Understanding the Environmental Impact of Printed Circuit Boards
In today's electronically driven world, the environmental footprint of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) is a growing concern. These essential components, forming the core of nearly every electronic device, contribute substantially to greenhouse gas emissions throughout their entire lifespan. From the initial acquisition of raw materials to their eventual disposal, the processes involved have a measurable impact on the planet.
A PCB's carbon footprint quantifies the total greenhouse gas emissions, predominantly carbon dioxide (CO2), linked to its full life cycle. This encompasses everything from extracting raw materials like copper, fiberglass, and epoxy resins, through energy-intensive manufacturing and assembly, to the ultimate disposal of the board. Industry analyses indicate that producing just one square meter of a PCB can release between 60 to 70 kilograms of CO2 equivalent, varying based on the specific materials and energy sources utilized.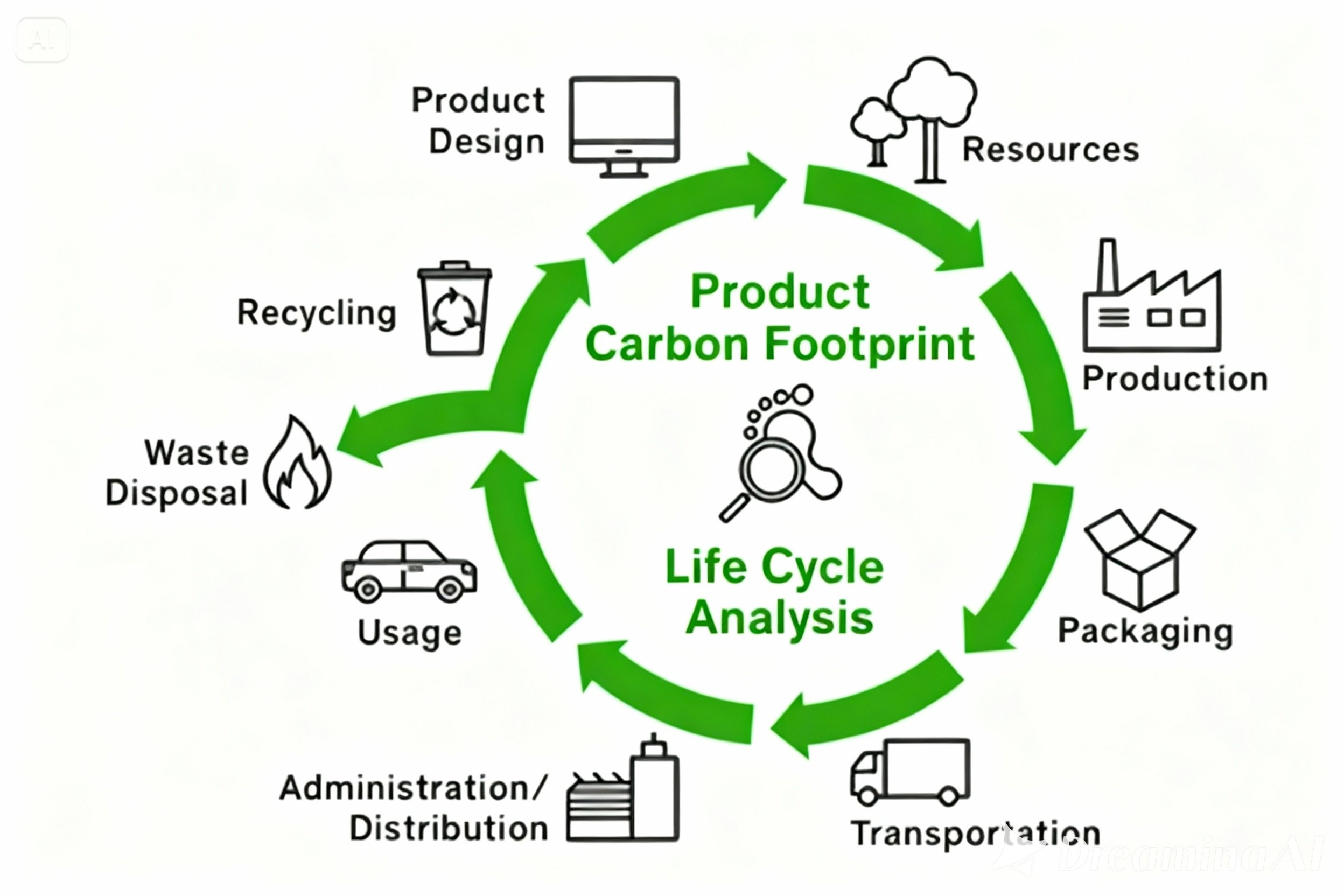
Emissions from Production and Disposal
A significant portion of these emissions stems from the high energy demands of manufacturing processes such as etching, laminating, and soldering. Beyond manufacturing, the extraction of metals through mining and the production of fiberglass also contribute to environmental degradation. At the end of a PCB's functional life, improper disposal can lead to the release of hazardous chemicals into the environment, further exacerbating its overall carbon footprint. Recognizing these impacts is the initial step toward developing and adopting lower-carbon PCB solutions.
Why Address the PCB Carbon Footprint?
The electronics industry continues its rapid expansion, with billions of devices produced annually. This escalating demand for PCBs inevitably amplifies their environmental impact. Elevated carbon emissions exacerbate climate change, while the prevalence of non-recyclable materials in traditional PCBs often results in landfill accumulation. There, toxic substances like lead and brominated flame retardants can leach into soil and water sources, posing severe ecological threats. This makes sustainable electronics manufacturing a critical imperative for mitigating global environmental harm.
Furthermore, both regulatory bodies and consumers are increasingly advocating for more environmentally conscious practices. Many nations have implemented stringent guidelines for electronic waste (e-waste) management, placing manufacturers under pressure to reduce their carbon footprints. By proactively addressing the carbon footprint of PCBs, companies can not only ensure compliance with evolving regulations but also cultivate trust among a growing demographic of environmentally aware customers, enhancing their brand reputation and market position.
Assessing the Full Environmental Impact of PCBs
A Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating the environmental impact of a PCB from its inception ("cradle") to its ultimate disposal ("grave"). An LCA for PCBs typically dissects the product's journey into five distinct stages: raw material acquisition, manufacturing, distribution, use, and end-of-life management. Each of these stages presents unique opportunities for reducing emissions and enhancing overall sustainability.
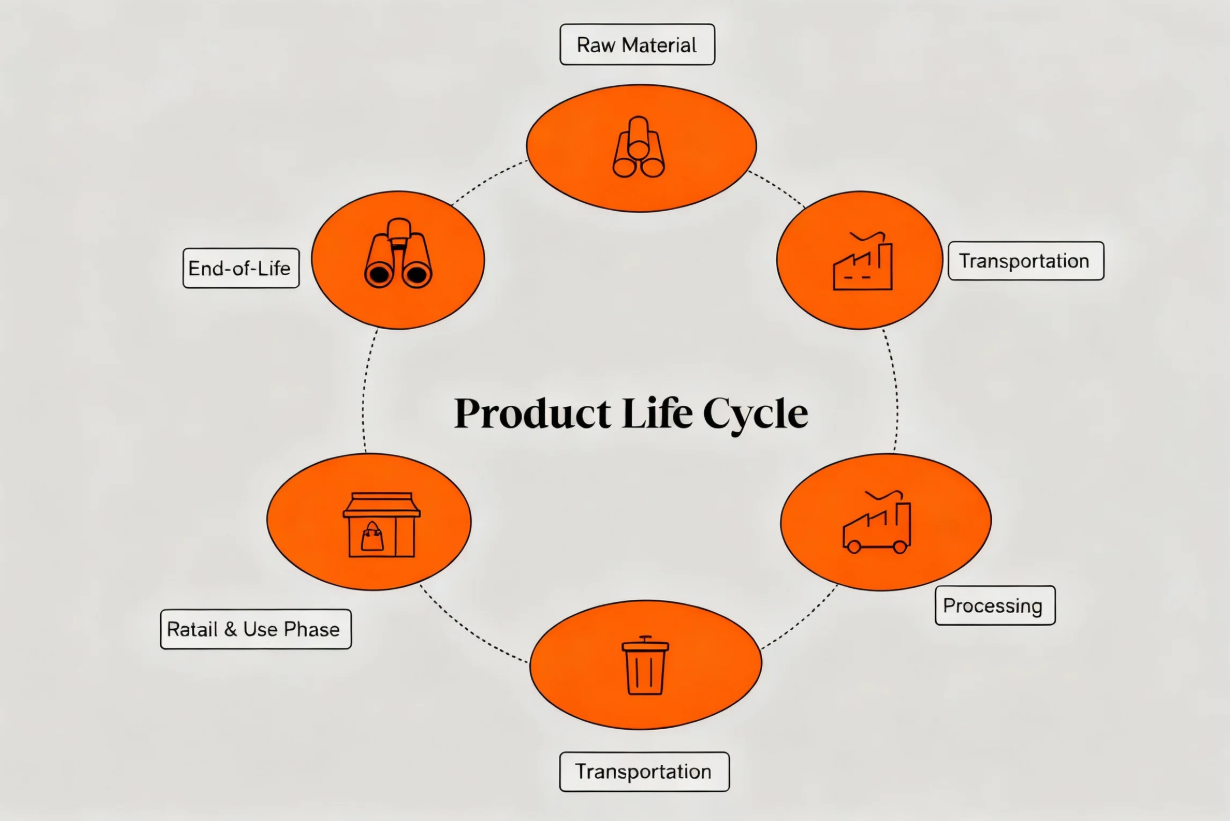
Key Stages and Mitigation Strategies
● Raw Material Acquisition: The mining of copper and the production of epoxy resins are processes that consume significant energy and generate substantial emissions. Integrating recycled metals and exploring alternative, more sustainable materials can drastically reduce the environmental burden at this initial stage.
● Manufacturing: This phase typically accounts for the largest share of emissions due to its intensive energy requirements. A strategic shift to renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, for production facilities can substantially lower the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing.
● Distribution: The global transportation of PCBs contributes to emissions. Implementing localized sourcing strategies and optimizing logistics can help minimize the environmental impact related to distribution.
● Use: While the operational phase of a PCB generally has a smaller direct environmental impact, designing for energy efficiency can lead to a reduction in the overall environmental footprint over the device's lifespan.
● End-of-Life: Crucial for preventing toxic waste and recovering valuable resources, proper recycling and disposal methods are paramount. Establishing robust recycling infrastructure ensures that materials are reclaimed rather than discarded.
By conducting an LCA study, manufacturers can pinpoint the highest-impact areas within their production processes and implement targeted changes. For instance, adopting low-carbon PCB designs that utilize fewer layers or optimizing copper usage can significantly decrease material requirements and energy consumption during the manufacturing phase.
Recyclable PCB Materials: A Game Changer for Carbon Reduction
Traditional PCBs, often constructed from PCB FR-4 material (a composite of fiberglass and epoxy resin), pose significant recycling challenges due to their complex, integrated structure. However, breakthroughs in material science are ushering in a new era of recyclable PCB materials. These innovative materials are specifically engineered for easier deconstruction and reuse, thereby diminishing waste and reducing the reliance on virgin natural resources.
Emerging Green Material Alternatives
One promising advancement involves the development of biodegradable substrates. Certain cutting-edge materials can, under specific conditions, dissolve in water, facilitating the straightforward separation and recycling of electronic components with minimal energy input. Research indicates that such materials have the potential to cut carbon emissions by up to 60% when compared to conventional substrates. Furthermore, the integration of recycled copper and other metals can substantially lower the environmental cost associated with extracting new raw materials.
Beyond biodegradables, plant-based fibers and halogen-free polymers are gaining traction as eco-friendly substitutes for traditional PCB constituents. These alternatives not only reduce the toxicity associated with PCB production and disposal but also streamline the recycling process. By systematically incorporating recyclable PCB materials into their production lines, manufacturers can significantly reduce electronic waste and contribute meaningfully to the overarching goal of sustainable electronics manufacturing.
Advantages of Embracing Low-Carbon PCB Manufacturing
Adopting manufacturing practices focused on reducing the carbon footprint of PCBs yields a broad spectrum of benefits that extend far beyond mere emission reduction. These advantages encompass financial, regulatory, and reputational gains.
Key Benefits
● Cost Savings: Employing recycled materials and implementing energy-efficient production processes can lead to substantial long-term cost reductions. For example, recovering copper from end-of-life PCBs diminishes the need for expensive and environmentally impactful mining operations.
● Regulatory Compliance: With an increasing number of regions enacting stringent regulations concerning e-waste and emissions, sustainable manufacturing practices enable companies to avoid penalties and fines, ensuring legal compliance.
● Enhanced Brand Reputation: Companies that visibly prioritize sustainability often resonate positively with environmentally conscious consumers and business partners. This commitment can significantly strengthen their market position and foster brand loyalty.
● Resource Conservation: The active recycling of materials plays a crucial role in reducing the demand for finite natural resources, such as copper and rare earth metals. This conservation effort helps ensure the long-term availability of these vital materials for future generations.
By prioritizing low-carbon PCB solutions, manufacturers can strategically align their operations with global sustainability objectives, such as achieving net-zero emissions, all while maintaining robust profitability and operational efficiency.
Obstacles to Adopting Recyclable Materials in PCBs
While the environmental and economic benefits of transitioning to recyclable PCB materials are evident, the adoption of these sustainable practices is not without its challenges. Several hurdles currently impede a widespread shift across the industry.
Performance, Cost, and Infrastructure Limitations
A primary concern is the performance parity of alternative materials. Some biodegradable substrates, for instance, may not yet offer the same levels of durability or thermal resistance as traditional options. This can limit their applicability, particularly in high-performance or mission-critical electronic devices where reliability is paramount.
Cost also remains a significant barrier. The research, development, and implementation of new, sustainable materials often necessitate considerable upfront investments in R&D, specialized equipment, and staff training. This financial burden can be particularly challenging for smaller manufacturers who may lack the capital to absorb such costs without external support or incentives. Furthermore, the existing recycling infrastructure for complex electronic components like PCBs is still underdeveloped in many parts of the world, making the efficient recovery and processing of materials difficult and, at times, cost-prohibitive.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and collaborative efforts across the industry are actively working to overcome these barriers. Governments and various organizations are also providing grants, subsidies, and programs designed to support sustainable electronics manufacturing, thereby easing the transition for companies committed to greener practices.
Advancing Towards Sustainable Electronics Manufacturing
Achieving true sustainability in fast turn PCB fabrication demands a multifaceted and integrated strategy. Manufacturers can implement several actionable steps to significantly reduce their PCB carbon footprint and foster a more environmentally responsible industry.
Strategic Steps for Greener Production
● Embrace Renewable Energy: Powering manufacturing facilities with renewable energy sources like solar or wind can dramatically cut greenhouse gas emissions. For example, a factory operating entirely on clean energy could potentially reduce its carbon output by 30-40%.
● Optimize Design for Efficiency: Simplifying PCB designs to minimize material and layer requirements can lead to substantial reductions in resource consumption and energy needs during the production phase. Efficient design is the first step in sustainable manufacturing.
● Invest in Recycling Partnerships: Collaborating with specialized recycling firms to recover valuable materials from end-of-life PCBs establishes a crucial circular supply chain, ensuring resources are reused rather than discarded.
● Integrate Green Materials: Gradually transition from traditional substrates to more recyclable, biodegradable, or otherwise environmentally friendly alternatives as technological advancements improve their performance and cost-effectiveness.
● Educate and Engage Stakeholders: Fostering a culture of environmental responsibility requires educating employees on sustainable practices and informing customers about the importance of these initiatives. This collective awareness strengthens the commitment to sustainability.
Effective implementation of these steps has the potential to transform the electronics industry, making sustainable manufacturing a tangible reality rather than a distant goal.
The Future Landscape of Sustainable PCB Production
The trajectory of PCB manufacturing is clearly moving towards a circular economy model, where materials are systematically reused, and waste generation is minimized. Continuous advancements in material science are steadily paving the way for the development of fully recyclable PCBs that do not compromise on performance or reliability. Furthermore, sophisticated digital tools, such as simulation software, are empowering engineers to design boards with an inherent minimal environmental impact by optimizing layouts and material usage before any physical production begins.
Industry-wide collaboration is another indispensable element for accelerating this transition. By actively sharing knowledge, best practices, and resources, manufacturers can collectively fast-track the adoption of low-carbon PCB solutions. Concurrently, governments and various organizations must continue to provide robust support through supportive policies, targeted funding, and incentive programs to ensure a smoother, more widespread shift toward sustainable electronics manufacturing practices.
Conclusion: Making an Impact with Sustainable PCB Materials
The carbon footprint of Printed Circuit Boards presents a substantial challenge for the electronics sector, but the strategic integration of recyclable and sustainable materials offers a potent solution. By conscientiously adopting eco-friendly practices, exploring innovative biodegradable substrates, and rigorously applying life cycle assessments, manufacturers are well-positioned to significantly reduce emissions, conserve vital resources, and meet evolving regulatory demands. While the path toward low-carbon PCB production may present its share of obstacles, the resulting benefits—both for the environment and for economic viability—are unequivocally worth the concerted effort. Working together, we can forge a future where cutting-edge electronics and environmental sustainability are seamlessly intertwined.
At AIVON, we are deeply committed to championing sustainable electronics manufacturing through our innovative solutions and unwavering dedication to quality service. We invite you to collaborate with us in building a greener, more responsible industry for tomorrow.