Differential Amplifier Basics with Formulas and Examples
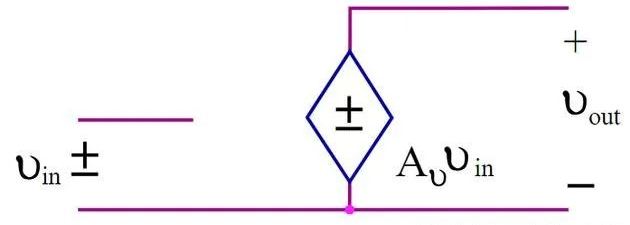
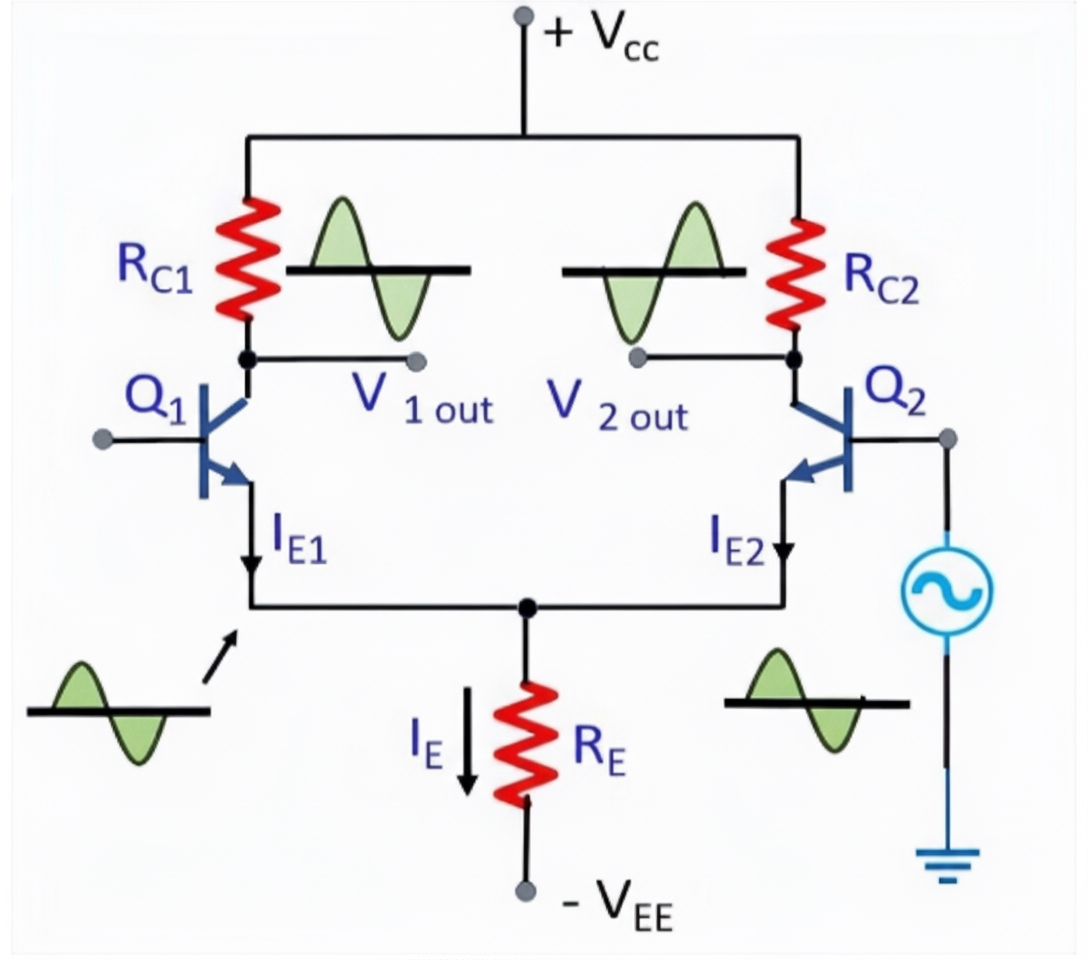
Differential amplifier overview covering BJT and op-amp implementations, transfer functions, Wheatstone-bridge and light/temperature sensor examples, plus instrumentation amplifier design.
Differential amplifier overview covering BJT and op-amp implementations, transfer functions, Wheatstone-bridge and light/temperature sensor examples, plus instrumentation amplifier design.
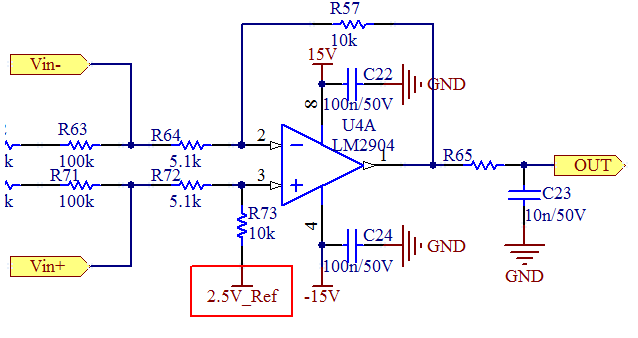
Differential amplifier design: resistor divider/gain and differential input derivations, plus output offset methods to shift signals for voltage sensing and MCU inputs.
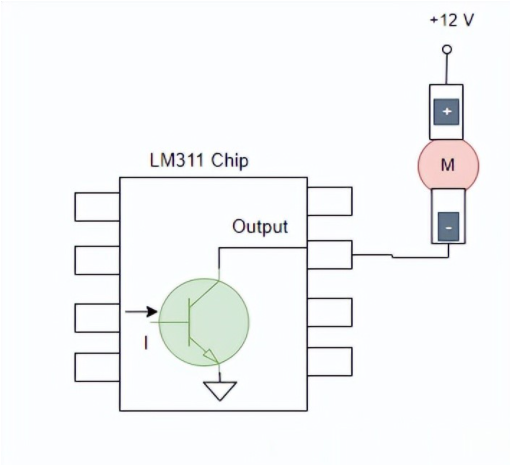
Technical overview of open-collector circuits, operation, transistor and TTL implementations, wiring, pull-up resistor considerations, advantages and limitations.
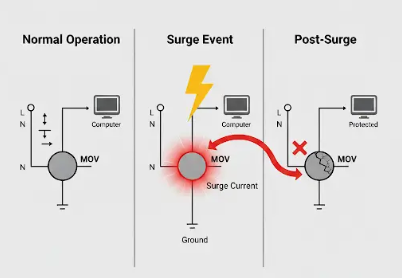
Technical overview of varistor functions and overvoltage protection, with behavior under switching?supply spikes and practical testing methods.
Technical overview of varistors: definition, zinc-oxide behavior and failure symptoms, bidirectional thyristor overvoltage protection circuit, and differences from thermistors.
Overview of IC amplifier types, applications, and effects on dynamic range, covering linear, power and operational amplifiers, noise, gain, saturation.
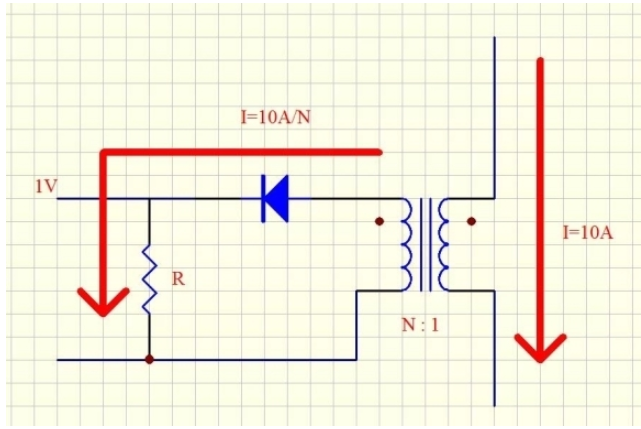
Design and operation of a current transformer for high-power converter current sensing, covering turn ratio, resistor power, core/diode choices and magnetizing inductance.
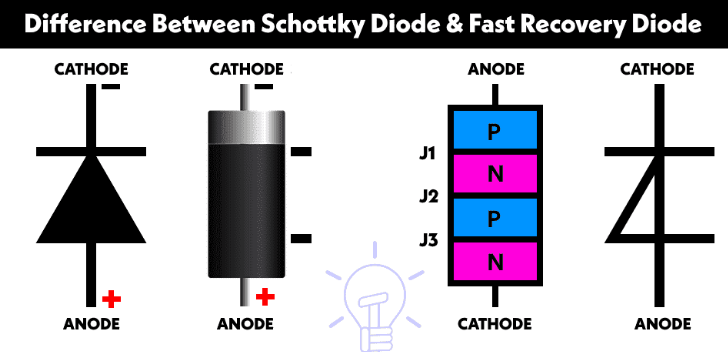
Technical overview of rectifier diodes: selection criteria (peak reverse voltage, forward current, VF, recovery time), differences vs fast-recovery diodes and PN junction operation
Practical guidance on varactor diode use and biasing in VCO circuits, covering drive techniques, isolation, dual-diode topology, and RF/Q trade-offs.
Overview of buffer amplifiers: operation, voltage and current buffer types, impedance matching, unity-gain op-amp implementation, and common applications.
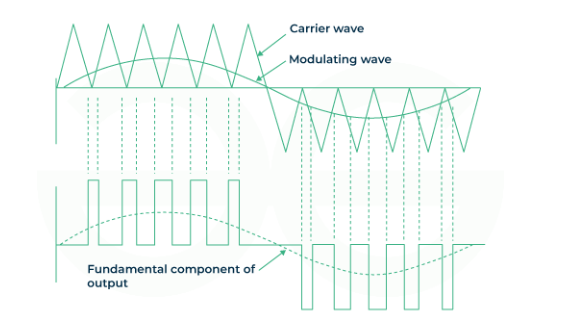
Overview of PWM: definition, frequency and duty cycle, digital encoding of analog signals, and practical applications such as servo and motor speed control.
Technical overview of instrumentation amplifier design, operation and gain derivation, covering three-op-amp topology, input buffering and CMRR.