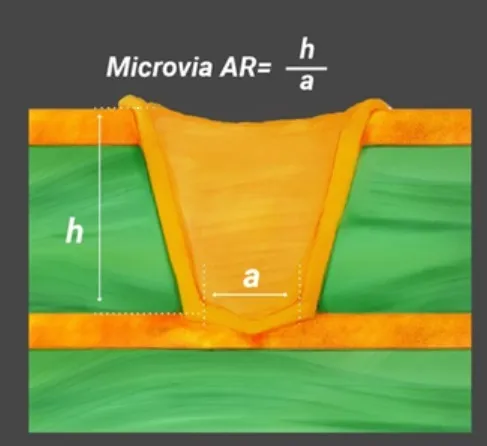
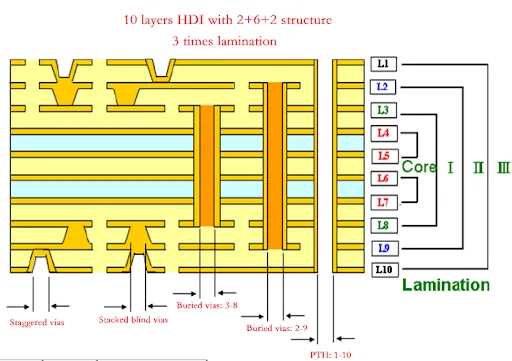
Introduction
For electronic hobbyists eager to dive into the world of printed circuit boards, starting with simple projects offers a practical entry point. Halogen-free PCB design is gaining attention due to its environmental benefits and compliance with sustainability standards. This article explores easy PCB projects tailored for beginners, focusing on halogen-free materials that reduce toxic emissions. Whether you're crafting simple electronics projects or exploring hobby electronics, these ideas will build your skills. Authored by Sophia Wang, a manufacturing specialist, this guide provides standard-aligned insights to ensure your first steps in PCB design are both safe and eco-friendly. Let's uncover why halogen-free options matter and how you can apply them in beginner PCB projects.
What Are Halogen-Free PCBs and Why Do They Matter
Halogen-free PCBs are circuit boards made without halogenated compounds like chlorine or bromine in their materials. These substances, often found in flame retardants, can release harmful toxins when burned or improperly disposed of. Choosing halogen-free materials aligns with environmental regulations and reduces health risks during manufacturing or recycling. For electronic hobbyists, this choice supports safer workspaces and sustainable practices.
The relevance of halogen-free design grows as industries prioritize eco-friendly solutions. Many regions enforce strict guidelines on hazardous substances, making these PCBs a forward-thinking option. Beyond compliance, they often exhibit comparable performance to traditional boards in terms of thermal stability and electrical properties. For beginners working on easy PCB projects, starting with halogen-free materials builds awareness of global standards and fosters responsible habits in hobby electronics.
Technical Principles of Halogen-Free PCB Materials
Understanding the composition of halogen-free PCBs is key for beginners. These boards use alternative flame retardants, often based on phosphorus or nitrogen compounds, to achieve fire resistance without toxic halogens. The base laminate typically adheres to specifications outlined in industry standards, ensuring reliability in simple electronics projects.
Thermal and mechanical properties remain critical. Halogen-free materials must withstand soldering temperatures and maintain structural integrity. Standards like IPC-4101E, which governs laminate materials for PCBs, provide guidelines on acceptable performance metrics. While these materials may have slightly different dielectric constants or moisture absorption rates compared to traditional options, they are suitable for low-complexity designs common in beginner PCB projects.
Environmental stress testing is another aspect to consider. Halogen-free PCBs are evaluated for ionic contamination and long-term durability under standards such as IPC-TM-650. For hobbyists, this means selecting materials that balance eco-friendliness with practical usability in small-scale applications. Awareness of these principles ensures your designs are both safe and functional.
Benefits of Halogen-Free PCBs for Hobbyists
For electronic hobbyists, halogen-free PCBs offer several advantages beyond environmental impact. First, they reduce exposure to harmful substances during soldering or rework, which is vital in home workshops lacking industrial ventilation. Second, many of these materials meet strict regulatory criteria, making them a future-proof choice as restrictions tighten globally.
PCB board cost is often a concern for beginners, but halogen-free options are increasingly accessible. While slightly more expensive than standard materials, their pricing gap narrows as demand grows. Additionally, working with these PCBs introduces hobbyists to industry trends, preparing them for more advanced projects. Simple electronics projects using halogen-free boards also contribute to a cleaner recycling process, aligning personal hobbies with broader sustainability goals.
Simple Halogen-Free PCB Projects for Beginners
Starting with beginner PCB projects helps build confidence in design and assembly. Below are three easy ideas using halogen-free materials, ideal for hobby electronics enthusiasts. Each project focuses on basic circuits while emphasizing practical skills.
LED Blinking Circuit
An LED blinking circuit is a classic starting point. This project requires minimal components: a microcontroller or timer IC, resistors, capacitors, and LEDs. Design a single-layer PCB layout following basic spacing rules from standards like IPC-2221B for general board design. Use halogen-free laminate to ensure eco-friendliness.
Begin by sketching a schematic with a simple oscillator circuit. Place components to minimize trace lengths for signal integrity. After design, verify the board against acceptability criteria in IPC-A-600K to spot potential flaws. This project teaches routing basics and soldering skills while showcasing halogen-free material handling.
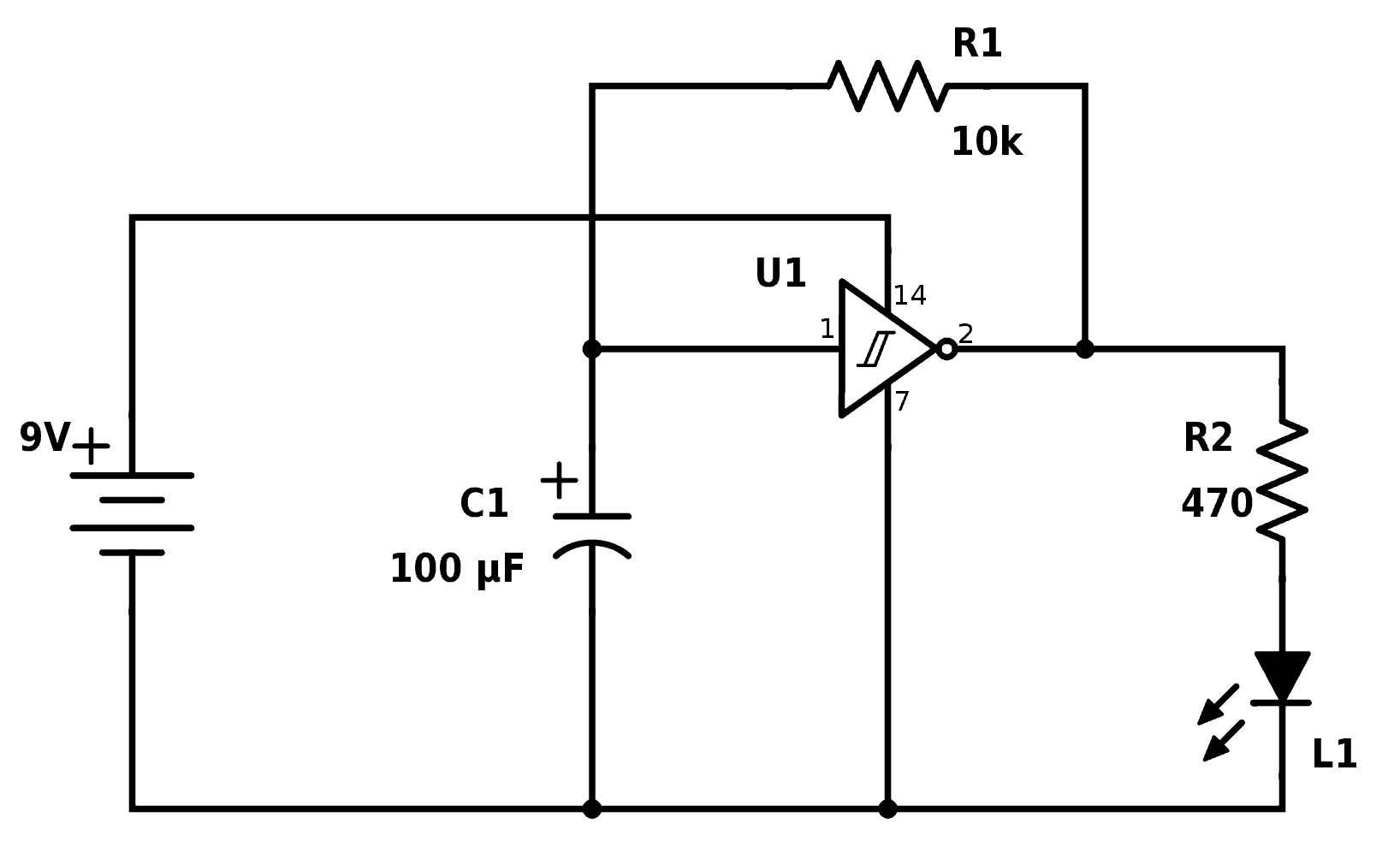
Basic Power Supply Module
A power supply module converts input voltage to a stable output for small devices. This project involves a voltage regulator, diodes, capacitors, and connectors. Opt for a halogen-free PCB substrate compliant with IPC-4101E specifications to ensure material safety.
Focus on thermal management by providing adequate copper area around the regulator for heat dissipation. Keep input and output traces separate to avoid noise. Testing the board under load aligns with methods in IPC-TM-650, ensuring reliability. This project introduces power electronics concepts and reinforces safe material choices.
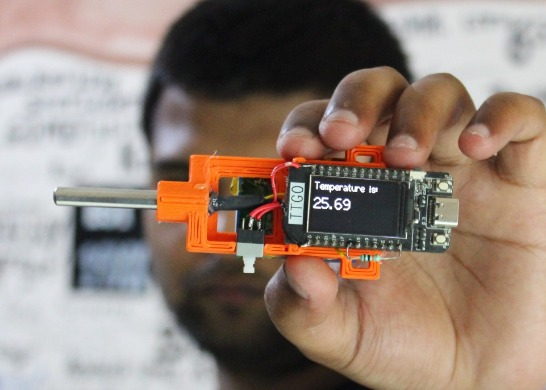
Temperature Sensor Display
A temperature sensor display uses a sensor IC, a small microcontroller, and a digital display. This slightly more complex project suits hobbyists ready to combine analog and digital elements. Select a halogen-free board material meeting environmental standards for low ionic contamination.
Plan the layout to isolate the sensor from heat-generating components. Follow trace width guidelines in IPC-2221B to handle current safely. This project builds skills in mixed-signal design and soldering precision, with halogen-free materials supporting a safer build process.
Best Practices for Designing Halogen-Free PCBs
Creating successful beginner PCB projects with halogen-free materials requires attention to detail. Here are actionable tips to guide electronic hobbyists through the process.
- Material Selection: Choose laminates meeting IPC-4101E standards for halogen-free properties. Verify supplier documentation to confirm compliance with environmental criteria.
- Design Simplicity: Keep layouts straightforward with single or double layers. Adhere to clearance and creepage distances as per IPC-2221B to prevent electrical issues.
- Thermal Considerations: Account for heat dissipation in components. Halogen-free materials may have different thermal conductivities, so plan copper pours accordingly.
- Testing and Inspection: After PCBA assembly, inspect boards against IPC-A-600K criteria for surface finish and via quality. Use basic multimeter checks to validate functionality.
- Documentation: Maintain clear schematics and layout files. Reference standards like IPC-2611 for generic terminology to ensure clarity in future revisions.
Following these practices ensures your simple electronics projects are reliable and aligned with industry expectations. Halogen-free design becomes second nature with consistent application of these principles.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Halogen-Free PCB Projects
Beginners often face hurdles when working with PCBs, even in easy projects. Halogen-free materials can present unique challenges, but solutions are within reach for hobby electronics enthusiasts.
One issue is sourcing suitable materials. Not all suppliers offer halogen-free laminates for small orders. Researching vendors who prioritize eco-friendly options helps overcome this. Cross-check material datasheets against IPC-4101E to confirm specifications.
Another challenge is soldering compatibility. Some halogen-free boards may require adjusted soldering profiles due to thermal properties. Refer to guidelines in IPC J-STD-001H for proper techniques, ensuring joints are robust without overheating the board.
Finally, design errors like incorrect trace widths can lead to failures. Use design rules from IPC-2221B to set minimum widths based on current needs. Double-check layouts before fabrication to avoid costly mistakes. Addressing these issues builds confidence in handling halogen-free PCB design.
Tools and Resources for Beginner PCB Projects
Equipping yourself with the right tools is essential for success in hobby electronics. For simple halogen-free PCB projects, focus on accessible and standard-compliant resources.
Basic tools include a soldering iron with temperature control, a multimeter for testing, and fine-tip tweezers for component placement. A well-lit workspace with proper ventilation is crucial when working with any PCB material, including halogen-free options.
For design, free or low-cost software options allow schematic capture and layout creation. Ensure your designs align with standards like IPC-2221B for spacing and routing. Online communities and forums focused on electronics provide peer support and project ideas without commercial bias.
Libraries of educational content, often referencing IPC and IEC standards, offer guidance on best practices. Leveraging these resources helps beginners navigate the complexities of PCB design while prioritizing safety and sustainability.
Conclusion
Embarking on simple halogen-free PCB projects opens a world of learning for electronic hobbyists. These beginner PCB projects, from LED circuits to temperature displays, build foundational skills while emphasizing eco-friendly materials. Halogen-free PCB design aligns with global sustainability trends and ensures safer working conditions. By following industry standards and best practices, hobbyists can create reliable simple electronics projects. With the right tools and knowledge, your journey in hobby electronics becomes both impactful and rewarding. Start small, stay informed, and contribute to a greener future through thoughtful design choices.
FAQs
Q1: What are the easiest halogen-free PCB projects for beginners?
A1: For electronic hobbyists, the easiest halogen-free PCB projects include LED blinking circuits and basic power supply modules. These require minimal components and simple layouts. Using materials compliant with IPC-4101E ensures eco-friendliness. Start with single-layer designs to learn routing and soldering basics while maintaining safety and sustainability in your workspace.
Q2: How does halogen-free PCB design benefit hobby electronics?
A2: Halogen-free PCB design reduces exposure to toxic substances during soldering, making it safer for hobby electronics enthusiasts. It also aligns with environmental regulations, promoting responsible practices. These materials perform well in simple electronics projects and prepare hobbyists for industry trends. Choosing them supports a cleaner recycling process.
Q3: Where can I find resources for easy PCB projects with halogen-free materials?
A3: Beginners can explore educational content referencing IPC and IEC standards for easy PCB projects. Online forums and non-commercial electronics communities offer project ideas and support. Libraries with technical guides on halogen-free materials are valuable. Always verify material compliance with standards like IPC-4101E for safety.
Q4: What standards should I follow for beginner PCB projects?
A4: For beginner PCB projects, follow standards like IPC-2221B for design spacing, IPC-4101E for material selection, and IPC-A-600K for board acceptability. These ensure reliability and safety in your designs. Adhering to such guidelines helps hobbyists create functional and eco-friendly halogen-free PCBs.
References
IPC-4101E — Specification for Base Materials for Rigid and Multilayer Printed Boards. IPC, 2021.
IPC-2221B — Generic Standard on Printed Board Design. IPC, 2012.
IPC-A-600K — Acceptability of Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
IPC-TM-650 — Test Methods Manual. IPC, Current Version.
IPC J-STD-001H — Requirements for Soldered Electrical and Electronic Assemblies. IPC, 2021.