Introduction
In modern network technology, remote direct memory access (RDMA) has become a key enabler for optimizing data transfer paths and improving overall network efficiency. RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) integrates RDMA with Ethernet, and its second generation, RoCE v2, delivers notable performance improvements and greater flexibility.
What is RoCE v2?
RoCE v2 is an RDMA protocol designed for low-latency, high-throughput data transfers over Ethernet environments. Compared with traditional multi-layered data transfer methods, RoCE v2 implements direct memory access between systems, minimizing CPU involvement and reducing communication latency. These characteristics make RoCE v2 well suited to environments with strict throughput and latency requirements, such as high-performance computing (HPC), data centers, and cloud computing.
RoCE v2 evolves from RoCE v1 by introducing several improvements that address prior limitations and enhance overall performance. The protocol leverages converged Ethernet infrastructure so that standard Ethernet traffic and RDMA traffic can coexist on the same network. This integration simplifies network management and removes the need for separate RDMA-only infrastructures.
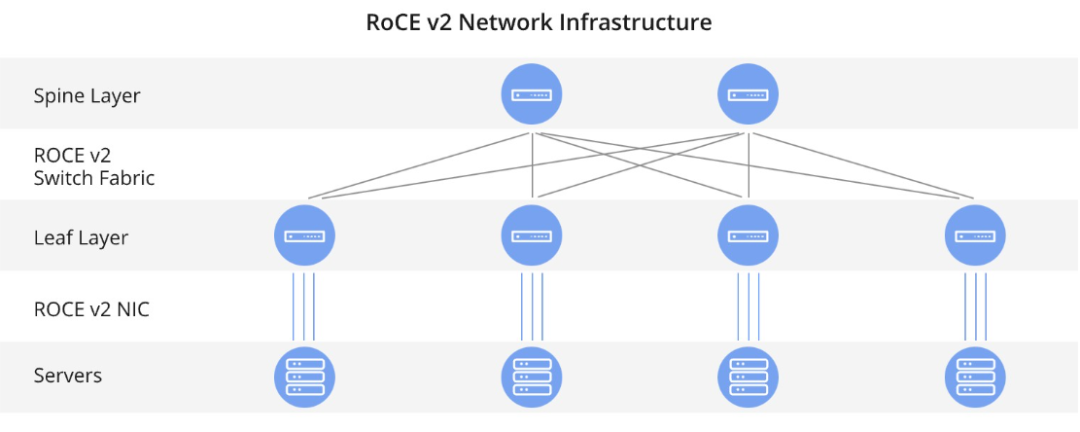
RoCE NICs
One core hardware component in the RoCE v2 ecosystem is the RoCE network interface card (RoCE NIC). These NICs are designed to efficiently support RDMA operations and to offload RDMA processing from the host CPU, thereby reducing data transfer latency and improving overall system performance.
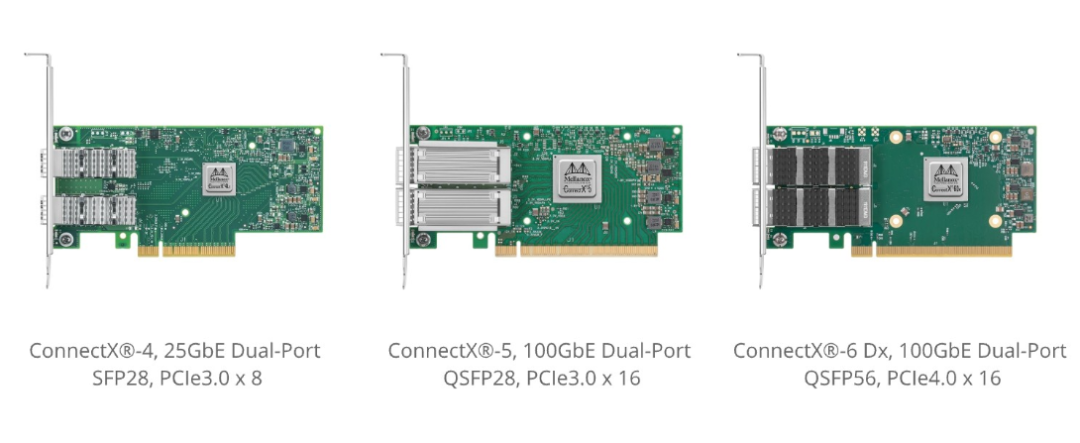
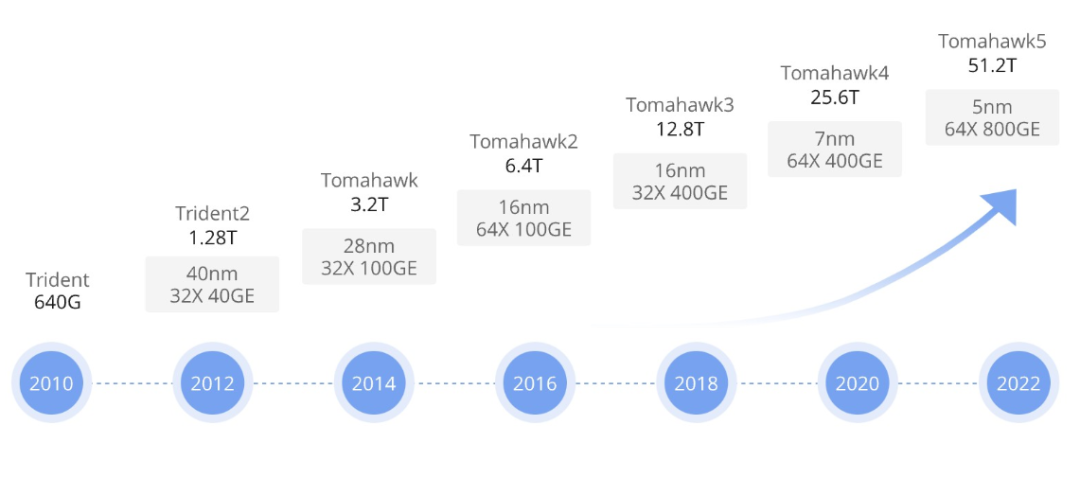
Switch ASICs and Tomahawk Series
High-performance network switches rely on forwarding ASIC technology. Broadly used ASIC families such as the Tomahawk series are deployed in many switch products. As the market evolves, newer generations like Tomahawk4 are increasingly adopted. These ASICs are central to high-speed, large-capacity packet forwarding.
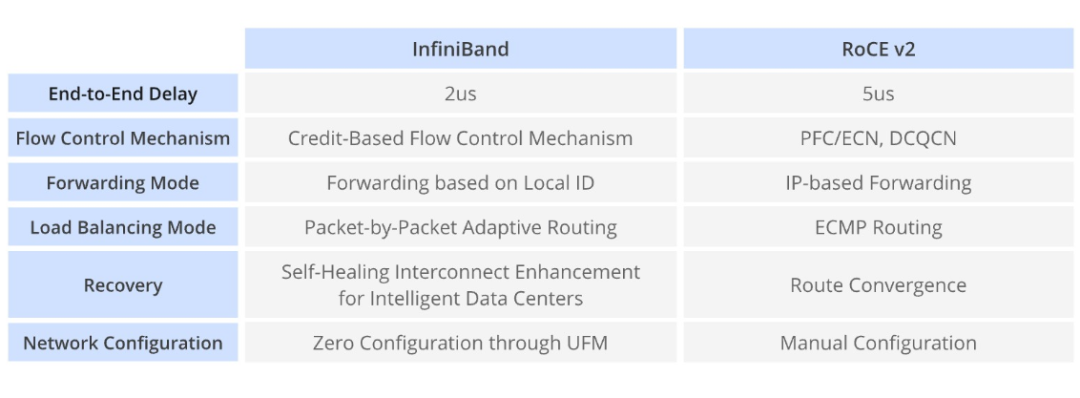
RoCE v2 Compared with InfiniBand
RoCE v2 and InfiniBand are both designed to provide high-speed, low-latency communications for data center and HPC environments. The following sections break down the key differences.
Physical Layer Architecture
RoCE v2: Runs on existing Ethernet infrastructure, allowing storage and regular data traffic to share the same network and easing integration with existing data center architectures. InfiniBand: Uses a separate, proprietary communications architecture that generally requires a dedicated InfiniBand network, including specific cabling and dedicated switching equipment.
Protocol Stack and Network Compatibility
RoCE v2: Implements RDMA over Ethernet and can integrate with standard TCP/IP protocol stacks, ensuring compatibility with common network protocols. InfiniBand: Uses a custom protocol stack optimized for low latency and high throughput, often requiring specific drivers and configuration.
Switching Mechanisms
RoCE v2: Can operate on Ethernet switches that support Data Center Bridging (DCB) features, enabling lossless Ethernet for RDMA traffic. InfiniBand: Relies on InfiniBand switches designed for minimal latency and maximal throughput to guarantee peak performance.
Congestion Management and Control
RoCE v2:
Congestion management: Relies on Ethernet switch features such as DCB to handle congestion. Enabling DCB creates a lossless Ethernet environment and helps avoid packet loss due to congestion. Congestion control: RoCE v2 itself does not include a comprehensive built-in congestion-control mechanism and depends largely on the underlying Ethernet infrastructure to manage congestion.
InfiniBand:
Congestion management: InfiniBand includes native congestion control features. It uses mechanisms such as credit-based flow control to prevent congestion even during traffic peaks. Congestion control: InfiniBand integrates adaptive routing and advanced congestion-control algorithms that dynamically adjust paths based on network conditions to prevent and reduce congestion.
Routing Mechanisms and Topology
RoCE v2:
Routing: Typically uses standard Ethernet routing protocols, such as RIP or OSPF, for path selection. As a result, RoCE v2 route selection follows mature Ethernet routing practices. Topology: Deployments are constrained by the underlying Ethernet infrastructure, so network design must consider existing Ethernet architectures when optimizing routes for RoCE v2.
InfiniBand:
Routing: Provides routing mechanisms specifically optimized for low-latency, high-throughput communication and supports multipath setups for redundancy and load balancing. Topology: Supports diverse topologies, including fat-tree, hypercube, and multi-path configurations. Topology choices directly influence routing and can be tailored for highly scalable, high-performance networks.
Choosing between RoCE v2 and InfiniBand depends on existing infrastructure, application requirements, and performance targets. RoCE v2 offers smoother integration into existing Ethernet networks and is suitable for upgrading performance without changing the underlying network. InfiniBand may be preferable for environments demanding the absolute lowest latency and highest scalability, where investment in dedicated network infrastructure is feasible.
UEC and a New Transport Protocol
On July 19, 2023, the Ultra Ethernet Consortium (UEC) was announced, with founding members including AMD, Arista, Broadcom, Cisco, Eviden, HPE, Intel, Meta, and Microsoft. These companies bring decades of experience in network infrastructure, AI, cloud, and HPC deployments. The consortium noted that while RDMA has delivered significant benefits since its inception, emerging AI and machine learning workloads have increased and complicated network traffic patterns. Large-block RDMA transfers can induce uneven link utilization and add load to networks.
In response, the UEC proposed developing a modern transport protocol that integrates RDMA features while addressing the efficiency, latency, and resource allocation needs of new workloads. The goal is to adapt transport mechanisms to the demands of contemporary applications.
Summary
RoCE v2 is an important RDMA technology that provides a practical solution for organizations seeking high-performance, low-latency data transfers. By integrating with Ethernet infrastructure and aligning with ongoing transport-protocol developments driven by industry consortia, RoCE v2 adapts to diverse environments from HPC to cloud computing. While RoCE v2 offers advantages in ease of integration and cost-effective upgrades, InfiniBand remains a strong option for deployments demanding the utmost performance and scalability. Organizations should evaluate their specific requirements and existing infrastructure when selecting the most appropriate RDMA solution.