finish and adherence to standards such as IPC-A-600K for acceptability criteria. Proper material selection minimizes risks of degradation and maintains consistent light reflection over time.
Insight: Balancing Aesthetics and Functionality in LED PCB Design
In LED PCB manufacturing, engineers often face the challenge of balancing aesthetics with functionality. While white solder mask enhances light reflection, it may show dirt or wear more visibly than black. In consumer facing products, this can impact perceived quality.
Conversely, black solder mask offers a sleek, modern appearance favored in premium electronics. However, its light absorption properties can compromise LED efficiency unless stray light control is the primary goal. Engineers must weigh these trade offs during the design phase.
A practical approach is to define the primary objective of the LED application. If efficiency and brightness are paramount, prioritize white solder mask and address aesthetic concerns through enclosure design. If visual appeal and light control are critical, black solder mask might be the better choice, supplemented by thermal management strategies.
Conclusion
Optimizing solder mask for enhanced light reflection in LED PCBs is a multifaceted task that requires careful consideration of reflectivity, thermal performance, and material properties. White solder mask stands out for its ability to maximize light output and aid in thermal management, making it a preferred choice for many LED applications. Black solder mask, while aesthetically appealing, often absorbs light and may introduce thermal challenges. By focusing on solder mask material selection, pairing with the right PCB surface finish, and adhering to industry standards like IPC-6012E and IPC-A-600K, electrical engineers can significantly enhance LED efficiency. Thoughtful design and testing ensure that the chosen solder mask aligns with both performance and application goals, delivering reliable and efficient LED systems.
FAQs
Q1: How does solder mask reflectivity impact LED efficiency in PCB design?
A1: Solder mask reflectivity directly affects how much light from LEDs is reflected or absorbed by the PCB surface. A high reflectivity mask, like white, bounces more light back, increasing brightness and enhancing LED efficiency. This reduces energy loss and improves performance in lighting applications. Engineers should prioritize reflectivity when efficiency is critical.
Q2: What are the main differences between white solder mask versus black solder mask for LED PCBs?
A2: White solder mask reflects more light, boosting brightness and aiding thermal management. Black solder mask absorbs light, reducing stray reflections but increasing heat. White offers better contrast for inspection, while black provides a modern aesthetic. The choice depends on whether enhancing LED efficiency or controlling light scatter is the priority.
Q3: What factors should guide solder mask material selection for LED PCB manufacturing?
A3: Solder mask material selection should consider reflectivity, thermal resistance, and compatibility with the PCB surface finish. Epoxy based masks are cost effective for general use, while polyimide based options suit high temperature environments. Adherence to standards like IPC-A-600K ensures quality and durability in LED PCB manufacturing processes.
Q4: How does PCB surface finish interact with solder mask to affect light reflection?
A4: PCB surface finish influences how light interacts with the solder mask. A glossy finish enhances specular reflection, focusing light in specific directions, while a matte finish diffuses light for even distribution. Pairing the right finish with a reflective solder mask optimizes light reflection and supports enhancing LED efficiency in designs.
References
IPC-6012E: Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
IPC-A-600K: Acceptability of Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.