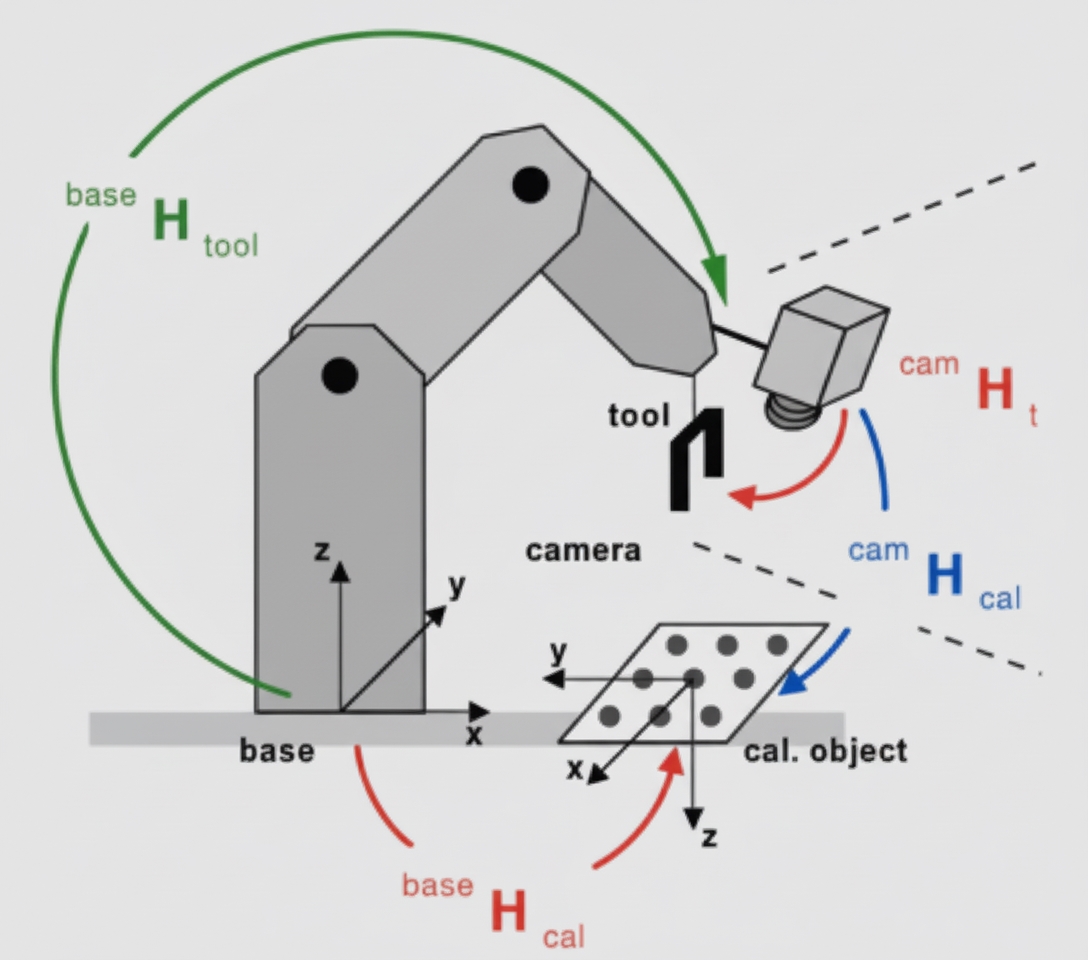
Overview
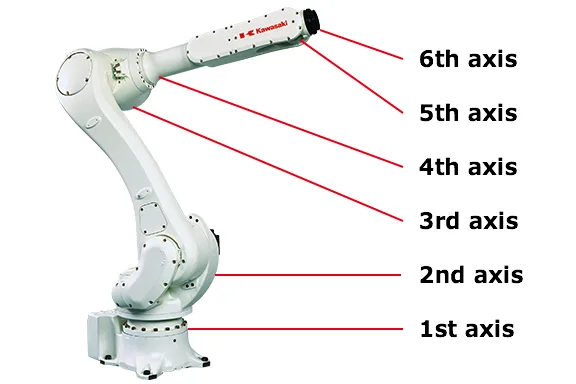
The current level of automation in industrial robots is striking. Five- and six-axis robots have many joints and can transmit motion and commands precisely, with parts coordinating closely to perform complex tasks. This raises questions about their transmission systems and the structure of their joints.
What is a Precision Reducer?
Joints are among the most important components of an industrial robot and the core motion element: the precision reducer. A precision reducer is a mechanism that transmits power with precision; it uses gear-based speed conversion to reduce motor rotational speed to the required output speed while increasing torque.
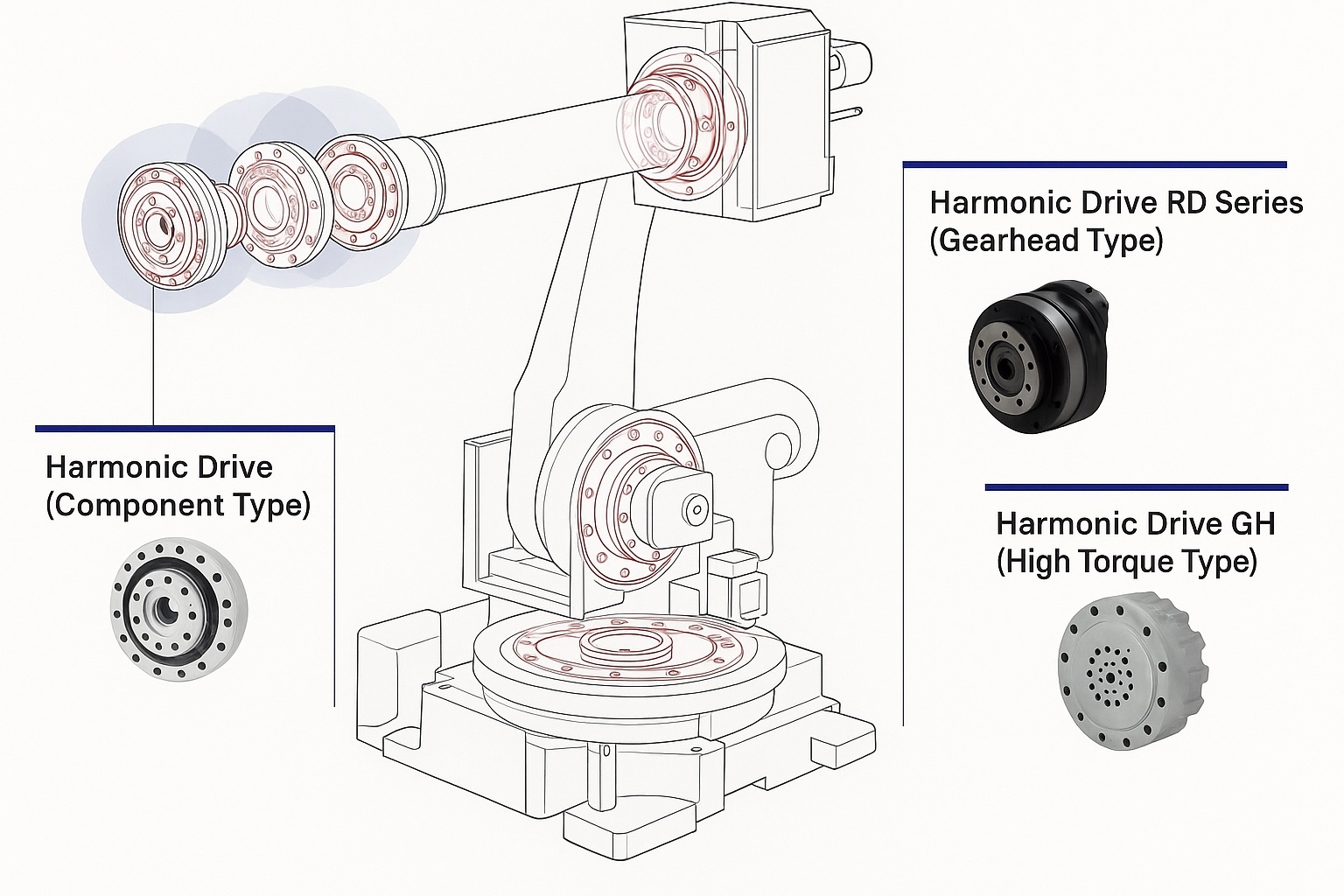
Design Requirements for Robot Joint Reducers
Reducer drives at robot joints require a short transmission chain, compact size, high power density, low mass, and ease of control. For medium- and high-load industrial robots, adequate stiffness, rotational accuracy, and stable motion precision are also required.
Market Landscape
There are relatively few manufacturers worldwide that can supply precision reducers at scale with reliable performance. Japanese companies occupy the majority of the market: Nabtesco's RV reducers account for about 60%, Harmonic Drive's harmonic reducers about 15%, and Sumitomo Heavy Industries is another significant supplier. Their share in robotics applications is especially dominant.
Teardown: Internal Structure
Teardown of a precision reducer reveals the internal mechanisms used to achieve compact, high-torque transmission with minimal backlash.
Nabtesco: Company Background
Nabtesco was formed by the merger of Teijin Seiki and Nabco, the latter having produced Japan's first automatic door in 1956. As manufacturers of motion control systems and components, both companies held high-end core technologies and substantial market shares in their respective fields.
As the world's largest manufacturer of precision cycloidal pinwheel reducers, Nabtesco produces high-performance reducers, hollow-shaft reducers, single-axis servo actuators, and controllers. Its precision products combine high torque, high rigidity, and strong resistance to overload impact with high accuracy and very low backlash. They are widely used in satellite and radar antennas, industrial robots, semiconductor manufacturing, and welding technology.