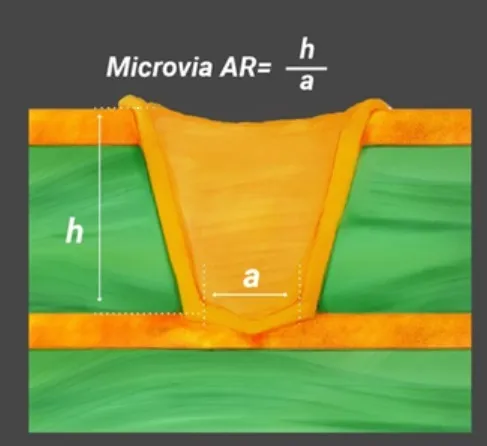
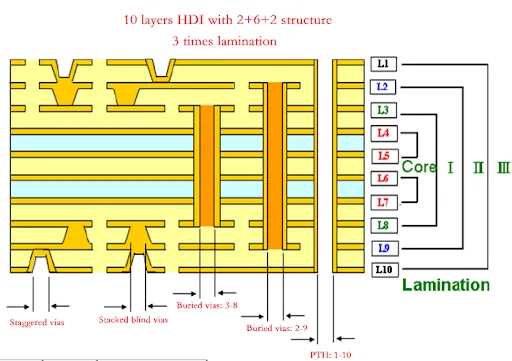
Introduction
Flexible printed circuit boards, often referred to as Flex PCBs, have become a cornerstone in modern electronics design due to their adaptability and compact form factor. Unlike rigid PCBs, these circuits can bend, fold, and conform to various shapes, making them ideal for innovative and space-constrained applications. Their unique properties enable engineers to push the boundaries of product design across multiple industries. This article explores the diverse industries and applications where Flex PCBs excel, focusing on their role in computers, automotives, cameras, peripherals, and military systems. By understanding the technical advantages and specific use cases, electrical engineers can better integrate Flex PCBs into their projects to achieve optimal performance and reliability.
What Are Flex-to-Install PCBs and Why Do They Matter?
Flex-to-Install PCBs are a type of flexible circuit designed to be bent or shaped during installation and remain in a fixed position afterward. Unlike dynamic flex circuits that endure repeated bending, these are intended for a one-time flex during assembly. Their importance lies in their ability to fit into irregular or confined spaces, reduce weight, and minimize the need for connectors or wiring harnesses. This results in improved reliability by reducing potential failure points. In industries where space optimization and durability are critical, Flex PCBs provide a solution that rigid boards cannot match. Their relevance is evident in applications requiring lightweight designs and complex geometries, ensuring seamless integration into advanced electronic systems.
Technical Principles Behind Flex-to-Install PCBs
Flex-to-Install PCBs are constructed using flexible substrates, typically polyimide or polyester films, which provide the necessary mechanical flexibility. These materials maintain electrical integrity while allowing the board to conform to specific shapes. The design often incorporates thin copper layers for conductivity, bonded to the substrate with adhesives or adhesive-less processes, as outlined in standards like IPC-6013D, which governs the qualification and performance of flexible printed boards.
The primary technical advantage is their ability to reduce assembly complexity. By eliminating bulky connectors, they lower the risk of signal loss or mechanical failure at connection points. Additionally, their lightweight nature contributes to overall system efficiency, especially in weight-sensitive applications. Engineers must consider factors such as bend radius and material fatigue during design to ensure long-term reliability, adhering to guidelines in IPC-2223D for flexible circuit design.
Industries and Applications for Flex-to-Install PCBs
Flex PCBs in Computers
In the computer industry, Flex PCBs play a vital role in enabling compact and high-performance devices. They are commonly used in laptops, tablets, and servers where space is limited. These circuits connect components like displays, keyboards, and storage drives, allowing for sleek designs without sacrificing functionality. Their ability to bend around tight corners makes them essential for modern ultrathin laptops. Engineers can leverage Flex PCBs to reduce the footprint of internal wiring, enhancing both aesthetics and thermal management within confined enclosures.
Flex PCBs in Automotives
Automotive electronics have seen a surge in the adoption of Flex PCBs due to the increasing complexity of vehicle systems. They are used in dashboard displays, infotainment systems, and sensor arrays where space and weight constraints are significant. Their flexibility allows integration into curved or irregular surfaces, such as steering wheel controls or door panels. Moreover, Flex PCBs withstand the vibrations and temperature variations typical in automotive environments, aligning with durability requirements specified in standards like ISO 16750-3 for environmental testing. This makes them a reliable choice for advanced driver assistance systems and electric vehicle battery management.
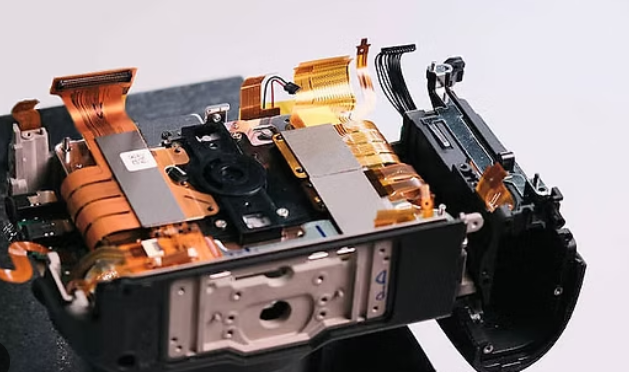
Flex PCBs in Cameras
Camera systems, from consumer-grade digital cameras to professional equipment, benefit greatly from Flex PCBs. These circuits are ideal for connecting image sensors, lenses, and control modules within compact camera bodies. Their flexibility allows for intricate routing in tight spaces, supporting features like foldable displays or rotating lenses. Additionally, Flex PCBs contribute to reducing the overall weight of portable devices, a critical factor for handheld cameras. Their application ensures high-speed data transmission between components, maintaining image quality and operational efficiency in demanding photography environments.
Flex PCBs in Peripherals
Peripheral devices, such as printers, scanners, and wearable gadgets, often incorporate Flex PCBs to achieve ergonomic and compact designs. In wearable technology, these circuits conform to the shape of the human body, enabling comfortable and lightweight products like fitness trackers or smartwatches. For larger peripherals, Flex PCBs simplify internal connections, reducing assembly time and potential errors. Their ability to handle dynamic movements in devices like foldable keyboards or adjustable stands enhances user experience while maintaining electrical performance. Engineers can rely on standards like IPC-A-600K for acceptability criteria to ensure quality in these applications.
Flex PCBs in Military Systems
Military applications demand the highest levels of reliability and performance, and Flex PCBs meet these stringent requirements. They are used in communication devices, unmanned systems, and wearable soldier gear where ruggedness and compactness are essential. Their lightweight construction reduces the burden on personnel, while their ability to conform to complex shapes allows integration into helmets, vests, or handheld equipment. Flex PCBs also withstand harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures and vibrations, as tested under standards like IEC 60068-2 for environmental testing. This ensures uninterrupted operation in critical defense scenarios.
Best Practices for Designing with Flex-to-Install PCBs
When integrating Flex-to-Install PCBs into a design, engineers should prioritize several key considerations to ensure performance and longevity. First, define the bend radius early in the design phase to avoid stressing the material beyond its limits, following guidelines in IPC-2223D. Second, select appropriate substrate materials based on thermal and mechanical requirements of the application. Polyimide, for instance, offers excellent heat resistance for high-temperature environments like automotive systems.
Additionally, minimize the number of layers in areas that will be flexed to reduce stiffness and potential delamination. Ensure proper strain relief at transition points between rigid and flex sections to prevent cracking. Finally, conduct thorough testing under simulated operating conditions to validate the design, referencing standards like IPC-6013D for performance specifications. These steps help achieve reliable integration across various industries.
Conclusion
Flex-to-Install PCBs offer unparalleled advantages in industries where space, weight, and design flexibility are paramount. Their applications span computers, automotives, cameras, peripherals, and military systems, enabling innovative solutions that rigid boards cannot provide. By understanding their technical principles and adhering to established design practices, electrical engineers can harness the full potential of Flex PCBs to meet the demands of modern electronics. As technology continues to evolve, these circuits will remain a critical component in shaping the future of compact and efficient devices across diverse sectors.
FAQs
Q1: How do Flex PCBs benefit computer designs?
A1: Flex PCBs in computers allow for compact and lightweight designs by connecting components in tight spaces. They are ideal for ultrathin laptops and tablets, reducing the need for bulky connectors. Their flexibility ensures efficient routing around complex internal layouts, improving thermal management and reliability in high-performance devices.
Q2: What makes Flex PCBs suitable for automotive applications?
A2: Flex PCBs in automotives excel due to their ability to fit into curved or confined spaces like dashboards and door panels. They withstand vibrations and temperature fluctuations, meeting strict environmental standards. This makes them perfect for infotainment systems, sensors, and battery management in electric vehicles.
Q3: Why are Flex PCBs critical for military equipment?
A3: Flex PCBs in military systems provide lightweight and rugged solutions for communication devices and wearable gear. They conform to complex shapes in helmets or vests and endure harsh conditions. Their reliability under extreme environments ensures consistent performance in critical defense operations.
Q4: How do Flex PCBs enhance camera functionality?
A4: Flex PCBs in cameras enable compact designs by connecting sensors and lenses in limited spaces. They support high-speed data transfer for maintaining image quality. Their lightweight and flexible nature is ideal for portable devices, ensuring seamless integration in consumer and professional camera systems.
References
IPC-6013D — Qualification and Performance Specification for Flexible Printed Boards. IPC, 2017.
IPC-2223D — Sectional Design Standard for Flexible/Rigid-Flexible Printed Boards. IPC, 2016.
IPC-A-600K — Acceptability of Printed Boards. IPC, 2020.
ISO 16750-3:2012 — Road Vehicles — Environmental Conditions and Testing for Electrical and Electronic Equipment. ISO, 2012.
IEC 60068-2:2018 — Environmental Testing. IEC, 2018.