Introduction
NVIDIA NVLink has become a key technology in high-performance computing (HPC) and artificial intelligence. This article examines NVLink, NVSwitch chips, NVLink servers, and NVLink switches to explain their roles in modern advanced computing.
Related evaluations
Collection: large-model technical capability evaluations
- 1. Challenges in evaluating network performance for large-model computing
- 2. AIGC general large-model product evaluation (2023)
- 3. Industrial application accuracy evaluation for artificial intelligence large models
- 4. AIGC general large-model product evaluation series
- 5. AIGC general large-model product evaluation (2023)
- 6. 2023 large-model capability assessment in China
What is NVIDIA NVLink
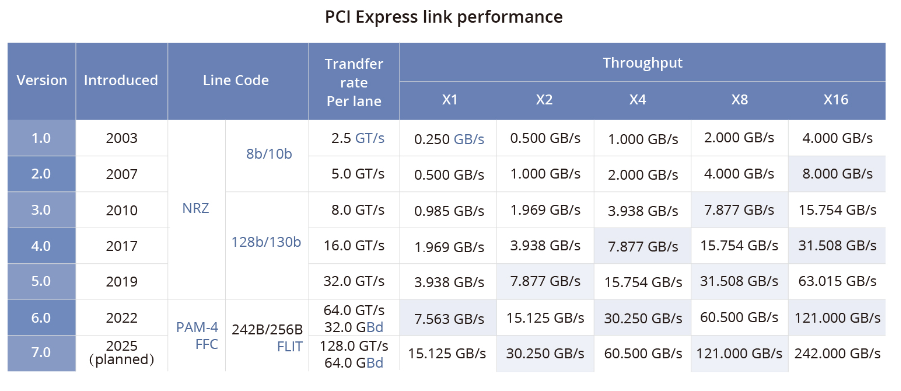
NVLink is a protocol designed to address communication limitations between GPUs inside a server. Unlike traditional PCIe switches, NVLink provides limited but high-bandwidth direct interconnects between GPUs within a server. NVLink 4 provides higher bandwidth, with each lane reaching 112 Gbps, about three times the per-lane rate of PCIe Gen5.
NVLink aims to provide a simplified, high-speed, point-to-point network for direct GPU interconnects, reducing overhead compared with conventional networks. By enabling CUDA acceleration at multiple levels, NVLink reduces communication-related network overhead. NVLink has evolved alongside GPU architectures, from NVLink 1 in the P100 to NVLink 4 in the H100. The key differences among NVLink 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, and 4.0 are connection topology, bandwidth, and performance.
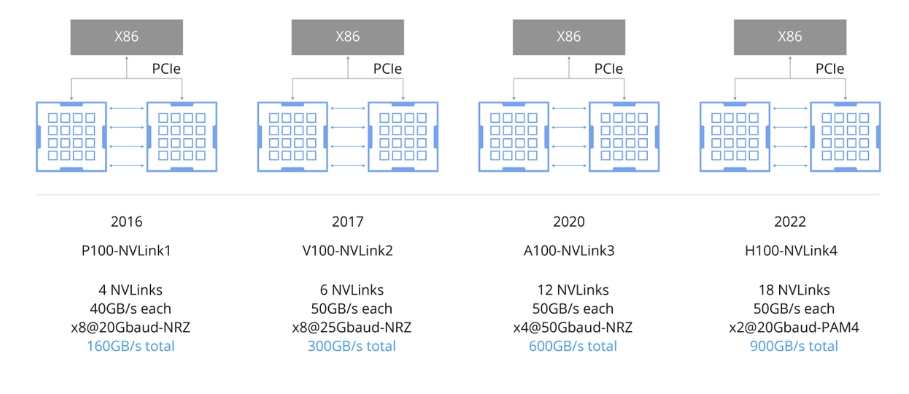
NVSwitch chip
The NVSwitch chip is a physical ASIC-like device that connects multiple GPUs via high-speed NVLink interfaces to increase intra-server communication and bandwidth. Third-generation NVSwitch can interconnect each GPU pair at rates up to 900 GB/s.
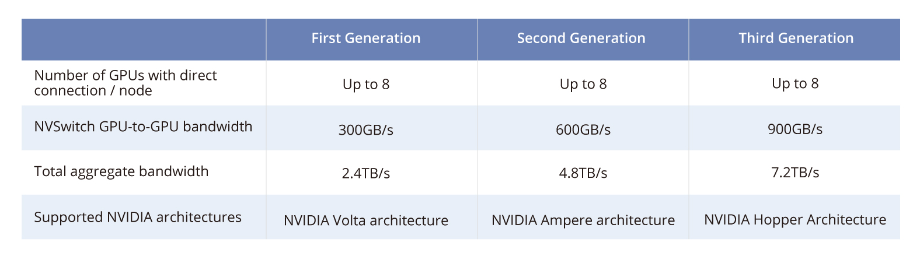
NVSwitch3 has 64 NVLink 4 ports, offering a total of 12.8 Tbps one-way bandwidth or 3.2 TB/s bidirectional bandwidth. A notable feature of the NVSwitch3 chip is integrated SHARP functionality, which aggregates and updates compute results across multiple GPU units to reduce network packets and improve compute efficiency.
NVLink servers
NVLink servers use NVLink and NVSwitch technologies to interconnect GPUs and are commonly found in NVIDIA DGX systems or OEM HGX servers with similar architectures. These servers use NVLink to provide strong GPU interconnectivity, scalability, and high-performance compute capability. In 2022 NVIDIA announced the fourth-generation DGX systems built around the DGX H100 server.
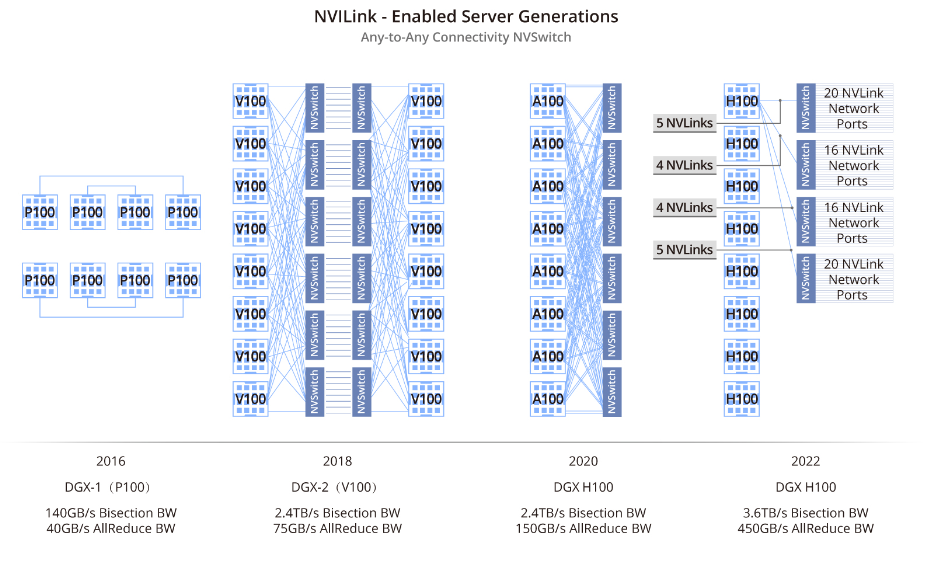
NVLink servers are used in scientific computing, artificial intelligence, big data processing, and data center environments. By providing high compute capability and efficient data handling, NVLink servers address demanding performance requirements in these fields and support ongoing technical development.
NVLink switch
In 2022 NVIDIA separated the NVSwitch chip into an NVLink switch product to connect GPUs across hosts. The product is offered in a 1U form factor with 32 OSFP ports; each OSFP port contains eight 112G PAM4 lanes. Each switch integrates two NVSwitch3 chips.
NVLink network
NVSwitch-based physical switches link multiple NVLink GPU servers into a large fabric network, called an NVLink network, addressing high-bandwidth and efficient GPU-to-GPU communication. Each server maintains its own address space, providing data transfer, isolation, and security for GPUs in the NVLink fabric. At system boot, the NVLink network establishes connections automatically via software PI and can change addresses during runtime.
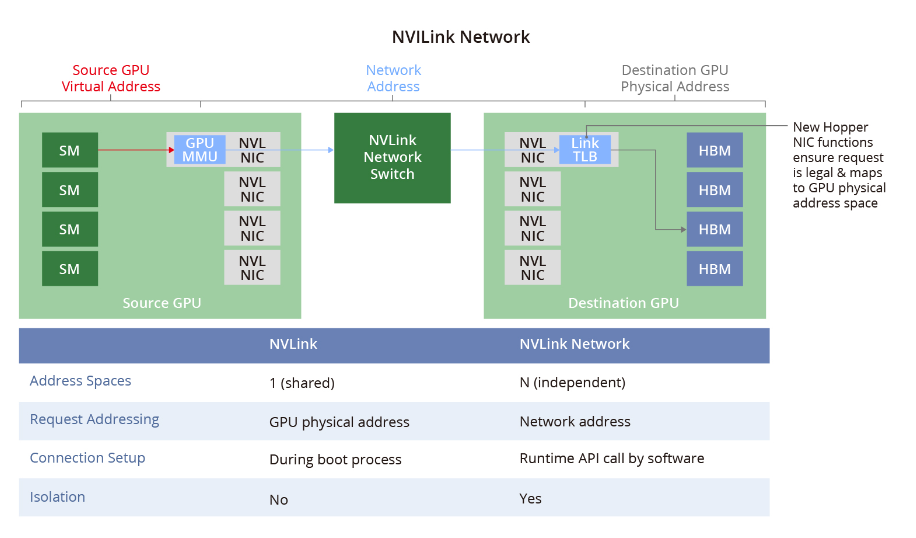
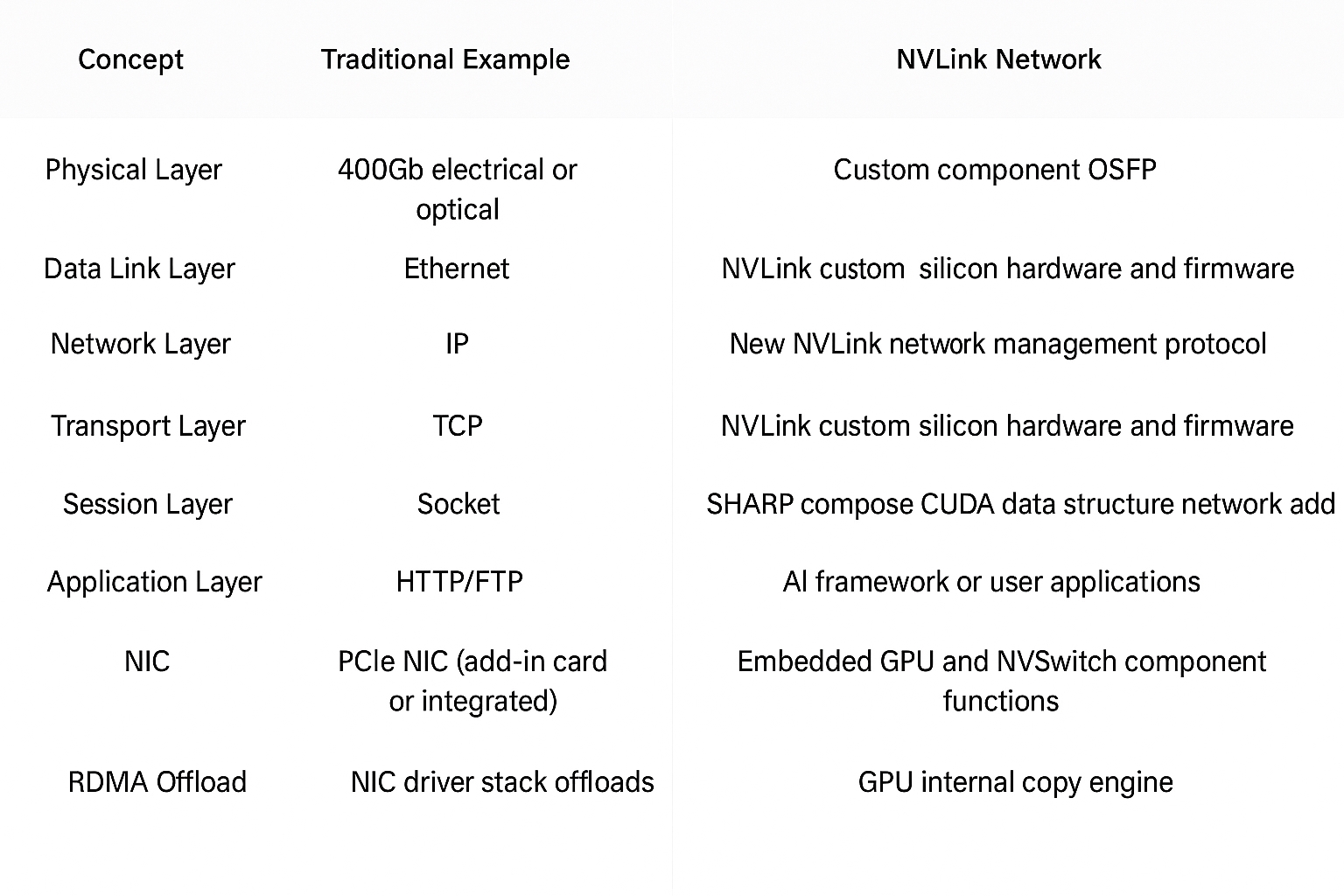
The figure compares NVLink networks with traditional Ethernet networks, illustrating how an NVLink fabric can be created independently of IP Ethernet and dedicated to GPU services.
InfiniBand network vs NVLink network
InfiniBand and NVLink are two different network technologies used in HPC and data center applications. Key differences include:
- Architecture and design: InfiniBand is an open-standard technology using multi-lane, high-speed serial links supporting point-to-point and multicast communication. NVLink is a proprietary technology from NVIDIA designed for high-speed direct GPU-to-GPU links.
- Use cases: InfiniBand is widely used in HPC clusters and large-scale data centers. NVLink is primarily used in large GPU clusters, HPC, and AI workloads.
- Bandwidth and latency: InfiniBand provides high bandwidth and low latency for general-purpose cluster communication. NVLink provides higher bandwidth and lower latency specifically for GPU-to-GPU data exchange and cooperative computation.
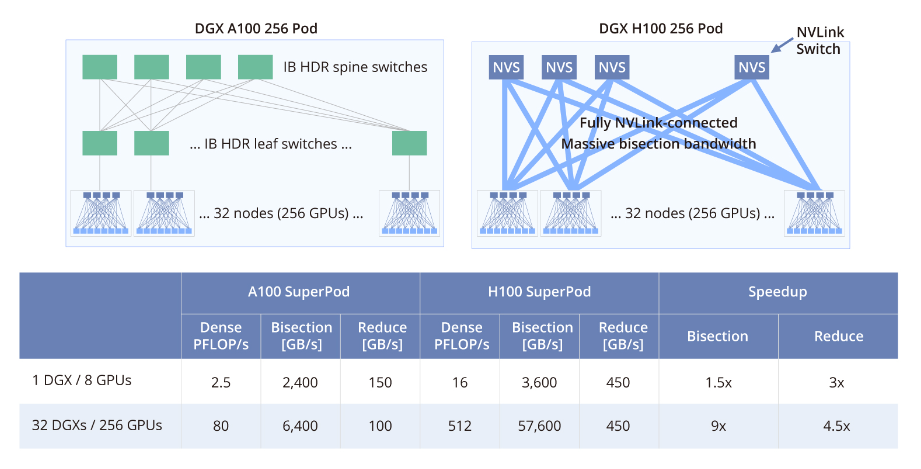
Conclusion
NVIDIA NVLink is a transformative technology in high-performance computing and AI. It strengthens GPU communication, improves performance, and enables seamless parallel processing, making it a critical component in many HPC and AI applications. As advanced computing continues to evolve, NVLink's importance and impact are likely to grow and drive further innovation.