What Does UL Certification Mean for Printed Circuit Boards?
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are foundational components in modern electronics, underpinning everything from advanced medical equipment to complex automotive systems. Given the increasing sophistication of electronic devices, guaranteeing their safety and consistent reliability is paramount. This is where UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification becomes indispensable. UL is a globally recognized safety science organization that establishes stringent benchmarks to ensure types of PCBs meet rigorous safety and performance criteria, thereby mitigating potential risks such as electrical shock and fire hazards. For design engineers, comprehending UL certification is vital for creating compliant, high-quality PCBs that instill consumer confidence.
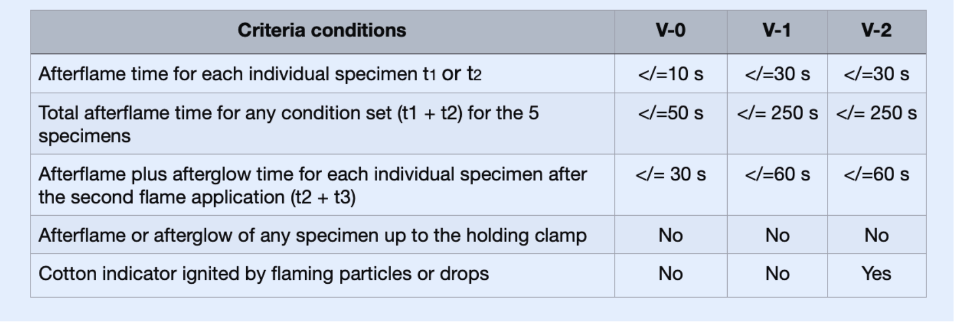
UL certification represents a globally respected mark of safety and quality. For PCBs specifically, this certification confirms that a board has undergone rigorous testing to conform to defined safety and performance standards, ensuring its reliable operation under specified conditions. This certification is particularly crucial in sectors where component failure could lead to severe consequences, such as in the automotive, aerospace, and medical device industries. A UL mark on a PCB signifies adherence to key standards like UL 796, which pertains to rigid and flexible PCBs, and UL 94, which details flammability testing for plastics. These standards collectively encompass the electrical, mechanical, and thermal characteristics of a PCB, verifying its resilience against stressors like high voltages, elevated temperatures, and various environmental exposures. For instance, UL 94 classifies materials based on their flammability, with the V-0 rating denoting the highest safety level—indicating that burning ceases within 10 seconds on a vertical specimen without any flaming drips.

Why Is UL Certification So Important for PCB Manufacturers and Designers?
UL certification transcends mere regulatory compliance; it serves as a significant competitive differentiator that bolsters market trust and enhances product appeal. Its importance for engineers and manufacturers cannot be overstated.
Ensuring Uncompromised Safety Standards
UL certification fundamentally assures that PCBs are safe for consumer and industrial use, significantly reducing the likelihood of electrical fires or shocks. For example, UL 796 mandates dielectric breakdown tests, confirming that a board can safely handle specified voltage levels—such as 500V for particular applications—without sustaining damage or failure.
Facilitating Global Market Access
In many key markets, particularly across North America, UL certification is often a mandatory requirement for electronic products. Without it, PCBs may face restrictions or outright bans from sale, severely limiting their market reach and commercial viability.
Building and Maintaining Consumer Trust
The UL mark is universally recognized by both consumers and regulatory bodies as an emblem of reliability and safety. With billions of UL marks appearing on products annually, its credibility and impact on purchasing decisions are substantial.
Adhering to Regulatory Frameworks
Achieving UL certification ensures that PCBs align with broader international standards, including IEC 60707 and CAN/CSA C22.2, which simplifies the process of complying with diverse regional and national regulations. For design engineers, proactively specifying UL-certified materials and processes during the early design stages can avert costly redesigns and delays, ultimately ensuring the final product consistently meets both safety and performance objectives.
What Are the Primary UL Standards Applicable to PCBs?
A thorough understanding of the specific UL standards relevant to PCBs is indispensable for achieving compliance. Engineers should be familiar with the following core standards.
UL 796: Safety Standards for Printed Wiring Boards
UL 796 is the foundational standard for both rigid and flexible printed wiring boards. It meticulously covers:
● Material Specifications: This ensures that base materials, such as FR4, meet stringent electrical and thermal performance benchmarks. For instance, the Comparative Tracking Index (CTI) quantifies a material's resistance to electrical breakdown, with Class 3 materials (175-249V) being suitable for higher-voltage applications.
● Construction Guidelines: The standard specifies precise requirements for trace widths, spacing, and via integrity to effectively prevent short circuits or electrical arcing. For high-frequency PCBs, maintaining controlled impedance—typically 50Ω—is crucial for preserving signal integrity.
● Performance Verification: This includes a series of thermal stress tests designed to simulate soldering conditions, ensuring the board can reliably withstand temperatures up to 260°C during reflow processes.
UL 796F: Standards for Flexible Printed Circuits
UL 796F specifically addresses the distinct requirements of flexible PCBs and rigid-flex PCBs, which are increasingly prevalent in compact electronics and wearable technology. This standard includes specialized tests for:
● Dynamic Bending Resilience: This test verifies that flexible PCBs can endure repeated bending cycles—for example, 10,000 cycles—without developing cracks or compromising functionality.
● Thermal Endurance: It confirms the PCB's performance at its maximum specified operating temperatures, typically ranging from 105°C to 150°C, depending on the chosen material.
UL 94: Flammability Testing for Plastic Materials
UL 94 evaluates the flammability characteristics of PCB materials, categorizing them into ratings such as V-0, V-1, and V-2. For example:
● V-0 Rating: Indicates that burning ceases within 10 seconds, and no flaming drips are permitted. This is the predominant standard for most FR4-based PCBs.
● V-1 Rating: Signifies that burning stops within 30 seconds, with no flaming drips allowed.
● V-2 Rating: Permits non-flaming drips, making it a less stringent classification than V-0.
H2: The Structured UL Certification Process for PCBs
Achieving UL certification involves a systematic and collaborative effort among designers, manufacturers, and UL auditors. Here’s a detailed overview of the process.
Step-by-Step Certification Overview
1. Design Validation: Engineers initiate the process by carefully selecting UL-recognized materials, such as Isola IS400, which has a glass transition temperature (Tg) of 150°C. They meticulously document all specifications, including trace widths—e.g., 0.2mm for a 1A current—and dielectric thickness, such as 0.1mm for high-voltage isolation.
2. Prototype Evaluation: Manufacturers then submit PCB prototypes to UL for comprehensive testing. These tests encompass thermal stress (e.g., 10 seconds at 288°C), dielectric withstand voltage (e.g., 1000V for 1 minute), and thorough flammability assessments.
3. Manufacturing Facility Audit: UL conducts unannounced inspections of the manufacturing facilities to ensure strict adherence to certified processes. This includes verifying material traceability and scrutinizing soldering conditions.
4. Certification Grant: Upon successful completion of all tests and audits, UL issues a certification, complete with a unique identifier (e.g., E488074), and grants authorization to apply the UL mark.
5. Sustained Compliance: To maintain ongoing certification, manufacturers are subject to periodic audits, which ensure consistent product quality and adherence to UL standards.
The entire certification process typically spans 6 to 12 weeks, with the cost for custom PCBs generally ranging from $5,000 to $20,000, depending on the complexity of the board. Proactive pre-certification design reviews can significantly reduce potential delays by identifying and resolving issues at an early stage.
Designing PCBs with UL Compliance as a Core Objective
Design engineers play a crucial role in securing UL compliance through informed and strategic design decisions. Here are practical tips to streamline this process.
Key Design Strategies for UL Compliance
● Utilize UL-Recognized Materials: Always select materials that are listed in UL’s 'Yellow Card' database. This resource provides detailed properties such as flammability ratings (e.g., V-0) and maximum operating temperatures (e.g., 130°C). For instance, Nan Ya NP-155F is a widely used FR4 material known for its UL 796 compliance.
● Optimize Trace and Spacing: Maintain appropriate creepage and clearance distances—e.g., 0.8mm for 250V applications—to effectively prevent electrical arcing. For high-speed designs, ensure meticulous impedance control, such as 100Ω for differential pairs, to avoid any signal degradation.
● Integrate Robust Thermal Management: Implement strategies such as thermal vias or extensive copper pours to efficiently dissipate heat, particularly for high-power PCBs operating at 50W or more. UL 796 mandates thermal stress testing to confirm long-term reliability under operational heat loads.
● Comprehensive Documentation of Specifications: Provide detailed Gerber files and Bills of Materials (BOMs) that explicitly state all UL requirements, including the specified solder mask type (e.g., Liquid Photoimageable (LPI)) and the precise placement for the UL mark in the silkscreen layer.
By addressing these critical factors early in the design cycle, engineers can avoid costly revisions and significantly accelerate the UL certification timeline.
Evolving Landscape: Challenges and Future Trends in UL Certification
While UL certification is fundamental, it does present challenges. The certification of highly complex PCBs, such as High-Density Interconnect (HDI) boards or those with embedded components, necessitates extensive testing, which can increase both costs and timelines. Moreover, emerging technologies like 3D-printed PCBs and advanced IoT devices are driving the need for new standards, as conventional UL tests may not fully encompass their unique characteristics.
Key Trends Shaping Future UL Certification
● Emphasis on Sustainability: UL is increasingly promoting eco-friendly materials, such as halogen-free laminates, to minimize environmental impact across the electronics industry.
● Enhanced Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): With rising signal speeds—e.g., 10Gbps for 5G applications—UL is expanding its EMC testing protocols to ensure PCBs do not cause undue interference with other electronic devices.
● Streamlined Certification Processes: UL is actively investigating digital tools and methodologies to reduce certification times, which has the potential to lower costs for manufacturers.
Engineers must remain informed about these evolving trends to future-proof their designs and ensure ongoing compliance in a rapidly changing technological landscape.
AIVON's Role in Supporting UL-Compliant PCB Manufacturing
For engineers who require UL-certified PCBs, establishing a partnership with a dependable and experienced manufacturer is paramount. AIVON's advanced manufacturing capabilities and streamlined global logistics are designed to simplify the entire process, ensuring the delivery of high-quality, compliant boards. Our rapid quick-turn prototyping services empower engineers to test and validate their designs swiftly, allowing for the early identification and resolution of any potential UL compliance issues.
With state-of-the-art facilities, AIVON maintains stringent control over critical parameters such as trace widths—down to 0.1mm—and impedance—with tolerances as precise as ±10%. This adherence to exacting standards ensures that all UL 796 requirements are consistently met. Furthermore, our robust global supply chain guarantees the timely procurement and delivery of UL-recognized materials, thereby helping engineers meet aggressive project deadlines without making any compromises on safety or performance.
Conclusion: Mastering UL Certification for Superior PCB Design
UL certification stands as a cornerstone in guaranteeing the safety and performance of printed circuit boards, offering engineers a reliable pathway to develop trustworthy, market-ready products. By diligently understanding pivotal standards like UL 796 and UL 94, integrating compliance into every stage of the design process, and forging partnerships with experienced manufacturers, engineers can navigate the certification landscape efficiently and effectively. As technology continues its rapid evolution, staying abreast of emerging trends such as sustainability initiatives and advancements in EMC testing will further elevate the quality and reliability of PCB designs.