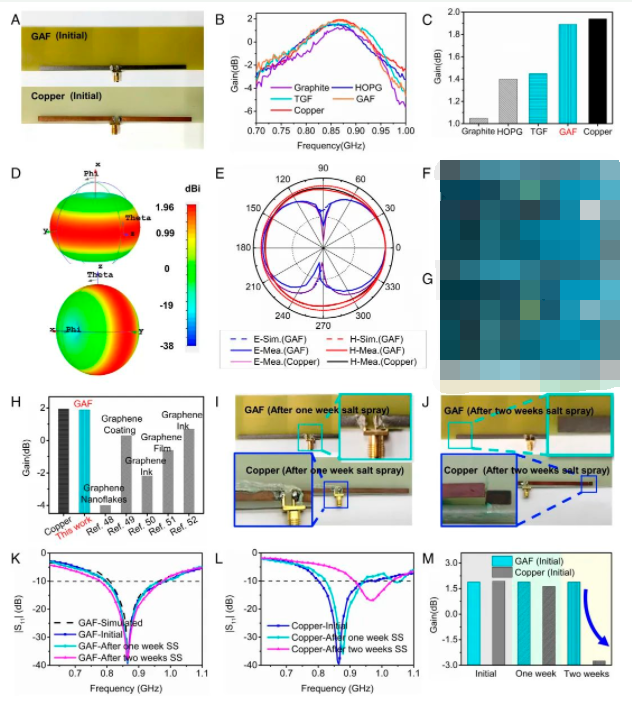
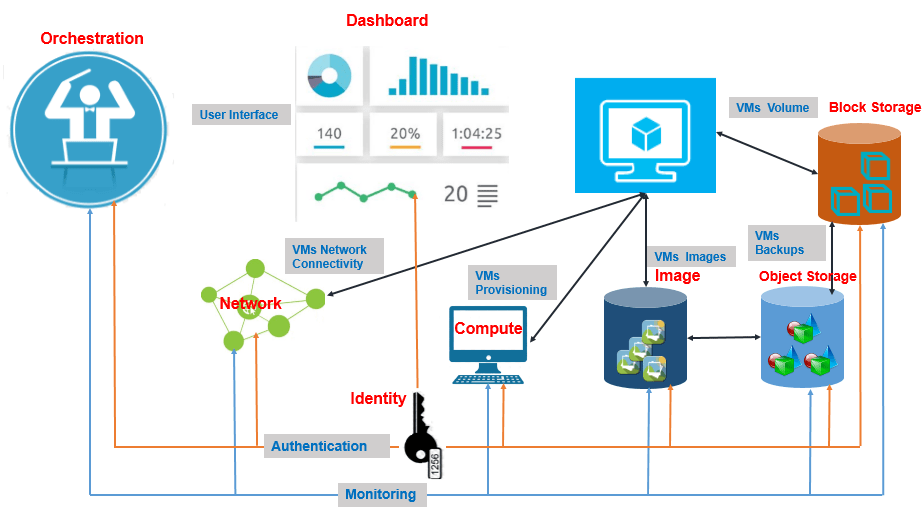
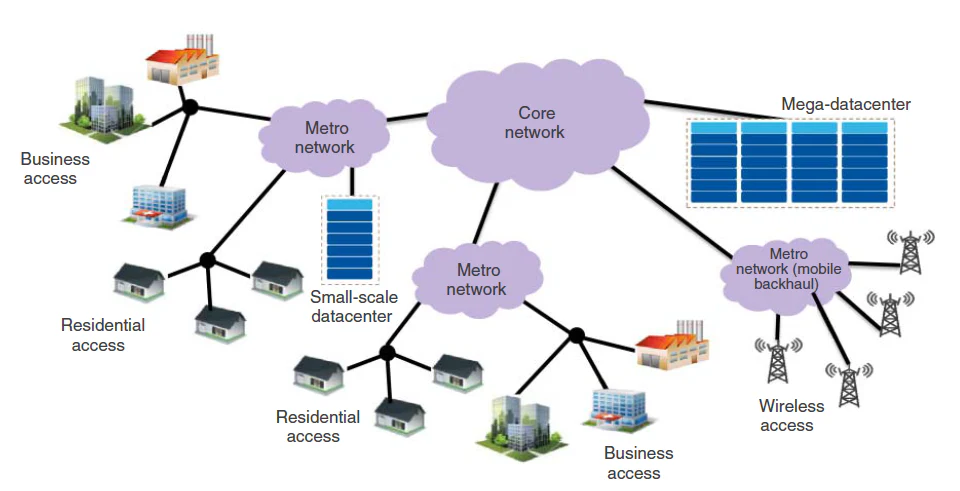
1. Verify wireless performance
As device numbers increase and frequency bands become more crowded, verifying that users receive the performance they expect from the network is a primary task. This requires using test equipment to scan the area for interference and to verify that units comply with all relevant standards.
2. Maintain very low latency
With the higher potential speeds enabled by 5G, devices must respond faster to maintain connections. Ensuring devices and the broadcast system respond within 1 to 2 milliseconds is necessary for smooth operation.
3. Ensure low packet loss rate
Alongside latency and higher speeds, low packet loss is required. A target of losing only 1 packet per 100 million should be tested to ensure all transmitters and receivers in the network meet this standard for smooth operation.
4. Antenna testing
Given the complexity of new broadcast signals, verifying that antennas meet specifications is essential. This includes tests for direction of arrival (DoA), direction of departure (DoD), polarization, and testing under challenging conditions such as interference and multipath scenarios.
5. Capacity testing
With a projected increase in connected devices and the need to deliver required performance to users and critical safety systems, ensuring the network can handle peak demand is vital. Before upgrading or deploying a new network, conduct load testing that includes problematic users and malfunctioning devices to ensure smooth operation.